Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the survival outcomes of percutaneous thermal ablation (RFA + microwaves) for patients presenting N0 non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) ineligible for surgery.
Materials and Methods
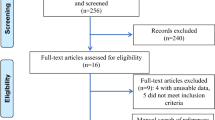
Eighty-seven patients from two comprehensive cancer centers were included. Eighty-two patients were treated with RFA electrodes and five with microwave antenna. Overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS) were estimated and predictive factors of local tumor progression, OS and DFS identified and compared by univariate and multivariate analyses
Results
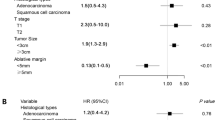
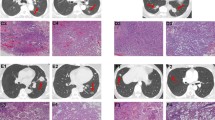
Median follow-up was 30.5 months (interquartile range 16.7–51) and tumor size was 21 mm (range 10–54 mm). Treatment was incomplete for 14 patients with a local tumor progression of 11.5, 18.3, and 21.1 % at 1, 2, and 3 years, respectively. Two patients presented with neurological (grade III or IV) complications, and one died of respiratory and multivisceral failure as a result of the procedure at 29 days. In univariate analysis, increasing tumor size (P = 0.003) was the only predictive factor related to risk of local tumor progression. 5-year OS and DFS were 58.1 and 27.9 %, respectively. Sex (P = 0.044), pathology (P = 0.032), and tumor size >2 cm (P = 0.046) were prognostic factors for DFS. In multivariate analysis, pathology (P = 0.033) and tumor size >2 cm (P = 0.032) were independent prognostic factors for DFS.
Conclusions
Oversized and overlapping ablation of N0 NSCLC was well tolerated, effective, with few local tumor progressions, even over long-term follow-up. Increasing tumor size was the main prognostic factor linked to OS, DFS, and local tumor progression.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Rami-Porta R, Ball D, Crowley J, Giroux DJ, Jett J, Travis WD et al (2007) The IASLC Lung Cancer Staging Project: proposals for the revision of the T descriptors in the forthcoming (seventh) edition of the TNM classification for lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol 2(7):593–602
Rami-Porta R, Tsuboi M (2009) Sublobar resection for lung cancer. Eur Respir J 33(2):426–435
Raz DJ, Zell JA, Ou SH, Gandara DR, Anton-Culver H, Jablons DM (2007) Natural history of stage I non-small cell lung cancer: implications for early detection. Chest 132(1):193–199
Qiao X, Tullgren O, Lax I, Sirzen F, Lewensohn R (2003) The role of radiotherapy in treatment of stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer 41(1):1–11
Fakiris AJ, McGarry RC, Yiannoutsos CT, Papiez L, Williams M, Henderson MA et al (2009) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for early-stage non-small-cell lung carcinoma: four-year results of a prospective phase II study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 75(3):677–682
Haasbeek CJ, Lagerwaard FJ, Antonisse ME, Slotman BJ, Senan S (2010) Stage I nonsmall cell lung cancer in patients aged> or= 75 years: outcomes after stereotactic radiotherapy. Cancer 116(2):406–414
Onishi H, Araki T, Shirato H, Nagata Y, Hiraoka M, Gomi K et al (2004) Stereotactic hypofractionated high-dose irradiation for stage I nonsmall cell lung carcinoma: clinical outcomes in 245 subjects in a Japanese multiinstitutional study. Cancer 101(7):1623–1631
Timmerman R, Paulus R, Galvin J, Michalski J, Straube W, Bradley J et al (2010) Stereotactic body radiation therapy for inoperable early stage lung cancer. JAMA 303(11):1070–1076
Ambrogi MC, Fanucchi O, Cioni R, Dini P, De LA, Cappelli C et al (2011) Long-term results of radiofrequency ablation treatment of stage I non-small cell lung cancer: a prospective intention-to-treat study. J Thorac Oncol 6(12):2044–2051
Beland MD, Wasser EJ, Mayo-Smith WW, Dupuy DE (2010) Primary non-small cell lung cancer: review of frequency, location, and time of recurrence after radiofrequency ablation. Radiology 254(1):301–307
Fernando HC, De HA, Landreneau RJ, Gilbert S, Gooding WE, Buenaventura PO et al (2005) Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of non-small cell lung cancer in marginal surgical candidates. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 129(3):639–644
Hiraki T, Gobara H, Iishi T, Sano Y, Iguchi T, Fujiwara H et al (2007) Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for clinical stage I non-small cell lung cancer: results in 20 nonsurgical candidates. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 134(5):1306–1312
Lanuti M, Sharma A, Willers H, Digumarthy SR, Mathisen DJ, Shepard JA (2012) Radiofrequency ablation for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: management of locoregional recurrence. Ann Thorac Surg 93(3):921–927
Pennathur A, Luketich JD, Abbas G, Chen M, Fernando HC, Gooding WE et al (2007) Radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of stage I non-small cell lung cancer in high-risk patients. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 134(4):857–864
Simon CJ, Dupuy DE, DiPetrillo TA, Safran HP, Grieco CA, Ng T et al (2007) Pulmonary radiofrequency ablation: long-term safety and efficacy in 153 patients. Radiology 243(1):268–275
Trotti A, Colevas AD, Setser A, Rusch V, Jaques D, Budach V et al (2003) CTCAE v3.0: development of a comprehensive grading system for the adverse effects of cancer treatment. Semin Radiat Oncol 13(3):176–181
Rubins J, Unger M, Colice GL (2007) American College of Chest Physicians. Follow-up and surveillance of the lung cancer patient following curative intent therapy: ACCP evidence-based clinical practice guideline (2nd edition). Chest 132(3):355S–367S
de Baere T (2011) Lung tumor radiofrequency ablation: where do we stand? Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 34(2):241–251
Hiraki T, Sakurai J, Tsuda T, Gobara H, Sano Y, Mukai T, Hase S, Iguchi T, Fujiwara H, Date H, Kanazawa S (2006) Risk factors for local progression after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors: evaluation based on a preliminary review of 342 tumors. Cancer 107(12):2873–2880
Schoellnast H, Deodhar A, Hsu M, Moskowitz C, Nehmeh SA, Thornton RH et al (2012) Recurrent non-small cell lung cancer: evaluation of CT-guided radiofrequency ablation as salvage therapy. Acta Radiol 53(8):893–899
Kodama H, Yamakado K, Takaki H, Kashima M, Uraki J, Nakatsuka A, Takao M, Taguchi O, Yamada T, Takeda K (2012) Lung radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of unresectable recurrent non-small-cell lung cancer after surgical intervention. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 35(3):563–569
Grieco CA, Simon CJ, Mayo-Smith WW, DiPetrillo TA, Ready NE, Dupuy DE (2006) Percutaneous image-guided thermal ablation and radiation therapy: outcomes of combined treatment for 41 patients with inoperable stage I/II non-small-cell lung cancer. J Vasc Interv Radiol 17(7):1117–1124
Ambrogi MC, Fontanini G, Cioni R, Faviana P, Fanucchi O, Mussi A (2006) Biologic effects of radiofrequency thermal ablation on non-small cell lung cancer: results of a pilot study. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 131(5):1002–1006
Giraud P, Antoine M, Larrouy A, Milleron B, Callard P, De RY et al (2000) Evaluation of microscopic tumor extension in non-small-cell lung cancer for three-dimensional conformal radiotherapy planning. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 48(4):1015–1024
Yasui K, Kanazawa S, Sano Y, Fujiwara T, Kagawa S, Mimura H et al (2004) Thoracic tumors treated with CT-guided radiofrequency ablation: initial experience. Radiology 231(3):850–857
Cerfolio RJ, Bryant AS (2009) Survival of patients with true pathologic stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg 88(3):917–922
Crabtree TD, Denlinger CE, Meyers BF, El NI, Zoole J, Krupnick AS et al (2010) Stereotactic body radiation therapy versus surgical resection for stage I non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 140(2):377–386
Acknowledgments
We thank Pippa McKelvie-Sebileau and Jone Iriondo-Alberdi for medical editorial assistance.
Conflict of interest
Jean Palussiere declares no conflict of interest. Philippe Lagarde declares no conflict of interest. Anne Aupérin declares no conflict of interest. Frédéric Deschamps declares no conflict of interest. François Chomy declares no conflict of interest. Thierry de Baere declares no conflict of interest.
Statement of Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Statement of Human and Animal Rights
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Palussiere, J., Lagarde, P., Aupérin, A. et al. Percutaneous Lung Thermal Ablation of Non-surgical Clinical N0 Non-small Cell Lung Cancer: Results of Eight Years’ Experience in 87 Patients from Two Centers. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 38, 160–166 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-0999-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-014-0999-6