Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the effect of umbilical vein (UV) blood flow measured by color-directed pulsed-wave Doppler on perinatal outcome of fetuses with lean and/or hypocoiled umbilical cord after 24 weeks of gestation.
Methods
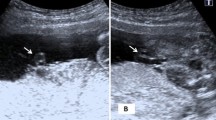
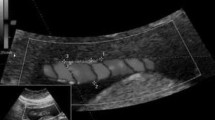
Two hundred and forty-four women with singleton fetus after 24 weeks of gestation were studied. Umbilical cord area, umbilical vessel cross-sectional area and antenatal umbilical coiling index (UCI) were calculated and compared with Doppler parameters including UV blood flow volume in ml/min/kg, UV peak systolic velocity in cm/s, and umbilical artery pulsatility index.
Results
Thirty-eight (15.5%) fetuses had lean umbilical cord (area < 10th percentile). A significant difference between fetuses with and those without lean cord was found in terms of: UCI (0.17 ± 0.06 vs. 0.35 ± 0.08, P < 0.001), cord cross-sectional area (89.6 ± 11.7 vs. 198.7 ± 33.7 mm2, P < 0.001), Wharton’s jelly amount (36.5 ± 11.2 vs. 125.2 ± 34.1 mm2, P < 0.001), UV blood flow (83.4 ± 15.8 vs. 131.0 ± 19.8 ml/min/kg, P < 0.001), and UV blood flow mean velocity (8.6 ± 3.7 vs. 12.1 ± 2.8 cm/s, P < 0.05). A significant positive correlation was found between antenatal UCI and UV blood flow (r = 0.73, P < 0.001).
Conclusion
Fetuses with lean and/or hypo-coiled umbilical cord showed a noticeable decrease in UV blood flow of sufficient magnitude that could affect fetal growth, and this could explain the higher prevalence of fetal intrapartum complications in growth-restricted fetuses.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Di Nero E, Chezzi F, Raio L, Franchi M, D’addrio V (2001) Umbilical cord morphology and pregnancy outcome. Eur J Obstet Gnecol Reprod Biol 69:150–156
Bruch JF, Sibony O, Benali K, Challer C, Blot P, Nessmann C (1997) Computerized microscope morphometry of umbilical vessels from pregnancies with intrauterine growth retardation and abnormal umbilical artery Doppler. Hum Pathol 28:1139–1145
Delaat M, Franx A, Nickkels PGD, Visser GHA (2006) Prenatal ultrasonographic prediction of the umbilical coiling index at birth and adverse perinatal outcome. Ultrasound Obestet Gynecol 28:704–709
Galan HL, Jozwik M, Rigano S, Regnault TR, Hobbins JC, Battaglia FC, Ferrazzi E (1999) Umbilical vein blood flow determination in the ovine fetus: comparison of Doppler ultrasonographic and steady-state diffusion techniques. Am J Obstet Gynecol 181:1149–1153
Rigano S, Bozzo M, Ferrazzi E, Bellotti M, Battaglia FC, Galan HL (2001) Early and persistent reduction in umbilical vein blood flow in the growth-restricted fetus: a longitudinal study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 185:834–838
Strong TH, Finberg HJ, Mattox JH (1994) Antepartum diagnosis of noncoiled umbilical cords. Am J Obstet Gynecol 170:1729–1733
Raio L, Ghezzi F, Di Naro E et al (1999) Prenatal diagnosis of a “lean” umbilical cord: a simple marker for fetuses at risk of being small for gestational age at birth. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 13:176
Barbieri C, Cecatti JG, Souza CE, Marussi EF, Costa JV (2008) Inter- and intra-observer variability in sonographic measurements of the cross-sectional diameters and area of the umbilical cord and its vessels during pregnancy. Reprod Health 5:5
Sebire NJ (2007) Patho-physiological significance of abnormal umbilical cord coiling index. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 30(6):804–806
Kiserud T, Eik-Nes H, Blaas HG, Hellevik LR, Simensen B (1994) Ductus venosus blood velocity and the umbilical circulation in seriously growth retarded fetuses. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 4:109–114
Barbera A, Galan HL, Ferrazzi E, Rigano S, Jozwik M, Battaglia FC, Pardi G (1999) Relationship of umbilical vein blood flow to growth parameters in the human fetus. Am J Obstet Gynecol 181:174–179
Di Naro E, Ghezzi F, Raio L et al (2001) Umbilical vein blood flow in fetuses with normal and lean umbilical cord. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 17:224
Di Naro E, Raio L, Ghezzi F et al (2002) Longitudinal changes of the umbilical vein blood flow in normal and growth retarded fetuses. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 81:527
Silver RK, Dooley SL, Tamura RK (2001) Umbilical cord size and amniotic fluid volume in prolonged pregnancy. Am J Obestet Gynecol 18:348
Labarrere C, Sebastiani M, Siminovich E (1985) Absence of Wharton’s jelly around the umbilical arteries: an unusual cause of perinatal mortality. Placenta 6:555
Malpas P, Symonds EM (1966) Observations on the structure of the human umbilical cord. Surg Gynecol Obstet 123:746–750
Ghezzi F, Raio L, Dinero E, Franchi M, Balestreri D, D’addario V (2001) Nomogram of Wharton’s jelly as depicted in the sonographic cross section of the umbilical cord. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 18:121–125
Otsubo Y, Yoneyama Y, Suzuki S, Sawa R, Araki T (1999) Sonographic evaluation of umbilical cord insertion with umbilical coiling index. J Clin Ultrasound 27(6):340–341
Georgiou HM, Rice GE, Walker SP, Wein P, Gude NM, Permezel M (2001) The effect of vascular coiling on venous perfusion during experimental umbilical cord encirclement. Am J Obstet Gynecol 184:673–678
Degani S, Lewingsky RM, Berger H, Spiegel D (1995) Sonographic estimation of umbilical coiling index and correlation with Doppler flow characteristics. Obstet Gynecol 86:990–993
Predanic M, Perni SC, Chervenak FA (2006) Antenatal umbilical coiling index and Doppler flow characteristics. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 28(5):699–703
Reynolds SRM (1978) Mechanisms of placento fetal blood flow. Obstet Gynecol 51:245–249
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
El behery, M.M., Nouh, A.A., Alanwar, A.M. et al. Effect of umbilical vein blood flow on perinatal outcome of fetuses with lean and/or hypo-coiled umbilical cord. Arch Gynecol Obstet 283, 53–58 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-009-1272-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-009-1272-0