Abstract
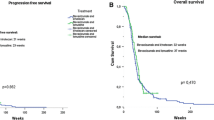
We evaluated the efficacy of carboplatin, irinotecan, and bevacizumab among bevacizumab-naïve, recurrent glioblastoma (GBM) patients in a phase 2, open-label, single arm trial. Forty eligible patients received carboplatin (area under the plasma curve [AUC] 4 mg/ml-min) on day one, while bevacizumab (10 mg/kg) and irinotecan (340 mg/m2 for patients on CYP3A-enzyme-inducing anti-epileptics [EIAEDs] and 125 mg/m2 for patients not on EIAEDs) were administered on days 1 and 14 of every 28-day cycle. Patients were evaluated after each of the first two cycles and then after every other cycle. Treatment continued until progressive disease, unacceptable toxicity, non-compliance, or voluntary withdrawal. The primary endpoint was progression-free survival at 6 months (PFS-6) and secondary endpoints included safety and median overall survival (OS). All patients had progression after standard therapy. The median age was 51 years. Sixteen patients (40%) had a KPS of 90–100, while 27 (68%) were at first progression. The median time from original diagnosis was 11.4 months. The PFS-6 rate was 46.5% (95% CI: 30.4, 61.0%) and the median OS was 8.3 months [95% confidence interval (CI): 5.9, and 10.7 months]. Grade 4 events were primarily hematologic and included neutropenia and thrombocytopenia in 20 and 10%, respectively. The most common grade 3 events were neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, fatigue, and infection in 25, 20, 13, and 10%, respectively. Eleven patients (28%) discontinued study therapy due to toxicity and 17 patients (43%) required dose modification. One patient died due to treatment-related intestinal perforation. The addition of carboplatin and irinotecan to bevacizumab significantly increases toxicity but does not improve anti-tumor activity to that achieved historically with single-agent bevacizumab among bevacizumab-naïve, recurrent GBM patients. (ClinicalTrials.gov number NCT00953121).



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MG:
-
Malignant glioma
- ITT:
-
Intent-to treat
- ANC:
-
Absolute neutrophil count
- AST:
-
Aspartate aminotransferase
- CNS:
-
Central nervous system
- CR:
-
Complete response
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma
- KPS:
-
Karnofsky performance status
- ORR:
-
Overall response rate
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- PD:
-
Progressive disease
- PFS:
-
Progression-free survival
- PR:
-
Partial response
- SD:
-
Stable disease
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Cohen MH, Shen YL, Keegan P, Pazdur R (2009) FDA drug approval summary: bevacizumab (Avastin) as treatment of recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Oncologist 14:1131–1138
Wick W, Weller M, van den Bent M, Stupp R (2010) Bevacizumab and recurrent malignant gliomas: a European perspective. J Clin Oncol 28:e188–e189. doi:10.1200/JCO.2009.26.9027 author reply e190–182
Friedman HS, Prados MD, Wen PY, Mikkelsen T, Schiff D, Abrey LE, Yung WK, Paleologos N, Nicholas MK, Jensen R, Vredenburgh J, Huang J, Zheng M, Cloughesy T (2009) Bevacizumab alone and in combination with irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 27:4733–4740
Kreisl TN, Kim L, Moore K, Duic P, Royce C, Stroud I, Garren N, Mackey M, Butman JA, Camphausen K, Park J, Albert PS, Fine HA (2009) Phase II trial of single-agent bevacizumab followed by bevacizumab plus irinotecan at tumor progression in recurrent glioblastoma. J Clin Oncol 27:740–745
Lamborn KR, Chang SM, Prados MD (2004) Prognostic factors for survival of patients with glioblastoma: recursive partitioning analysis. Neuro-oncol 6:227–235
Ballman KV, Buckner JC, Brown PD, Giannini C, Flynn PJ, LaPlant BR, Jaeckle KA (2007) The relationship between six-month progression-free survival and 12-month overall survival end points for phase II trials in patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Neuro-oncology 9:29–38
Wu W, Lamborn KR, Buckner JC, Novotny PJ, Chang SM, O’Fallon JR, Jaeckle KA, Prados MD (2010) Joint NCCTG and NABTC prognostic factors analysis for high-grade recurrent glioma. Neuro-oncology 12:164–172. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nop019
Plate KH, Breier G, Weich HA, Risau W (1992) Vascular endothelial growth factor is a potential tumour angiogenesis factor in human gliomas in vivo. Nature 359:845–848
Millauer B, Shawver LK, Plate KH, Risau W, Ullrich A (1994) Glioblastoma growth inhibited in vivo by a dominant-negative Flk-1 mutant. Nature 367:576–579
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2000) Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature 407:249–257
Dvorak HF (2002) Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a critical cytokine in tumor angiogenesis and a potential target for diagnosis and therapy. J Clin Oncol 20:4368–4380
Jain RK (2005) Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 307:58–62
Winkler F, Kozin SV, Tong RT, Chae SS, Booth MF, Garkavtsev I, Xu L, Hicklin DJ, Fukumura D, di Tomaso E, Munn LL, Jain RK (2004) Kinetics of vascular normalization by VEGFR2 blockade governs brain tumor response to radiation: role of oxygenation, angiopoietin-1, and matrix metalloproteinases. Cancer Cell 6:553–563
Tong RT, Boucher Y, Kozin SV, Winkler F, Hicklin DJ, Jain RK (2004) Vascular normalization by vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 blockade induces a pressure gradient across the vasculature and improves drug penetration in tumors. Cancer Res 64:3731–3736
Lee CG, Heijn M, di Tomaso E, Griffon-Etienne G, Ancukiewicz M, Koike C, Park KR, Ferrara N, Jain RK, Suit HD, Boucher Y (2000) Anti-Vascular endothelial growth factor treatment augments tumor radiation response under normoxic or hypoxic conditions. Cancer Res 60:5565–5570
Inai T, Mancuso M, Hashizume H, Baffert F, Haskell A, Baluk P, Hu-Lowe DD, Shalinsky DR, Thurston G, Yancopoulos GD, McDonald DM (2004) Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling in cancer causes loss of endothelial fenestrations, regression of tumor vessels, and appearance of basement membrane ghosts. Am J Pathol 165:35–52
Wildiers H, Guetens G, De Boeck G, Verbeken E, Landuyt B, Landuyt W, de Bruijn EA, van Oosterom AT (2003) Effect of antivascular endothelial growth factor treatment on the intratumoral uptake of CPT-11. Br J Cancer 88:1979–1986
Willett CG, Boucher Y, di Tomaso E, Duda DG, Munn LL, Tong RT, Chung DC, Sahani DV, Kalva SP, Kozin SV, Mino M, Cohen KS, Scadden DT, Hartford AC, Fischman AJ, Clark JW, Ryan DP, Zhu AX, Blaszkowsky LS, Chen HX, Shellito PC, Lauwers GY, Jain RK (2004) Direct evidence that the VEGF-specific antibody bevacizumab has antivascular effects in human rectal cancer. Nat Med 10:145–147
Batchelor TT, Sorensen AG, di Tomaso E, Zhang WT, Duda DG, Cohen KS, Kozak KR, Cahill DP, Chen PJ, Zhu M, Ancukiewicz M, Mrugala MM, Plotkin S, Drappatz J, Louis DN, Ivy P, Scadden DT, Benner T, Loeffler JS, Wen PY, Jain RK (2007) AZD2171, a Pan-VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor, normalizes tumor vasculature and alleviates edema in glioblastoma patients. Cancer Cell 11:83–95
Wen PY, Macdonald DR, Reardon DA, Cloughesy TF, Sorensen AG, Galanis E, Degroot J, Wick W, Gilbert MR, Lassman AB, Tsien C, Mikkelsen T, Wong ET, Chamberlain MC, Stupp R, Lamborn KR, Vogelbaum MA, van den Bent MJ, Chang SM (2010) Updated response assessment criteria for high-grade gliomas: response assessment in neuro-oncology working group. J Clin Oncol 28:1963–1972
Vredenburgh JJ, Desjardins A, Herndon JE 2nd, Marcello J, Reardon DA, Quinn JA, Rich JN, Sathornsumetee S, Gururangan S, Sampson J, Wagner M, Bailey L, Bigner DD, Friedman AH, Friedman HS (2007) Bevacizumab plus irinotecan in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. J Clin Oncol 25:4722–4729
Pocock SJ (1982) Interim analyses for randomized clinical trials: the group sequential approach. Biometrics 38:153–162
Vredenburgh JJ, Desjardins A, Herndon JE 2nd, Dowell JM, Reardon DA, Quinn JA, Rich JN, Sathornsumetee S, Gururangan S, Wagner M, Bigner DD, Friedman AH, Friedman HS (2007) Phase II trial of bevacizumab and irinotecan in recurrent malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res 13:1253–1259
Raizer JJ, Grimm S, Chamberlain MC, Nicholas MK, Chandler JP, Muro K, Dubner S, Rademaker AW, Renfrow J, Bredel M (2010) A phase 2 trial of single-agent bevacizumab given in an every-3-week schedule for patients with recurrent high-grade gliomas. Cancer 116:5297–5305. doi:10.1002/cncr.25462
Reardon DA, Desjardins A, Vredenburgh JJ, Gururangan S, Sampson JH, Sathornsumetee S, McLendon RE, Herndon JE 2nd, Marcello JE, Norfleet J, Friedman AH, Bigner DD, Friedman HS (2009) Metronomic chemotherapy with daily, oral etoposide plus bevacizumab for recurrent malignant glioma: a phase II study. Br J Cancer 101:1986–1994
Hasselbalch B, Lassen U, Hansen S, Holmberg M, Sorensen M, Kosteljanetz M, Broholm H, Stockhausen MT, Poulsen HS (2010) Cetuximab, bevacizumab, and irinotecan for patients with primary glioblastoma and progression after radiation therapy and temozolomide: a phase II trial. Neuro-oncology 12:508–516. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nop063
Gutin PH, Iwamoto FM, Beal K, Mohile NA, Karimi S, Hou BL, Lymberis S, Yamada Y, Chang J, Abrey LE (2009) Safety and efficacy of bevacizumab with hypofractionated stereotactic irradiation for recurrent malignant gliomas. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 75:156–163
Desjardins A, Reardon DA, Coan A, Marcello J, Herndon JE, 2nd, Bailey L, Peters KB, Friedman HS, Vredenburgh JJ (2011) Bevacizumab and daily temozolomide for recurrent glioblastoma. Cancer. doi:10.1002/cncr.26381
Yang JC, Haworth L, Sherry RM, Hwu P, Schwartzentruber DJ, Topalian SL, Steinberg SM, Chen HX, Rosenberg SA (2003) A randomized trial of bevacizumab, an anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody, for metastatic renal cancer. N Engl J Med 349:427–434
Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, Berlin J, Baron A, Griffing S, Holmgren E, Ferrara N, Fyfe G, Rogers B, Ross R, Kabbinavar F (2004) Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med 350:2335–2342
Miller K, Wang M, Gralow J, Dickler M, Cobleigh M, Perez EA, Shenkier T, Cella D, Davidson NE (2007) Paclitaxel plus bevacizumab versus paclitaxel alone for metastatic breast cancer. N Engl J Med 357:2666–2676
Sandler A, Gray R, Perry MC, Brahmer J, Schiller JH, Dowlati A, Lilenbaum R, Johnson DH (2006) Paclitaxel-carboplatin alone or with bevacizumab for non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 355:2542–2550
Friedman HS, Petros WP, Friedman AH, Schaaf LJ, Kerby T, Lawyer J, Parry M, Houghton PJ, Lovell S, Rasheed K, Cloughsey T, Stewart ES, Colvin OM, Provenzale JM, McLendon RE, Bigner DD, Cokgor I, Haglund M, Rich J, Ashley D, Malczyn J, Elfring GL, Miller LL (1999) Irinotecan therapy in adults with recurrent or progressive malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 17:1516–1525
Prados MD, Warnick RE, Mack EE, Chandler KL, Rabbitt J, Page M, Malec M (1996) Intravenous carboplatin for recurrent gliomas. A dose-escalating phase II trial. Am J Clin Oncol 19:609–612
Yung WK, Mechtler L, Gleason MJ (1991) Intravenous carboplatin for recurrent malignant glioma: a phase II study. J Clin Oncol 9:860–864
Batchelor TT, Gilbert MR, Supko JG, Carson KA, Nabors LB, Grossman SA, Lesser GJ, Mikkelsen T, Phuphanich S (2004) Phase 2 study of weekly irinotecan in adults with recurrent malignant glioma: final report of NABTT 97–11. Neuro-oncol 6:21–27
Gilbert MR, Supko JG, Batchelor T, Lesser G, Fisher JD, Piantadosi S, Grossman S (2003) Phase I clinical and pharmacokinetic study of irinotecan in adults with recurrent malignant glioma. Clin Cancer Res 9:2940–2949
Santisteban M, Buckner JC, Reid JM, Wu W, Scheithauer BW, Ames MM, Felten SJ, Nikcevich DA, Wiesenfeld M, Jaeckle KA, Galanis E (2009) Phase II trial of two different irinotecan schedules with pharmacokinetic analysis in patients with recurrent glioma: north central cancer treatment group results. J Neurooncol 92(2):165–175
Coggins CA, Elion GB, Houghton PJ, Hare CB, Keir S, Colvin OM, Bigner DD, Friedman HS (1998) Enhancement of irinotecan (CPT-11) activity against central nervous system tumor xenografts by alkylating agents. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 41:485–490
Patel VJ, Elion GB, Houghton PJ, Keir S, Pegg AE, Johnson SP, Dolan ME, Bigner DD, Friedman HS (2000) Schedule-dependent activity of temozolomide plus CPT-11 against a human central nervous system tumor-derived xenograft. Clin Cancer Res 6:4154–4157
Houghton PJ, Stewart CF, Cheshire PJ, Richmond LB, Kirstein MN, Poquette CA, Tan M, Friedman HS, Brent TP (2000) Antitumor activity of temozolomide combined with irinotecan is partly independent of O6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase and mismatch repair phenotypes in xenograft models. Clin Cancer Res 6:4110–4118
Castellino RC, Elion GB, Keir ST, Houghton PJ, Johnson SP, Bigner DD, Friedman HS (2000) Schedule-dependent activity of irinotecan plus BCNU against malignant glioma xenografts. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 45:345–349
Jain RK, Tong RT, Munn LL (2007) Effect of vascular normalization by antiangiogenic therapy on interstitial hypertension, peritumor edema, and lymphatic metastasis: insights from a mathematical model. Cancer Res 67:2729–2735
Reardon DA, Desjardins A, Peters KB, Vredenburgh JJ, Gururangan S, Sampson JH, McLendon RE, Herndon I, J. E., Coan A, Threatt S, Friedman AH, Friedman HS (2011) Phase II study of carboplatin, irinotecan and bevacizumab for recurrent glioblastoma after progression on bevacizumab therapy. Cancer (in press)
Claes A, Wesseling P, Jeuken J, Maass C, Heerschap A, Leenders WP (2008) Antiangiogenic compounds interfere with chemotherapy of brain tumors due to vessel normalization. Mol Cancer Ther 7:71–78. doi:10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-07-0552
Lamszus K, Kunkel P, Westphal M (2003) Invasion as limitation to anti-angiogenic glioma therapy. Acta Neurochir Suppl 88:169–177
Rubenstein JL, Kim J, Ozawa T, Zhang M, Westphal M, Deen DF, Shuman MA (2000) Anti-VEGF antibody treatment of glioblastoma prolongs survival but results in increased vascular cooption. Neoplasia 2:306–314
Ebos JM, Lee CR, Cruz-Munoz W, Bjarnason GA, Christensen JG, Kerbel RS (2009) Accelerated metastasis after short-term treatment with a potent inhibitor of tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 15:232–239
Paez-Ribes M, Allen E, Hudock J, Takeda T, Okuyama H, Vinals F, Inoue M, Bergers G, Hanahan D, Casanovas O (2009) Antiangiogenic therapy elicits malignant progression of tumors to increased local invasion and distant metastasis. Cancer Cell 15:220–231
de Groot JF, Fuller G, Kumar AJ, Piao Y, Eterovic K, Ji Y, Conrad CA (2010) Tumor invasion after treatment of glioblastoma with bevacizumab: radiographic and pathologic correlation in humans and mice. Neuro-oncology 12:233–242. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nop027
Iwamoto FM, Abrey LE, Beal K, Gutin PH, Rosenblum MK, Reuter VE, DeAngelis LM, Lassman AB (2009) Patterns of relapse and prognosis after bevacizumab failure in recurrent glioblastoma. Neurology 73:1200–1206
Keunen O, Johansson M, Oudin A, Sanzey M, Rahim SA, Fack F, Thorsen F, Taxt T, Bartos M, Jirik R, Miletic H, Wang J, Stieber D, Stuhr L, Moen I, Rygh CB, Bjerkvig R, Niclou SP (2011) Anti-VEGF treatment reduces blood supply and increases tumor cell invasion in glioblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:3749–3754. doi:10.1073/pnas.1014480108
Macdonald DR, Cascino TL, Schold SC Jr, Cairncross JG (1990) Response criteria for phase II studies of supratentorial malignant glioma. J Clin Oncol 8:1277–1280
Sathornsumetee S, Desjardins A, Vredenburgh JJ, McLendon RE, Marcello J, Herndon JE, Mathe A, Hamilton M, Rich JN, Norfleet JA, Gururangan S, Friedman HS, Reardon DA (2010) Phase II trial of bevacizumab and erlotinib in patients with recurrent malignant glioma. Neuro Oncol 12(12):1300–1310
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by NIH Grants 5P50-NS-20023 and 5 R37 CA11898; and a grant from Genentech Pharmaceuticals. The investigators wish to thank Wendy Gentry for her assistance in the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reardon, D.A., Desjardins, A., Peters, K.B. et al. Phase II study of carboplatin, irinotecan, and bevacizumab for bevacizumab naïve, recurrent glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 107, 155–164 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0722-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-011-0722-2