Abstract
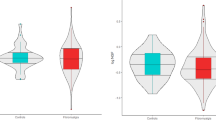
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is involved in neuronal survival and synaptic plasticity of the central and peripheral nervous system. BDNF appears to modulate nociceptive sensory inputs and pain hypersensitivity and has been studied in pathological situations, including chronic pain conditions and major depression. Increased serum BDNF levels have been recently reported in fibromyalgia (FM). In the present study, we assessed plasma BDNF levels in patients with FM and controls. Plasma BDNF was measured from 30 female patients with FM and 30 healthy age- and gender-matched volunteers using an enzyme immunoassay. FM patients showed higher levels of BDNF (FM = 167.1 ± 171.2 pg/mL) when compared with the control group (control = 113.8 ± 149.6 pg/mL) (P = 0.049; Mann–Whitney test). Six out of 30 controls presented superior values to the medium (15/15) of the patients with fibromyalgia (129 pg/mL) (P = 0.029, Fisher exact test). There was no correlation between plasma BDNF levels and age, disease duration, pain score, number of pain points and HAM-D score. Our results confirm previous findings of increased plasma BDNF levels in patients with FM, suggesting that BDNF may be involved in the pathophysiology of Fibromyalgia, despite high levels of depression.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mease P (2005) Fibromyalgia syndrome: review of clinical presentation, pathogenesis, outcome measures, and treatment. J Rheumatol Suppl 75:6–21
Gran JT (2003) The epidemiology of chronic generalized musculoskeletal pain. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 17:547–561
Katz RS, Wolfe F, Michaud K (2006) Fibromyalgia diagnosis: a comparison of clinical, survey, and American College of Rheumatology criteria. Arthritis Rheum 54:169–176
Meeus M, Nijs J (2007) Central sensitization: a biopsychosocial explanation for chronic widespread pain in patients with fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome. Clin Rheumatol 26:465–473
Schwarz MJ, Spath M, Muller-Bardorff H (1999) Relationship of substance P, 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid and tryptophan in serum of fibromyalgia patients. Neurosci Lett 259:196–198
Julien N, Goffaux P, Arsenault P (2005) Widespread pain in fibromyalgia is related to a deficit of endogenous pain inhibition. Pain 114:295–302
Kassam A, Patten SB (2006) Major depression, fibromyalgia and labour force participation: a population-based cross-sectional study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 7:4
Laske C, Stransky E, Eschweiler GW (2007) Increased BDNF serum concentration in fibromyalgia with or without depression or antidepressants. J Psychiatr Res 41:600–605
Suhr JA (2003) Neuropsychological impairment in fibromyalgia: relation to depression, fatigue, and pain. J Psychosom Res 55:321–329
Wu YJ, Kruttgen A, Moller JC, Len G, McAuliffe G, Ma C, Tai JP, Xu F (2004) Nerve growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and neurotrophin-3 are sorted to dense-core vesicles and released via the regulated pathway in primary rat cortical neurons. J Neurosci Res 75:825–834
Malcangio M, Lessmann V (2003) A common thread for pain and memory synapses? Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and trkB receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:116–121
Delafoy L, Gelot A, Ardid D (2006) Interactive involvement of brain derived neurotrophic factor, nerve growth factor, and calcitonin gene related peptide in colonic hypersensitivity in the rat. Gut 55:940–945
Groth R, Aanonsen L (2002) Spinal brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) produces hyperalgesia in normal mice while antisense directed against either BDNF or trkB, prevent inflammation-induced hyperalgesia. Pain 100:171–181
Wu K, Len GW, McAuliffe G (2004) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor acutely enhances tyrosine phosphorylation of the AMPA receptor subunit GluR1 via NMDA receptor-dependent mechanisms. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 130:178–186
Yoshimura R, Mitoma M, Sugita A et al (2007) Effects of paroxetine or milnacipran on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor in depressed patients. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 31:1034–1037
Karege F, Perret G, Bondolfi G (2002) Decreased serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in major depressed patients. Psychiatry Res 109:143–148
Aydemir O, Deveci A, Taneli F (2005) The effect of chronic antidepressant treatment on serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in depressed patients: a preliminary study. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29:261–265
Shimizu E, Hashimoto K, Okamura N, Koike K, Komatsu N, Kumakiri C, Nakazato M, Watanabe H, Shinoda N, Okada S, Iyo M (2003) Alterations of serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in depressed patients with or without antidepressants. Biol Psychiatry 54:70–75
Piccinni A, Marazziti D, Catena M et al (2007) Plasma and serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in depressed patients during 1 year of antidepressant treatments. J Affect Disord 105:279–283
Chen B, Dowlatshahi D, MacQueen GM (2001) Increased hippocampal BDNF immunoreactivity in subjects treated with antidepressant medication. Biol Psychiatry 50:260–265
Sarchielli P, Mancini ML, Floridi A et al (2007) Increased levels of neurotrophins are not specific for chronic migraine: evidence from primary fibromyalgia syndrome. J Pain 8:737–745
Hamilton M (1960) A rating scale for depression. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 23:56–62
Duric V, McCarson KE (2006) Effects of analgesic or antidepressant drugs on pain- or stress-evoked hippocampal and spinal neurokinin-1 receptor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene expression in the rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 319:1235–1243
Duric V, McCarson KE (2006) Persistent pain produces stress-like alterations in hippocampal neurogenesis and gene expression. J Pain 7:544–555
Nibuya M, Morinobu S, Duman RS (1995) Regulation of BDNF and trkB mRNA in rat brain by chronic electroconvulsive seizure and antidepressant drug treatments. J Neurosci 15:7539–7547
Lee J, Duan W, Mattson MP (2002) Evidence that brain-derived neurotrophic factor is required for basal neurogenesis and mediates, in part, the enhancement of neurogenesis by dietary restriction in the hippocampus of adult mice. J Neurochem 82:1367–1375
Sairanen M, Lucas G, Ernfors P (2005) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and antidepressant drugs have different but coordinated effects on neuronal turnover, proliferation, and survival in the adult dentate gyrus. J Neurosci 25:1089–1094
Pezet S, Cunningham J, Patel J (2002) BDNF modulates sensory neuron synaptic activity by a facilitation of GABA transmission in the dorsal horn. Mol Cell Neurosci 21:51–62
Pezet S, Malcangio M, Lever IJ (2002) Noxious stimulation induces Trk receptor and downstream ERK phosphorylation in spinal dorsal horn. Mol Cell Neurosci 21:684–695
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haas, L., Portela, L.V.C., Böhmer, A.E. et al. Increased Plasma Levels of Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) in Patients with Fibromyalgia. Neurochem Res 35, 830–834 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0129-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-010-0129-z