Abstract
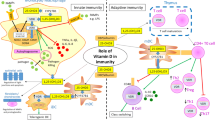
Lately, vitamin D has been linked with metabolic and immunological processes, which established its role as an essential component of human health preservation. Vitamin D has been defined as natural immune modulators, and upon activation of its receptors (VDRs), it regulates calcium metabolism, cellular growth, proliferation and apoptosis, and other immunological functions. Epidemiological data underline a strong correlation between poor vitamin D status and higher risk for chronic inflammatory illnesses of various etiologies, including autoimmune diseases. Epidemiological, genetic, and basic studies indicated a potential role of vitamin D in the pathogenesis of certain systemic and organ-specific autoimmune diseases. These studies demonstrate correlation between low vitamin D and prevalence of diseases. In addition, VDRs’ polymorphisms observed in some of these autoimmune diseases may further support a plausible pathogenic link. Notably, for some autoimmune disease, no correlation with vitamin D levels could be confirmed. Thus, in the current review we present the body of evidence regarding the plausible roles of vitamin D and VDR’s polymorphism in the pathogenesis of autoimmunity. We summarize the data regarding systemic (i.e., systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.) and organ-specific (i.e., multiple sclerosis, diabetes mellitus, primary biliary cirrhosis, etc.) autoimmune diseases, in which low level of vitamin D was found comparing to healthy subjects. In addition, we discuss the correlations between vitamin D levels and clinical manifestations and/or activity of diseases. In this context, we address the rational for vitamin D supplementation in patients suffering from autoimmune diseases. Further studies addressing the mechanisms by which vitamin D affects autoimmunity and the proper supplementation required are needed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnson Y, Amital H, Shoenfeld Y (2007) Vitamin D and autoimmunity: new aetiological and therapeutic considerations. Ann Rheum Dis 66(9):1137–1142
Holick MF (2007) Vitamin D, deficiency. N Engl J Med 357(3):266–281
Peelen E, Knippenberg S, Muris AH, Thewissen M, Smolders J, Tervaert JW et al (2011) Effects of vitamin D on the peripheral adaptive immune system: a review. Autoimmun Rev 10(12):733–743
Toubi E, Shoenfeld Y (2010) The role of vitamin D in regulating immune responses. Isr Med Assoc J 12(3):174–175
Pelajo CF, Lopez-Benitez JM, Miller LC (2010) Vitamin D and autoimmune rheumatologic disorders. Autoimmun Rev 9(7):507–510
Shapira Y, Agmon-Levin N, Shoenfeld Y (2010) Mycobacterium tuberculosis, autoimmunity, and vitamin D. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 38(2–3):169–177
Chen S, Sims GP, Chen XX, Gu YY, Lipsky PE (2007) Modulatory effects of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 on human B cell differentiation. J Immunol 179(3):1634–1647
Cutolo M, Plebani M, Shoenfeld Y, Adorini L, Tincani A (2011) Vitamin D endocrine system and the immune response in rheumatic diseases. Vitam Horm 86:327–351
Joshi S, Pantalena LC, Liu XK, Gaffen SL, Liu H, Rohowsky-Kochan C et al (2011) 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) ameliorates Th17 autoimmunity via transcriptional modulation of interleukin-17A. Mol Cell Biol 31(17):3653–3669
Khoo AL, Koenen HJ, Chai LY, Sweep FC, Netea MG, van der Ven AJ et al (2012) Seasonal variation in vitamin D(3) levels is paralleled by changes in the peripheral blood human T cell compartment. PLoS One 7(1):e29250
Antico A, Tampoia M, Tozzoli R, Bizzaro N (2012) Can supplementation with vitamin D reduce the risk or modify the course of autoimmune diseases? A systematic review of the literature. Autoimmun Rev 12(2):127–136
Souberbielle JC, Body JJ, Lappe JM, Plebani M, Shoenfeld Y, Wang TJ et al (2010) Vitamin D and musculoskeletal health, cardiovascular disease, autoimmunity and cancer: recommendations for clinical practice. Autoimmun Rev 9(11):709–715
Broder AR, Tobin JN, Putterman C (2010) Disease-specific definitions of vitamin D deficiency need to be established in autoimmune and non-autoimmune chronic diseases: a retrospective comparison of three chronic diseases. Arthritis Res Ther 12(5):R191
Shoenfeld N, Amital H, Shoenfeld Y (2009) The effect of melanism and vitamin D synthesis on the incidence of autoimmune disease. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 5(2):99–105
Oren Y, Shapira Y, Agmon-Levin N, Kivity S, Zafrir Y, Altman A et al (2010) Vitamin D insufficiency in a sunny environment: a demographic and seasonal analysis. Isr Med Assoc J 12(12):751–756
Shapira Y, Agmon-Levin N, Shoenfeld Y (2010) Defining and analyzing geoepidemiology and human autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 34(3):J168–J177
Carmi G, Amital H (2011) The geoepidemiology of autoimmunity: capsules from the 7th International Congress on Autoimmunity, Ljubljana, Slovenia, May 2010. Isr Med Assoc J 13(2):121–127
Miheller P, Muzes G, Hritz I, Lakatos G, Pregun I, Lakatos PL et al (2009) Comparison of the effects of 1,25 dihydroxyvitamin D and 25 hydroxyvitamin D on bone pathology and disease activity in Crohn's disease patients. Inflamm Bowel Dis 15(11):1656–1662
Cutolo M, Pizzorni C, Sulli A (2011) Vitamin D endocrine system involvement in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Autoimmun Rev 11(2):84–87
Kivity S, Agmon-Levin N, Blank M, Shoenfeld Y (2009) Infections and autoimmunity—friends or foes? Trends Immunol 30(8):409–414
Liu PT, Stenger S, Li H, Wenzel L, Tan BH, Krutzik SR et al (2006) Toll-like receptor triggering of a vitamin D-mediated human antimicrobial response. Science 311(5768):1770–1773
Barzilai O, Sherer Y, Ram M, Izhaky D, Anaya JM, Shoenfeld Y (2007) Epstein–Barr virus and cytomegalovirus in autoimmune diseases: are they truly notorious? A preliminary report. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1108:567–577
Yenamandra SP, Lundin A, Arulampalam V, Yurchenko M, Pettersson S, Klein G et al (2009) Expression profile of nuclear receptors upon Epstein–Barr virus induced B cell transformation. Exp Oncol 31(2):92–96
Kamen DL, Cooper GS, Bouali H, Shaftman SR, Hollis BW, Gilkeson GS (2006) Vitamin D deficiency in systemic lupus erythematosus. Autoimmun Rev 5(2):114–117
Cutolo M, Otsa K (2008) Review: vitamin D, immunity and lupus. Lupus 17(1):6–10
Borba VZ, Vieira JG, Kasamatsu T, Radominski SC, Sato EI, Lazaretti-Castro M (2009) Vitamin D deficiency in patients with active systemic lupus erythematosus. Osteoporos Int 20(3):427–433
Kim HA, Sung JM, Jeon JY, Yoon JM, Suh CH (2011) Vitamin D may not be a good marker of disease activity in Korean patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatol Int 31(9):1189–1194
Ruiz-Irastorza G, Egurbide MV, Olivares N, Martinez-Berriotxoa A, Aguirre C (2008) Vitamin D deficiency in systemic lupus erythematosus: prevalence, predictors and clinical consequences. Rheumatol (Oxford) 47(6):920–923
Amital H, Szekanecz Z, Szucs G, Danko K, Nagy E, Csepany T et al (2010) Serum concentrations of 25-OH vitamin D in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) are inversely related to disease activity: is it time to routinely supplement patients with SLE with vitamin D? Ann Rheum Dis 69(6):1155–1157
Lopez-Robles C, Rios-Fernandez R, Callejas-Rubio JL, Ortego-Centeno N (2011) Vitamin D deficiency in a cohort of patients with systemic lupus erythematous from the South of Spain. Lupus 20(3):330–331
Esdaile JM, Abrahamowicz M, Grodzicky T, Li Y, Panaritis C, du Berger R et al (2001) Traditional Framingham risk factors fail to fully account for accelerated atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 44(10):2331–2337
Wu PW, Rhew EY, Dyer AR, Dunlop DD, Langman CB, Price H et al (2009) 25-hydroxyvitamin D and cardiovascular risk factors in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 61(10):1387–1395
Luo XY, Yang MH, Wu FX, Wu LJ, Chen L, Tang Z et al (2012) Vitamin D receptor gene BsmI polymorphism B allele, but not BB genotype, is associated with systemic lupus erythematosus in a Han Chinese population. Lupus 21(1):53–59
Ozaki Y, Nomura S, Nagahama M, Yoshimura C, Kagawa H, Fukuhara S (2000) Vitamin-D receptor genotype and renal disorder in Japanese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Nephron 85(1):86–91
Sakulpipatsin W, Verasertniyom O, Nantiruj K, Totemchokchyakarn K, Lertsrisatit P, Janwityanujit S (2006) Vitamin D receptor gene BsmI polymorphisms in Thai patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 8(2):R48
Kornberg A, Blank M, Kaufman S, Shoenfeld Y (1994) Induction of tissue factor-like activity in monocytes by anti-cardiolipin antibodies. J Immunol 153(3):1328–1332
Orbach H, Zandman-Goddard G, Amital H, Barak V, Szekanecz Z, Szucs G et al (2007) Novel biomarkers in autoimmune diseases: prolactin, ferritin, vitamin D, and TPA levels in autoimmune diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1109:385–400
Agmon-Levin N, Blank M, Zandman-Goddard G, Orbach H, Meroni PL, Tincani A et al (2011) Vitamin D: an instrumental factor in the anti-phospholipid syndrome by inhibition of tissue factor expression. Ann Rheum Dis 70(1):145–150
Lindqvist PG, Epstein E, Olsson H (2009) Does an active sun exposure habit lower the risk of venous thrombotic events? A D-lightful hypothesis. J Thromb Haemost 7(4):605–610
Boissier MC, Semerano L, Challal S, Saidenberg-Kermanac'h N, Falgarone G (2012) Rheumatoid arthritis: from autoimmunity to synovitis and joint destruction. J Autoimmun 39(3):222–8
Welsh P, Peters MJ, Sattar N (2011) Is vitamin D in rheumatoid arthritis a magic bullet or a mirage? The need to improve the evidence base prior to calls for supplementation. Arthritis Rheum 63(7):1763–1769
Zold E, Szodoray P, Nakken B, Barath S, Kappelmayer J, Csathy L et al (2011) Alfacalcidol treatment restores derailed immune-regulation in patients with undifferentiated connective tissue disease. Autoimmun Rev 10(3):155–162
Kroger H, Penttila IM, Alhava EM (1993) Low serum vitamin D metabolites in women with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 22(4):172–177
Cutolo M, Otsa K, Laas K, Yprus M, Lehtme R, Secchi ME et al (2006) Circannual vitamin d serum levels and disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: Northern versus Southern Europe. Clin Exp Rheumatol 24(6):702–704
Patel S, Farragher T, Berry J, Bunn D, Silman A, Symmons D (2007) Association between serum vitamin D metabolite levels and disease activity in patients with early inflammatory polyarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 56(7):2143–2149
Straube S, Derry S, Moore RA, McQuay HJ (2010) Vitamin D for the treatment of chronic painful conditions in adults. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010(1):CD007771
Laragione T, Shah A, Gulko PS (2012) The vitamin D receptor regulates rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblast invasion and morphology. Mol Med 18(1):194–200
Baker JF, Baker DG, Toedter G, Shults J, Von Feldt JM, Leonard MB (2012) Associations between vitamin D, disease activity, and clinical response to therapy in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 30(5):658–64
Hiraki LT, Munger KL, Costenbader KH, Karlson EW (2012) Dietary intake of vitamin d during adolescence and risk of adult onset systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 64(12):1829–36
Harari M, Dramsdahl E, Shany S, Baumfeld Y, Ingber A, Novack V et al (2011) Increased vitamin D serum levels correlate with clinical improvement of rheumatic diseases after Dead Sea climatotherapy. Isr Med Assoc J 13(4):212–215
Wen H, Baker JF (2011) Vitamin D, immunoregulation, and rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Rheumatol 17(2):102–107
Leventis P, Patel S (2008) Clinical aspects of vitamin D in the management of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol (Oxford) 47(11):1617–1621
Ibn Yacoub Y, Amine B, Laatiris A, Wafki F, Znat F, Hajjaj-Hassouni N (2012) Bone density in Moroccan women with systemic scleroderma and its relationships with disease-related parameters and vitamin D status. Rheumatol Int 32(10):3143–8
Gambichler T, Chrobok I, Hoxtermann S, Kreuter A (2010) Significantly decreased serum 25-hydroxyvitamin d levels in a large German systemic sclerosis cohort. J Rheumatol 38(11):2492–2493, author reply 4
Rios Fernandez R, Fernandez Roldan C, Callejas Rubio JL, Ortego Centeno N (2010) Vitamin D deficiency in a cohort of patients with systemic scleroderma from the south of Spain. J Rheumatol 37(6):1355, author reply 6
Vacca A, Cormier C, Piras M, Mathieu A, Kahan A, Allanore Y (2009) Vitamin D deficiency and insufficiency in 2 independent cohorts of patients with systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 36(9):1924–1929
Seriolo B, Molfetta L, Cutolo M (2011) Seasonal variations in serum levels of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol 30(3):445–446
Arnson Y, Amital H, Agmon-Levin N, Alon D, Sanchez-Castanon M, Lopez-Hoyos M et al (2011) Serum 25-OH vitamin D concentrations are linked with various clinical aspects in patients with systemic sclerosis: a retrospective cohort study and review of the literature. Autoimmun Rev 10(8):490–494
Caramaschi P, Dalla Gassa A, Ruzzenente O, Volpe A, Ravagnani V, Tinazzi I et al (2010) Very low levels of vitamin D in systemic sclerosis patients. Clin Rheumatol 29(12):1419–1425
Muller K, Oxholm P, Sorensen OH, Thymann M, Hoier-Madsen M, Bendtzen K (1990) Abnormal vitamin D3 metabolism in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 49(9):682–684
Szodoray P, Horvath IF, Papp G, Barath S, Gyimesi E, Csathy L et al (2010) The immunoregulatory role of vitamins A, D and E in patients with primary Sjogren's syndrome. Rheumatol (Oxford) 49(2):211–217
Agmon-Levin N, Kivity S, Tzioufas AG, Lopez Hoyos M, Rozman B, Efes I et al (2012) Low levels of vitamin-D are associated with neuropathy and lymphoma among patients with Sjogren's syndrome. J Autoimmun 39(3):234–239
Cutolo M (2008) Vitamin D, or hormone D deficiency in autoimmune rheumatic diseases, including undifferentiated connective tissue disease. Arthritis Res Ther 10(6):123
Zold E, Szodoray P, Gaal J, Kappelmayer J, Csathy L, Gyimesi E et al (2008) Vitamin D deficiency in undifferentiated connective tissue disease. Arthritis Res Ther 10(5):R123
Hajas A, Sandor J, Csathy L, Csipo I, Barath S, Paragh G et al (2011) Vitamin D insufficiency in a large MCTD population. Autoimmun Rev 10(6):317–324
Robinson AB, Thierry-Palmer M, Gibson KL, Rabinovich CE (2012) Disease activity, proteinuria, and vitamin D status in children with systemic lupus erythematosus and juvenile dermatomyositis. J Pediatr 160(2):297–302
Sadovnick AD (2012) Genetic background of multiple sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev 11(3):163–166
Sellner J, Kraus J, Awad A, Milo R, Hemmer B, Stuve O (2011) The increasing incidence and prevalence of female multiple sclerosis—a critical analysis of potential environmental factors. Autoimmun Rev 10(8):495–502
Hanwell HE, Banwell B (2011) Assessment of evidence for a protective role of vitamin D in multiple sclerosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812(2):202–212
Ascherio A, Munger KL, Simon KC (2010) Vitamin D and multiple sclerosis. Lancet Neurol 9(6):599–612
Simpson S Jr, Taylor B, Blizzard L, Ponsonby AL, Pittas F, Tremlett H et al (2010) Higher 25-hydroxyvitamin D is associated with lower relapse risk in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 68(2):193–203
Smolders J, Thewissen M, Theunissen R, Peelen E, Knippenberg S, Menheere P et al (2011) Vitamin D-related gene expression profiles in immune cells of patients with relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 235(1–2):91–97
Sternberg Z (2012) Autonomic dysfunction: a unifying multiple sclerosis theory, linking chronic cerebrospinal venous insufficiency, vitamin D(3), and Epstein–Barr virus. Autoimmun Rev 12(2):250–9
Stein MS, Liu Y, Gray OM, Baker JE, Kolbe SC, Ditchfield MR et al (2011) A randomized trial of high-dose vitamin D2 in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Neurology 77(17):1611–1618
Burton JM, Kimball S, Vieth R, Bar-Or A, Dosch HM, Cheung R et al (2010) A phase I/II dose-escalation trial of vitamin D3 and calcium in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 74(23):1852–1859
Smolders J, Peelen E, Thewissen M, Cohen Tervaert JW, Menheere P, Hupperts R et al (2010) Safety and T cell modulating effects of high dose vitamin D3 supplementation in multiple sclerosis. PLoS One 5(12):e15235
Simon KC, Munger KL, Xing Y, Ascherio A (2010) Polymorphisms in vitamin D metabolism related genes and risk of multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 16(2):133–138
Agliardi C, Guerini FR, Saresella M, Caputo D, Leone MA, Zanzottera M et al (2011) Vitamin D receptor (VDR) gene SNPs influence VDR expression and modulate protection from multiple sclerosis in HLA-DRB1*15-positive individuals. Brain Behav Immun 25(7):1460–1467
Kivity S, Agmon-Levin N, Zisappl M, Shapira Y, Nagy EV, Danko K et al (2011) Vitamin D and autoimmune thyroid diseases. Cell Mol Immunol 8(3):243–247
Twig G, Shina A, Amital H, Shoenfeld Y (2012) Pathogenesis of infertility and recurrent pregnancy loss in thyroid autoimmunity. J Autoimmun 38(2–3):J275–J281
Goswami R, Marwaha RK, Gupta N, Tandon N, Sreenivas V, Tomar N et al (2009) Prevalence of vitamin D deficiency and its relationship with thyroid autoimmunity in Asian Indians: a community-based survey. Br J Nutr 102(3):382–386
Effraimidis G, Badenhoop K, Tijssen JG, Wiersinga WM (2012) Vitamin D deficiency is not associated with early stages of thyroid autoimmunity. Eur J Endocrinol 167(1):43–48
Lin WY, Wan L, Tsai CH, Chen RH, Lee CC, Tsai FJ (2006) Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms are associated with risk of Hashimoto's thyroiditis in Chinese patients in Taiwan. J Clin Lab Anal 20(3):109–112
Stefanic M, Papic S, Suver M, Glavas-Obrovac L, Karner I (2008) Association of vitamin D receptor gene 3'-variants with Hashimoto's thyroiditis in the Croatian population. Int J Immunogenet 35(2):125–131
Stefanic M, Karner I, Glavas-Obrovac L, Papic S, Vrdoljak D, Levak G et al (2005) Association of vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism with susceptibility to Graves' disease in Eastern Croatian population: case–control study. Croat Med J 46(4):639–646
Garcia-Manzanares A, Tenias JM, Lucendo AJ (2012) Bone mineral density directly correlates with duodenal Marsh stage in newly diagnosed adult celiac patients. Scand J Gastroenterol 8–9(47):927–36
Lerner A, Shapira Y, Agmon-Levin N, Pacht A, Ben-Ami Shor D, Lopez HM et al (2012) The clinical significance of 25OH-vitamin D status in celiac disease. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 42(3):322–330
Boucher BJ (2011) Vitamin D, insufficiency and diabetes risks. Curr Drug Targets 12(1):61–87
Wolden-Kirk H, Overbergh L, Christesen HT, Brusgaard K, Mathieu C (2011) Vitamin D and diabetes: its importance for beta cell and immune function. Mol Cell Endocrinol 347(1–2):106–120
Takiishi T, Gysemans C, Bouillon R, Mathieu C (2010) Vitamin D and diabetes. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 39(2):419–446, table of contents
Sorensen IM, Joner G, Jenum PA, Eskild A, Torjesen PA, Stene LC (2012) Maternal serum levels of 25-hydroxy-vitamin D during pregnancy and risk of type 1 diabetes in the offspring. Diabetes 61(1):175–178
Bizzarri C, Pitocco D, Napoli N, Di Stasio E, Maggi D, Manfrini S et al (2010) No protective effect of calcitriol on beta-cell function in recent-onset type 1 diabetes: the IMDIAB XIII trial. Diabetes Care 33(9):1962–1963
Aljabri KS, Bokhari SA, Khan MJ (2010) Glycemic changes after vitamin D supplementation in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus and vitamin D deficiency. Ann Saudi Med 30(6):454–458
McCarthy D, Duggan P, O'Brien M, Kiely M, McCarthy J, Shanahan F et al (2005) Seasonality of vitamin D status and bone turnover in patients with Crohn's disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 21(9):1073–1083
Joseph AJ, George B, Pulimood AB, Seshadri MS, Chacko A (2009) 25 (OH) vitamin D level in Crohn's disease: association with sun exposure & disease activity. Indian J Med Res 130(2):133–137
Simmons JD, Mullighan C, Welsh KI, Jewell DP (2000) Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism: association with Crohn's disease susceptibility. Gut 47(2):211–214
Selmi C, Meroni PL, Gershwin ME (2012) Primary biliary cirrhosis and Sjogren's syndrome: autoimmune epithelitis. J Autoimmun 39(1–2):34–42
Kempinska-Podhorecka A, Wunsch E, Jarowicz T, Raszeja-Wyszomirska J, Loniewska B, Kaczmarczyk M et al (2012) Vitamin d receptor polymorphisms predispose to primary biliary cirrhosis and severity of the disease in polish population. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2012:408723
Tanaka A, Nezu S, Uegaki S, Kikuchi K, Shibuya A, Miyakawa H et al (2009) Vitamin D receptor polymorphisms are associated with increased susceptibility to primary biliary cirrhosis in Japanese and Italian populations. J Hepatol 50(6):1202–1209
Marzano AV, Trevisan V, Eller-Vainicher C, Cairoli E, Marchese L, Morelli V et al (2012) Evidence for vitamin D deficiency and increased prevalence of fractures in autoimmune bullous skin diseases. Br J Dermatol 167(3):688–91
Akar A, Orkunoglu FE, Tunca M, Tastan HB, Kurumlu Z (2007) Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphisms are not associated with alopecia areata. Int J Dermatol 46(9):927–929
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Nancy Agmon-Levin and Emanuel Theodor contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Agmon-Levin, N., Theodor, E., Segal, R.M. et al. Vitamin D in Systemic and Organ-Specific Autoimmune Diseases. Clinic Rev Allerg Immunol 45, 256–266 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-012-8342-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-012-8342-y