Abstract
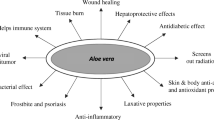
Aloe vera is used for vigor, wellness and medicinal purposes since rigvedic times. Health benefits of aloe vera include its application in wound healing, treating burns, minimizing frost bite damage, protection against skin damage from x-rays, lung cancer, intestinal problems, increasing high density lipoprotein (HDL), reducing low density lipoprotein (LDL), reducing blood sugar in diabetics, fighting acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS), allergies and improving immune system. Phytochemistry of aloe vera gel has revealed the presence of more than 200 bioactive chemicals. Aloe vera gel is extracted from its leaves and appropriate processing techniques are needed for stabilization as well as preparation of the end products. The industries involved in processing of aloe vera need Government surveillance to ensure that the aloe vera products have beneficial bio-active chemicals as per claims of the manufacturers. Regulatory bodies also need to look into the safety and toxicological aspects of aloe vera products for food applications. The claims made for medicinal value of aloe products should be supported by authentic and approved clinical trial data. It is presumptive to mention that nutraceutical claims of aloe products made by the manufacturers are numerous. However, approved clinical evidences are available only for lowering LDL, increasing HDL, decreasing blood glucose level, treating genital herpes and psoriases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alemdar S, Agaoglu S (2009) Investigations of in-vitro antimicrobial activity of aloe vera juice. J Anim Vet Adv 8(1):99–102
Ang NU, Intaphan P, Saengo E (1996) Development of orange aloe vera jam. Proceeding of the 13th Rajamangala institute of technology annual conference: Food science and home economics Lampang (Thailand), pp 39–45
Anonymous (2006) For Aloe vera as semi finish products like gel, powder and finish products like aloe vera drink or fizzy tablets. Technology transfer and project management network, Ensymm consulting of biotechnology. http://www.ensymm.com/pdf/ensymmProjectstudyAloeVeraproduction.pdf. Accessed on 5 October 2010
Anonymous (2008) Aloe vera: History, science and medicinal uses. http://www.healingaloe.com Accessed 5 October 2010
Antoni FG, Pablo S, Susana S, Carmen R (2003) Effect of heat treatment and dehydration on bioactive polysaccharide acemannan and cell wall polymers from Aloe barbdensis miller. Carbohydr Polym 51:397–405
Atherton P (1997) Aloe vera: myth or medicine. http://www.positivehealth.com Accessed 28 December 2010
Atherton P (1998) First aid plant. Chem Brit 34:33–36
Bozzi A, Perrin C, Austin S, Arce Vera F (2007) Quality and authenticity of commercial aloe vera gel powders. Food Chem 103(1):22–30
Bradley PR (1992) British herbal compendium. British Herbal Medicine Association
Cerqveira L, McKnight LS, Rodriguez S, Turner CE (1999) Bifurcated method to process aloe whole leaf. US Patent 5 925 357
Chan HT, Cavaletto CG (1986) Effects of deareation and storage temperature on quality of aseptically packaged guava puree. J Food Sci 51:165–168
Choi S, Chung MH (2003) A review on the relationship between Aloe vera components and their biological effects. Semin Integr Med 1:53–62
Christaki EV, Florou-Paneri PC (2010) Aloe vera: a plant for many uses. J Food Agric Environ 8(2):245–249
Coats BC (1979) Hypollergenic stabilized aloe vera gel. US Patent number 4 178 172
Coats BC (1994) Methods of processing stabilized aloe vera gel obtained from the whole aloe vera leaf. US Patent 5 356 811
Dagne E, Bisrat D, Viljoen A, Van Wyk BE (2000) Chemistry of aloe species. Curr Org Chem 4:1055–1078
Davis RH (1997) Aloe vera- A scientific approach. Vantage Press Inc, New York, pp 290–306
Do-Sang L, Ryu II, Kap-Sang L, Yang-See S, Seung-Ho C (1999) Optimisation in the preparation of aloe vinegar by Acetobactor sp. and inhibitory effect against lipase activity. Hanguk Nongwhahak Hoechi 42:105–110
Eison-Perchonok MH, Downes TW (1982) Kinetics of ascorbic acid oxidation as a function of dissolved oxygen concentration and temperature. J Food Sci 47:765–773
Eshun K, He Q (2004) Aloe vera: a valuable ingredient for the food, pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries: a review. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 44:91–96
Farnsworth NR, Fong HHS, Mahady GB (1999) Aloe vera gel. In: WHO monographs on selected medicinal plants Vol 1. Malta pp 43–49
Femenia A, Sanchez ES, Simal S, Rosello C (1999) Compositional features of polysaccharides from Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis Miller) plant tissues. Carbohydr Polym 39:109–117
Gautam S, Awasthi P (2007) Nutrient composition and physio-chemical characteristics of Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis) powder. J Food Sci Technol 44(2):224–225
Ghannam N, Kingston M, Al-Meshaal IA, Tariq M, Parman NS, Woodhouse N (1986) The antidiabetic activity of aloe: preliminary clinical and experimental observation. Horm Res 24(4):288–294
Gjestad G (1971) Chemical studies of aloe vera juice. Adv Front Plant Sci 28:110–112
Gowda D, Neelisiddaiah B, Anjaneyalo Y (1980) Structural studies of polysaccharides from Aloe saponaria and Aloe vanbalenni. Carbohydr Res 83:402–405
Grindlay D, Reynolds T (1986) The aloe vera phenomenon: a review of the properties and modern uses of the leaf parenchyma gel. J Ethnopharmacol 16:117–151
Hamman JH (2008) Composition and application of aloe vera leaf gel. Molecules 13:1599–1616
Harding TBC (1979) Aloes of the world: a checklist, index and code. Excelsa 9:57–94
Hastuti S (1999) Fresh beverage from aloe vera. Butetin Ilmiah Instiper (Indonesia) 6:39–45
He Q, Liu C, Zhang T (2002) Study on nonenzymatic browning of aloe products and its inhibition methods. Food Sci (Chenses) 23(10):53–56
Hernadez RJ, Giacin JR (1998) Factors affecting permeation, sorption and migration process in package- products system. In: Food storage stability. CRC Press, Boca Raton, Florida USA, pp 269–329
Hirat T, Suga T (1983) The efficiency of aloe plants, chemical constituents and biological activities. Cosmetics and Toiletries 98:105–108
Homcare Iberica SA (1983) Stabilization of a clear gel from aloe vera leaves. Span ES 502 307. Patent of Introduction
Hu Y, Xu J, Hu Q (2003) Evaluation of antioxidant potential of aloe vera (Aloe barbdensis Miller) extracts. J Agric Food Chem 51(26):7788–7791
Hunter D, Frumkin A (1991) Adverse reaction to Vit E and aloe vera preparations after dermabration and chemical peel. Cutis 47(3):193–195
Hutter J, Salman M (1996) Anti-inflammatory C-glucosyl chromone from Aloe barbadensis. J Nat Prod 59(5):541–543
Kacem B, Mathews RF, Grandall PG, Cornell JA (1987) Non-enzymatic browning in aseptic packaged orange drinks: effects of amino acids, dearation and anaerobic storage. J Food Sci 52:1665–1667
Kemper KJ, Chiou V (1999) Aloe vera. Longwood herbal task and The Center for Holistic Pediatric Education and Research http://www.longwoodherbal.org/aloe/aloe.pdf. Accessed 4 October 2010
Kennedy FC, Rivera ZS, Loyd LL, Warner FP, Jumel K (1992) L-ascorbic acid stability in aseptically processed orange juice in tetra brick cartons and the effect of oxygen. Food Chem 45:327–331
Lachenmeier K, Kuepper U, Musshoff F, MadeaB RH, Lachenmeier DW (2005) Quality control of aloe vera beverages. Electronic J Environ Agric Food Chem 4(4):1033–1042
Lawless J, Allen J (2000) Aloe vera- Natural wonder care. Harper Collins Publishers, Hammersmith, pp 5–12
Lee EH, Choi SD (1994) Studies on the manufacture of aloe yoghurt. J Agric Technol Res Institute Chinju University (Korea Republic) 7:55–59
Lee J, Hand-Yoon YH (1997) Characteristics of aloe vera suspended liquid yoghurt inoculated with Lactobacillus Casei YIT 9018. Korean J Animal Sci 39:93–100
Luta G, McAnalley BH (2005) Aloe vera: chemical composition and methods used to determine its presence in commercial products. GlycoSci Nutr 6(4):1–12
Maret RH (1975) Process for preparing extract of aloe vera. US Patent 3 878 197
Maughan RG (1984) Methods to increase colour fastness of stabilized aloe vera. US Patent 4 465 629
Meadows TP (1980) Aloe as a humectant in new skin preparation. Cosmet Toiletries 95(11):51–56
Moor ED, McAnalley BH (1995) A drink containing mucilaginous polysaccharides and its preparations. US Patent 5 443 830
Morrow DM, Rappaport MJ, Strick RA (1980) Hypersensitivity to aloe. Arch Dermatol 116:106–1065
Newton LE (1979) In defense of the name aloe vera. Cactus Succul J GB 41:29–30
Ni Y, Tizard IR (2004) Analytical methodology: The gel-analysis of aloe pulp and its derivatives. In: Reynolds T (ed) Aloes the genus aloe. CRC, Boca Raton, pp 111–126
Ovadova RG, Lapchich VF, Ovodov YS (1975) Polysaccharides in Aloe arboresens. Khimija Prirodykh Soedinenii 11:3–5
Peng SY, Norman J, Curtin G, Corrier D, Mc Daniel HR, Busbee D (1991) Decreased mortality of Norman murine sarcoma in mice treated with the immunomodulator, Acemannan. Mol Biother 3:79–87
Qian H (2002) Study on the technology of aloe gel freeze dried powder. Food Fermentation Industry 28:49–52
Ramachandra CT, Srinivasa Rao P (2008) Processing of aloe vera leaf gel: a review. Am J Agril Biol Sci 3(2):502–510
Robert HD (1997) Aloe vera: a scientific approach. Vantage Press Inc, New York
Saccu D, Bogoni P, Procida G (2001) Aloe exudate: characterization by reversed phase HPLC and headspace GC–MS. J Agric Food Chem 49(10):4526–4530
Sadler GD, Braddock RJ (1990) Oxygen permealibity of low density polyethylene as a function of lomonene absorption: an approach to modeling flavour (Scalping). J Food Sci 55:587–590
Seoshin Y, Lee KS, Lee JS, Lee CH (1995) Preparation of yoghurt added with Aloe vera and its quality characteristics. J Korean Soc Food Nutr 24:254–260
Shah AH, Qureshi S, Tariq M, Ageel AM (1989) Toxicity studies on six plants used in the traditional Arab system of medicine. Phytother Res 3:25–29
Shelton M (1991) Aloe vera, its chemical and therapeutic properties. Int J Dermatol 30:679–683
Sims P, Ruth M, Zinmerman ER (1971) Effect of aloe vera on Herpes simplex and Herpes virus (strains Zoster). Aloe vera of American Archive 1:239–240
Singh A, Singh AK (2009) Optimization of processing variables for the preparation of herbal bread using Aloe vera gel. J Food Sci Technol 46(4):335–338
Sydiskis RJ, Owen DG, Lohr JL, Rosler KHA, Blomster RN (1991) Inactivation of enveloped viruses by anthraquinones extracted from plants. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 35(12):2463–2466
Tramell DJ, Dalsis DE, Malone CT (1986) Effect of oxygen on taste, ascorbic acid loss and browning for HTST pasteurized, single strength orange juice. J Food Sci 51:1021–1023
Tucker AO, Duke JA, Foster S (1989) Botanical nomenclature of medicinal plants. In: Cracker LE, Simon JE (eds) Herbs, spices, and medicinal plants, vol 4. AR Oryx Press, Phoenix, pp 169–242
Tyler V (1994) Herbs of choice. In: The therapeutic use of phyto medicine. Binghamton Pharmaceutical Products Press, New York, pp 131–135
Vogler BK, Ernst E (1999) Aloe vera: a systematic review of its clinical effectiveness. Br J Gen Pract 49:823–828
Waller GR, Mangiafica S, Ritchey CR (1978) A chemical investigation of Aloe barbedensis Miller. Proc Okla Acad Sci 58:69–76
Wang YT (1993) Bases of aloe certification. Aloe Today 27–29
Wei L, Chuncheng Y, Huafeng Z, Rugang Y (2004) Preparation of aloe-herbs health beverage. Food Sci China 25:207–209
Yagi A, Shibata S, Nishioka I, Iwarde S, Ishida Y (1982) Cardiac stimulant action of constituents of Aloe saponaria. J Pharm Sci 71:739–741
Yaron A, Cohen E, Arad SM (1992) Stabilization of aloe vera gel by interaction with sulfated polysaccharides from micro algae and with xantham gum. J Agric Food Chem 40:1316–1320
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahlawat, K.S., Khatkar, B.S. Processing, food applications and safety of aloe vera products: a review. J Food Sci Technol 48, 525–533 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0229-z
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13197-011-0229-z