Abstract
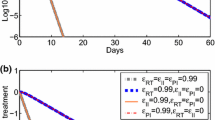
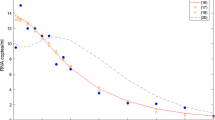
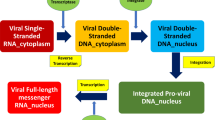
We present an immunological model that considers the dynamics of CD4+ T cells interacting with free virions, reverse transcriptase inhibiting drugs and protease inhibiting drugs. We divide the T cells into multiple classes and use impulsive differential equations to describe the drug activity. As expected, we find that insufficient dosing of either drug corresponds to high viral load and a large population of infectious T cells. The model further predicts that, in the absence of physiological limits on tolerable drug concentrations, sufficiently frequent dosing with the reverse transcriptase inhibitor alone could theoretically maintain the CD4+ T cell count arbitrarily close to the T cell count in the uninfected immune system. However, for frequent dosing of the protease inhibitor alone, the limiting T cell populations may not be enough to maintain the immune system. Furthermore, frequent dosing of both drugs has the same net effect on the T cell population as frequent dosing of the reverse transcriptase inhibitor only. Thus, the two drug classes can have fundamentally different effects on the long-term dynamics and the reverse transcriptase inhibitor, in particular, plays a crucial role in maintaining the immune system. We also provide estimates for the dosing intervals of each drug that could theoretically sustain the T cell population at a desired level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin, D. J., N. J. White and R. M. Anderson (1998). The dynamics of drug action on the within-host population growth of infectious agents: melding pharmacokinetics with pathogen population dynamics. J. Theor. Biol. 194, 313–339.
Bainov, D. D. and P. S. Simeonov (1989). Systems with Impulsive Effect, Chichester: Ellis Horwood Ltd.
Bainov, D. D. and P. S. Simeonov (1993). Impulsive Differential Equations: Periodic Solutions and Applications, Burnt Mill: Longman Scientific and Technical.
Bainov, D. D. and P. S. Simeonov (1995). Impulsive Differential Equations: Asymptotic Properties of the Solutions, Singapore: World Scientific.
Calloway, D. S. and A. S. Perelson (2002). HIV-1 infection and low steady state viral loads. Bull. Math. Biol. 64, 29–64.
Cammack, N., P. Rouse, C. L. Marr, P. J. Reid, R. E. Boehme, J. A. Coates, C. R. Penn and J. M. Cameron (1992). Cellular metabolism of (−) enantiomer 2′-deoxy-3′-thiacytidine. Biochem. Pharmacol. 43, 2059–2064.
Covert, D. J. and D. Kirschner (2000). Revisiting early models of the host-pathogen interactions in HIV infection. Comments Theor. Biol. 5:6, 383–411.
Ghani, A. C., W. E. Henley, C. A. Donnelly, S. Mayer and R. M. Anderson (2001). Comparison of the effectiveness of non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor-containing and protease inhibitor-containing regimens using observational databases. AIDS 15:9, 1133–1142.
Haase, A. T. et al. (1996). Quantitative image analysis of HIV-1 infection in lymphoid tissue. Science 274, 985–989.
Ho, D. D., A. U. Neumann, A. S. Perelson, W. Chen, J. M. Leonard and M. Markowitz (1995). Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature 373:6510, 123–126.
Hoggard, P. G. and D. J. Back (2002). Intracellular pharmacology of nucleoside analogues and protease inhibitors: role of transport molecules. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 15, 3–8.
Janeway, C., P. Travers, M. Walport and M. J. Shlomchik (2001). Immunobiology 5: The Immune System in Health and Disease, New York: Garland Publishing.
Kepler, T. B. and A. S. Perelson (1998). Drug concentration heterogeneity facilitates the evolution of drug resistance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 11514–11519.
Lakshmikantham, V., D. D. Bainov and P. S. Simeonov (1989). Theory of Impulsive Differential Equations, Singapore: World Scientific.
MATLAB. A licensed software program produced by The Math Works, Inc., Natick MA, USA.
Moyle, G. (2003). Finally, the new drug classes arrive. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 16, 1–3.
Nelson, P. W., J. E. Mittler and A. S. Perelson (2001). Effect of drug efficacy and the eclipse phase of the viral life cycle on estimates of HIV viral dynamic parameters. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 26, 405–412.
Nelson, P. W. and A. S. Perelson (2002). Mathematical analysis of delay differential equation models of HIV-1 infection. Math. Biosci. 171:1, 73–94.
Nowak, M. A., S. Bonhoeffer, G. M. Shaw and R. M. May (1997). Anti-viral drug treatment: dynamics of resistance in free virus and infected cell populations. J. Theor. Biol. 184, 203–217.
Nowak, M. A. and R. M. May (2000). Virus Dynamics, Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Perelson, A. S. (2002). Modelling viral and immune system dynamics. Nat. Rev.: Immunol. 2, 28–36.
Perelson, A. S. and P. W. Nelson (1999). Mathematical analysis of HIV-1 dynamics in vivo. SIAM Rev. 41, 3–44.
Rodman, J. R., P. Robbins, P. M. Flynn and A. A. Fridland (1996). A systemic and cellular model for zidovudine plasma concentrations and intracellular phosphorylation in patients. J. Infect. Dis. 174, 490–499.
Schacker, T. W., J. P. Hughes, T. Shea, R. W. Coombs and L. Corey (1998). Biological and virologic characteristics of primary HIV infection. Ann. Intern. Med. 128:8, 613–620.
Wahl, L. M. and M. A. Nowak (2000). Adherence and drug resistance: predictions for therapy outcome. Proc. R. Soc. London, Ser. B 267, 835–843.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smith, R.J., Wahl, L.M. Distinct effects of protease and reverse transcriptase inhibition in an immunological model of HIV-1 infection with impulsive drug effects. Bull. Math. Biol. 66, 1259–1283 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulm.2003.12.004
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bulm.2003.12.004