Abstract
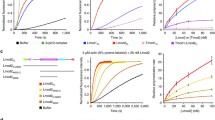
CapZ is a widely distributed and highly conserved, heterodimeric protein, that nucleates actin polymerization and binds to the barbed ends of actin filaments, preventing the addition or loss of actin monomers. CapZ interaction with actin filaments was shown to be of high affinity and decreased in the presence of PIP2. CapZ was located in nascent Z-lines during skeletal muscle myofibrillogenesis before the striated appearance of thin filaments in sarcomers. In this study, the stabilization and the anchorage of thin filaments were explored through identification of CapZ partners in the Z-line. Fish (sea bass) striated white muscle and its related Z-line proteins were selected since they correspond to the simplest Z-line organization. We report here the interaction between purified CapZ and α-actinin, a major component of Z filaments and polar links in Z-discs. Affinity of CapZ for α-actinin, estimated by fluorescence and immunochemical assays, is in the μ m range. This association was found to be independent of actin and shown to be weakened in the presence of phosphoinositides. Binding contacts on the α-actinin molecule lie in the 55 kDa repetitive domain. A model including CapZ/α-actinin/titin/actin interactions is proposed considering Luther's 3D Z-line reconstruction.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Astier C, Lebart MC, Labbe JP, Roustan C and Benyamin Y (1992) Interaction of titin fragments with a-actinin. Mol Biol Cell 3: 362a.
Astier C, Labbe JP, Roustan C and Benyamin Y (1993) Effects of different enzymatic treatments on the release of titin fragments from rabbit skeletal myofibrils-Purification of an 800 kDa titin polypeptide. Biochem J 290: 731-734.
Astier C, Raynaud F, Lebart MC, Roustan C and Benyamin Y (1998) Binding of a titin native fragment to actin is regulated by PIP2. FEBS Lett. 429: 95-98.
Bayer EA and Wilchek M (1990) Protein biotinylation. Methods in Enzymology 184: 138-160.
Benyamin Y, Roustan C and Boyer M (1986) Anti-actin antibodies. Chemical modification allows the selective production of antibodies to the N-terminal region. J Immunol Methods 86: 21-29.
Bullard B, Sainsbury G and Miller N (1990) Digestion of proteins associated with the Z-disc by calpain. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 11: 271-279.
Casella JF, Craig SW, Maack DJ and Brown AE (1987) CapZ(36/32), a barbed end actin-capping protein, is a component of the Z-line of skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol 105: 371-379.
Casella JF and Cooper JA (1991) Purification of CapZ from chick skeletal muscle. Meth in Enzymol 193: 140-154.
Casella JF and Torres MA (1994) Interaction of CapZ with actin: the NH2-terminal domains of the a1-and b-subunits are not required for actin capping, and a1b and a2b heterodimers bind differentially to actin. J Biol Chem 269: 6992-6998.
Engvall E (1980) Enzyme immunoassay ELISA and EMIT. In: Neufeld EF and Ginsberg V (eds) Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 70 (pp. 419-439) Academic Press, New York.
Eilertsen K, Kazmierski ST and Keller TCS (1997) Interaction of a-actinin with a cellular titin. Eur J Cell Biol 74: 361-364.
Franzini-Armstrong C (1973) The structure of a simple Z-line. J Cell Biol 58: 630-642.
Fukami K, Furuhashi K, Inagaki M, Endo T, Hatano S and Takanawa T (1992) Requirement of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate for alpha-actinin function. Nature 359: 150-152.
Fukami K, Sawada N, Endo T and Takenawa T (1996) Identification of a PIP2 binding site in chicken skeletal muscle a-actinin. J Biol Chem 271: 2646-2650.
Fürst D, Nave R, Osborn R and Weber K (1988) The organisation of titin filaments in the half sarcomere revealed by monoclonal antibodies in immunoelectronic microscopy: a map of ten nonrepetitive epitopes starting at the Z-line extends to the M-line. J Cell Biol 160: 1563-1572.
Furuhashi K, Inagaki M, Hatano S, Fukami K and Takenawa T (1992) Inositol phospholipid-induced suppression of F-actin-gelating activity of smooth muscle filamin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 184: 1261-1265.
Gautel M, Leonard K and Labeit S (1993) Phosphorylation of KSP motifs in the C-terminal region of titin in differentiating myoblasts. EMBO J 12: 3827-3834.
Gautel M, Goulding D, Bullard B, Weber K, and Furst DO (1996) The central Z-disc region of titin is assembled from a novel repeat in variable copy numbers. J Cell Sci 109: 2747-2754.
Gonsior SM, Gautel M and Hinssen H (1998) A six-module human nebulin fragment bundles actin filaments and induces actin polymerization. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 19: 225-235.
Harsanyi V and Garamvolgyi N (1969) On the Z substance of striated muscle. Acta Biochem Biophys Acad Sci Hung 4: 259-264.
Heiss SG and Cooper JA (1991) Regulation of CapZ, an actin capping protein of chicken muscle, by anionic phospholipids. Biochemistry 30: 8753-8758.
Ivanenkov V, Dimlich R and Jamieson G (1996) Interaction of S100a(0) protein with the actin capping protein CapZ. Characterization of a S100a(0) putative binding site in CapZ a subunit. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 221: 46-50.
Janmey PA and Matsudaira PT (1988) Functional comparison of villin and gelsolin. Effects of Ca2+, KCl, and polyphosphoinositides. J Biol Chem 263: 16738-16743.
Janmey PA and Stossel TP (1987) Modulation of gelsolin function by PIP2. Nature 325: 362-364.
Janmey PA and Stossel TP (1989) Gelsolin-polyphosphoinositides interaction. Full expression of gelsolin inhibiting function by polyphosphoinositides in vesicular form and inactivation by dilution, aggregation or masking of the inositol. J Biol Chem 264: 4825-4831.
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 224: 680-685.
Lebart MC, Mejean C, Boyer M, Roustan C and Benyamin Y (1990) Localization of a new a-actinin binding site on the COOH-terminal part of the actin sequence. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 173: 120-126.
Lebart MC, Mejean C, Roustan C and Benyamin Y (1993) Further characterization of the a-actinin-actin interface and comparison with filamin binding sites. J Biol Chem 268: 5642-5648.
Lebart MC, Mejean C, Casanova D, Audemard E, Derancourt J, Roustan C and Benyamin Y (1994) Characterization of the actin-binding site on smooth muscle filamin. J Biol Chem 269: 4279-4284.
Linke WA, Ivemeyer M, Labeit S, Hinssen H, Rüegg JC and GautelM (1997) Actin-titin interaction in cardiac myofibrils: probing a physiological role. Biophys J 73: 905-919.
Luther PK (1991) Three-dimensional reconstruction of a simple Z-band in fish muscle. J Cell Biol 113: 1043-1055.
Luther PK (1995) Symmetry of a vertebrate muscle basketweave Z-band. J Struct Biol 115(3): 275-282.
Maruyama K, Sawada H, Kimura S, Ohashi K, Higuchi H and Umazume Y (1984) Connectin filaments in stretched skinned fibers of frog skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol 99: 1391-1397.
McGough A, and Way M (1995) Molecular model of an actin filament capped by a severing protein. J Struct Biol 115: 144-150.
Mejean C, Lebart MC, Boyer M, Roustan C and Benyamin Y (1992) Localization and identification of actin structures involved in the filamin-actin interaction. Eur J Biochem 209: 555-562.
Mejean C, Lebart MC, Roustan C and Benyamin Y (1995) Inhibition of actin-dystrophin interaction by inositide phosphate. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 210: 152-158.
Mimura N, and Asano A (1986) Isolation and characterization of a conserved actin binding domain from rat hepatic actinogelin, rat skeletal muscle, and chicken gizzard a-actinin. J Biol Chem 261: 10680-10687.
Nave R, Furst DO and Weber K (1990) Interaction of alpha-actinin and nebulin in vitro. Support for the existence of a fourth filament system in skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett 269: 163-166.
Nyitrai M, Hild G, Lakos Z and Somogyi B (1998) Effect of Ca2+-Mg2+ exchange on the flexibility and/or conformation of the small domain in monomeric actin. Biophys J 74: 2474-2481.
Ohtsuka H, Yajima H, Maruyama K and Kimura S (1997). The N-terminal Z repeat 5 of connectin/titin binds to the C-terminal region of alpha-actinin. Biochem Biophys Res Com 235: 1-3.
Ohtsuka HO, Yajima H, Maruyama K and Kimura S (1997) Binding of th N-terminal 63 kDa portion of connectin/titin to a-actinin as revealed by the yeast two-hybrid system. FEBS Lett 401: 65-67.
Papa I, Mejean C, Lebart MC, Astier C, Roustan C, Benyamin Y, Alavarez C, Verrez-Bagnis V and Fleurence J (1995) Isolation and properties of white skeletal muscle alpha-actinin from sea-trout (Salmo trutta) and bass (Dicentrarchus labrax). Comp Biochem Physiol 112B: 271-282.
Schafer DA, Waddle JA and Cooper JA (1993) Localization of CapZ during myofibrillogenesis in cultured chicken muscle. Cell Motil Cytoskelet 25: 317-35.
Schafer DA, Hug C and Cooper JA (1995) Inhibition of CapZ during myofibrillogenesis alters assembly of actin filaments. J Cell Biol 128: 61-70.
Schafer D, Jennings P and Cooper J (1996) Dynamics of capping protein and actin assembly in vitro: uncapping barbed ends by phosphoinositides. J Cell Biol 135: 169-179.
Schroeter JP, Bretaudiere JP, Sass R and Goldstein M (1996) Three dimensional structure of the Z-band in a normal mammalian skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol 133: 571-583.
Sorimachi H, Freiburg A, Kolmerer B, Ishiura S, Stier G, Gregorio CC, Labeit D, Linke WA, Suzuki K and Labeit S (1997) Tissue-specific expression and ca-actinin binding properties of the Z-disc titin: implications for the nature of vertebrate Z-discs. J Mol Biol 270: 688-695.
Takahashi K and Hattori A (1989) Alpha-actinin is a component of the Z-filament, a structural backbone of skeletal muscle Z-discs. J Biochem 105: 529-536.
Taylor RG, Papa I, Astier C, Ventre F, Benyamin Y and Ouali A (1997) Muscle cytoskeleton integrity is not dependent on thin filament integrity. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 18: 285-294.
Trinick J (1991) Elastic filaments and giant proteins in muscle. Curr Op Cell Biol 3: 112-119.
Trinick J (1994) Titin and nebulin: protein rulers in muscle? TIBS 19: 405-408.
Trombitas K and Pollack G (1993) Elastic properties of the titin filament in the Z line region of vertebrate striated muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil Res 14: 416-422.
Tskhovrebova LA (1991) Vertebrate muscle Z-line structure: an electron microscopic study of negatively-stained myofibrils. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 12: 425-438.
Usmanova A, Astier C, Lebart MC, Kwiatek O, Papa I, Boyer M, Roustan C and Benyamin Y (1997) Analysis of long range structural effects induced by DNase-I interaction with actin monomeric form or complexed to CapZ. Biochimie 79: 485-492.
Van der Loop F, Van der Ven P, Fürst D, Gautel M, Van Der Eys G and Ramakaers F (1996) Integration of titin into the sarcomers of differentiating human skeletal muscle cells. Eur J Cell Biol 69: 301-307.
Vigoreaux JO (1994) The muscle Z band: lessons in stress management. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 15: 237-255.
Wang K and Wright J (1988) Architecture of the sarcomere matrix of skeletal muscle: immunoelectronic microscopy evidence suggests that a set of parallel inextensible nebulin filaments anchored at the Z-line. J Cell Biol 107: 2199-2212.
Wang SM and Jeng CJ (1992) Interaction between titin and alpha-actinin. Biomedical Res 13: 197-202.
Wang K (1996) Titin/connectin and nebulin: giant protein rulers of muscle structure and function. Adv Biophys 33: 123-134.
Winkler J, Lünsdorf H and Jockusch BM (1997) Flexibility and fine structure of smooth-muscle a-actinin. Eur J Biochem 248: 193-199.
Yamaguchi M, Izumimoto M, Robson RM and Stromer MH (1985) Fine structure of wide and narrow vertebrate muscle Z-lines. A proposed model and computer simulation of Z-line architecture. J Mol Biol 184: 621-643.
Yan Y, Winograd E, Viel A, Cronon T, Harrison SC and Branton D (1993) Cristal structure of the repetitive segments of spectrin. Science 262: 2027-2030.
Young P, Ferguson C, Banuelos S and Gautel M (1998) Molecular structure of the sarcomeric Z-disc: two types of titin interactions lead to an asymmetrical sorting of a-actinin. EMBO J 17: 1614-1624.
Yu FX, Johnston PA, Sudhof TC and Yin HL (1990) gCap39, a calcium ion-and polyphosphoinositide-regulated actin capping protein. Science 250: 1413-1415.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Papa, I., Astier, C., Kwiatek, O. et al. Alpha actinin–CapZ, an anchoring complex for thin filaments in Z-line. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 20, 187–197 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005489319058
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005489319058