Abstract
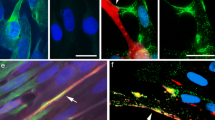
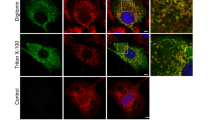
Annexin VII exists in a 47 kDa and a 51 kDa isoform with the 51 kDa protein being the only isoform present in skeletal muscle. Expression of the 51 kDa isoform during myogenesis and localization was studied in cells after conversion into myogenic cells by transduction with MyoD and in mouse and human myogenic cell lines. MyoD expression in NIH3T3 and C3H10T1/2 fibroblasts led to disappearance of the mRNA specific for the 47kDa isoform and appearance of the 51 kDa isoform-specific mRNA. The overall amount of annexin VII protein was reduced in myogenic converted cells. Both in undifferentiated and differentiated cells annexin VII was localized by immunofluorescence microscopy to punctate structures which were distributed all over the cell. A GFP annexin VII fusion protein showed a similar distribution. Cell fractionation studies indicated that annexin VII is equally distributed between cytosol and membrane fractions in undifferentiated cells, while in differentiated cells it is exclusively present in the membrane fraction. By sucrose gradient centrifugation of postnuclear supernatants we identified two distinct annexin VII-containing membrane populations that cofractionated with caveolin 3- and sorcin-containing membranes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali SM, Geisow JM and Burgoyne RD (1989) A role for calpactin in calcium dependent exocytosis in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature 340: 313–315.
Ausubel FM, Brent R, Kingston RE, Moore DD, Seidman JG, Smith JA and Struhl K (1998) Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, Vol 1, John Wiley, New York.
Braun T, Bober E, Buschhausen-Denker G, Kohtz S, Grzeschik K and Arnold HH (1989) Differential expression of myogenic determination genes in muscle cells: possible autoactivaion by the Myf gene products. EMBO J 8: 3617–3625.
Brownawell AM and Creutz CE (1997) Calcium-dependent binding of sorcin to the N-terminal domain of synexin (annexin VII). J Biol Chem 272: 22182–22190.
Burger A, Berendes R, Voges D, Huber R and Demange P (1993) A rapid and efficient purification method for recombinant annexin V for biophysical studies. FEBS Lett 329: 25–28.
Burns AL, Magendzo K, Shirvan A, Srivastava M, Rojas ER, Alijani MR and Pollard HB (1989) Calcium channel activity of purified human synexin and structure of the human synexin gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 3798–3802.
Creutz CE, Pazoles CJ and Pollard HB (1978) Identification and purification of an adrenal medullary protein (synexin) that causes calcium dependent aggregation of isolated chromaffin granules. J Biol Chem 253: 2858–2866.
Diakonova M, Gerke V, Ernst J, Liautard JP, Gusse GVD and Griffiths G (1997) Localization of five annexins in J774 macrophages and on isolated phagosomes. J Cell Sci 110: 1199–1213.
Douglass EC, Valentine M, Etcubanas E, Parham D, Webber BL, Houghton PJ and Green AA (1987) A specific chromosomal abnormality in rhabdomyosarcoma. Cytogenet Cell Genet 45: 148–155.
Drust DS and Creutz CE (1988) Aggregation of chromaffin granules by calpactin at micromolar levels of calcium. Nature 331: 88–91.
Edmondson DG, Cheng T-C, Cserjesi P, Chakraborty T and Olson EN (1992) Analysis of the myogenin promotor reveals an indirect pathway for positive autoregulation mediated by the muscle-specific enhancer MEF-2. Mol Cell Biol 12: 3665–3677.
Eller M, Stedman HH, Sylvester JE, Fertels SH, Rubinstein NA, Kelly AM and Sarkar S (1989) Nucleotide sequence of full length human embryonic myosin heavy chain cDNA. Nucl Acids Res 17: 3591–3592.
Emans N, Gorvel J-P, Walter C, Gerke V, Keller R, Griffiths G and Gruenberg J (1993) Annexin II is a major component of fusogenic endosomal vesicles. J Cell Biol 120: 1357–1369.
Fiedler K, Lafont F, Parton RG and Simons K (1995) Annexin XIIIb: a novel epithelial specific annexin is implicated in vesicular traffic to the apical plasma membrane. J Cell Biol 128: 1043–1053.
Gautel M, Leonard K and Labeit S (1993) Phosphorylation of KSP motifs in the C-terminal region of titin in differentiating myoblasts. EMBO J 12: 3827–3834.
Glenney JR, Tack B and Powell MA (1987) Calpactins: two distinct Ca2+-regulated phospholipid-and actin-binding proteins isolated from lung and placenta. J Cell Biol 104: 503–511.
Harder T, Kellner R, Parton RG and Gruenberg J (1997) Specific release of membrane-bound annexin II and cortical cytoskeletal elements by sequestration of membrane cholesterol. Mol Biol Cell 8: 533–545.
Hazelton BJ, Houghton JA, Parham DM, Douglass EC, Torrance PM, Holt H and Houghton PJ (1987) Characterization of cell lines derived from xenografts of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res 47: 4501–4507.
Huber R, Römisch J and Paques EP (1990) The crystal and molecular structure of human annexin V, an anticoagulant protein that binds to calcium and membranes. EMBO J 9: 3867–3874.
Jost M, Zeuschner D, Seemann J, Weber K and Gerke V (1997) Identification and characterization of a novel type of annexin-membrane interaction: Ca2+ is not required for the association of annexin II with early endosomes. J Cell Sci 110: 221–228.
Kuijpers GA, Lee G and Pollard HB (1992) Immunolocalization of synexin (annexin VII) in adrenal chromaffin granules and chro-maffin cells: evidence for a dynamic role in the secretory process. Cell Tissue Res 269: 323–330.
Lafont F, Lecat S, Verkade P and Simons K (1998) Annexin XIIIb associates with lipid microdomains to function in apical delivery. J Cell Biol 142: 1413–1427.
Langanger G, Demey J and Adam H (1983) 1,4-Diazobizyklo-(2,2,2)-Oktan (DABCO) verzögert das Ausbleichen von Immunfluoreszenzpräparaten. Mikroskopie 40: 237–241.
Lin Z, Lu M-H, Schultheiss T, Choi J, Holtzer S, Dilullo C, Fischmann DA and Holtzer H (1994) Sequential appearance of muscle-specific proteins in myoblasts as a function of time after cell division: evidence for a conserved myoblast differentiation program in skeletal muscle. Cell Motil Cytoskel 29: 1–19.
Loomis WF (1969) Developmental regulation of alkaline phosphatase in Dictyostelium discoideum. J Bact 100: 417–422.
Loomis WF and Kuspa A (1984) Biochemical and genetic analysis of prestalk specific acid phosphatase in Dictyostelium. Dev Biol 102: 498–503.
Ludolph DC and Konieczny SF (1995) Transcription factor families: muscling in on the myogenic program. FASEB J 9: 1595–1604.
Magendzo K, Shirvan A, Cultraro C, Srivastava M, Pollard HB and Burns AL (1991) Alternative splicing of human synexin mRNA in brain, cardiac, and skeletal muscle alters the unique N-terminal domain. J Biol Chem 266: 3228–3232.
Marsh JL, Erfle M and Wykes EJ (1984) The pIC plasmid and phage vectors with versatile cloning sites for recombinant selection by insertional inactivation. Gene 32: 481–485.
Molkentin JD and Olson EN (1996) Defining the regulatory networks for muscle development. Curr Opin Genet Dev 6: 445–453.
Nixon GF, Mignery GA and Somlyo AV (1994) Immunogold localization of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptors and characterization of ultrastructural features of the sarcoplasmic reticulum in phasic and tonic smooth muscle. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 15: 682–700.
Parton RG, Joggerst B and Simons K (1994) Regulated internalization of caveolae. J Cell Biol 127: 1199–1215.
Pear WS, Nolan GP, Scott ML and Baltimore D (1993) Production of high-titer helper-free retroviruses by transient transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 8392–8396.
Pepperkok R, Scheel J, Horstmann H, Hauri HP, Griffiths G and Kreis TE (1993) Beta-COP is essential for biosynthetic membrane transport from the endoplasmatic reticulum to the Golgi complex in vivo. Cell 74: 71–82.
Raynal P and Pollard HB (1994) Annexins: the problem of assessing the biological role for a gene family of multifunctional calcium-and phospholipid-binding proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1197: 63–93.
Riviére I, Brose K and Mulligan RC (1995) Effects of retroviral vector design on expression of human adenosine deaminase in murine bone marrow transplant recipients engrafted with genetically modified cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 6733–6737.
Russo S, Tomatis D, Collo G, Tarone G and Tatò F (1998) Myogenic conversion of NIH3T3 cells by exogenous MyoD family members: dissociation of terminal differentiation from myotube formation. J Cell Sci 111: 691–700.
Russo-Marie F (1992) Annexins, phospholipase A2 and the glucocorticoids. In: Moss SE (ed.) The Annexins (pp. 35–46). Portland Press, London/Chapel Hill.
Schiaffino S, Gorza L, Sartore S, Saggin L and Carli M (1986) Embryonic myosin heavy chain as a differentiation marker of developing human skeletal muscle and rhabdomyosarcoma. A monoclonal antibody study. Exp Cell Res 163: 211–220.
Schleicher M, Gerisch G and Isenberg G (1984) New actin-binding proteins from Dictyostelium discoideum. EMBO J 3: 2095–2100.
Selbert S, Fischer P, Pongratz D, Stewart M and Noegel AA (1995) Expression and localization of annexin VII (synexin) in muscle cells. J Cell Sci 108: 85–95.
Springer MS and Blau HM (1997) High-efficiency retroviral infection of primary myoblasts. Somat Cell Mol Genet 23: 203–209.
Sugawara I, Mizumoto K, Ohkochi E, Hamada H, Tsuruo T and Mori S (1989) Immunocytochemical identification and localization of the Mr 22,000 calcium-binding protein (sorcin) in an adriamycin-resistant myelogenous leukemia cell line. Jpn J Cancer Res 80: 469–474.
Towbin H, Staehelin T and Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76: 4350–4354.
Weber FE, Vaughan KT, Reinach FC and Fischmann DA (1993) Complete sequence of human fast-type and slow-type muscle myosin-binding-protein C (MyBP-C). Differential expression, conserved domain structure and chromosome assignment. Eur J Biochem 216: 661–669.
Weydert A, Daubas P, Lazaridis I, Barton PJR, Garner I, Leader DP, Bonhomme F, Catalan J, Simon D, Guenet J-L, Gros F and Buckingham ME (1985) Genes for skeletal muscle myosin heavy chains are clustered and are not located on the same mouse chromosome as a cardiac myosin heavy chain gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 7183–7187.
Wice BM and Gordon JI (1992) A strategy for isolation of cDNAs encoding proteins affecting human intestinal epithelial cell growth and differentiation: characterization of a novel gut-specific N-myristoylated annexin. J Cell Biol 116: 405–422.
Yoshizaki H, Tanabe S, Arai K, Murakami A, Wada Y, Ohnukuchi M, Hashimoto Y and Maki M (1992) Effects of calphobindin II (annexin VI) on procoagulant and anticoagulant of cultured endothelial cells. Chem Pharm Bull 40: 1860–1863.
Zaks WJ and Creutz CE (1991) Ca2+-dependent annexin self-association on membrane surfaces. Biochemistry 30: 9607–9615.
Zhang-Keck Z-Y, Burns AL and Pollard HB (1993) Mouse synexin (annexin VII) polymorphism and a phylogenetic comparison with other synexins. Biochem J 289: 735–741.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clemen, C.S., Hofmann, A., Zamparelli, C. et al. Expression and localisation of annexin VII (synexin) isoforms in differentiating myoblasts. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 20, 669–679 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005524623337
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1005524623337