Abstract
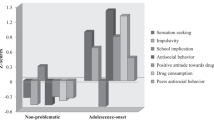
Hypotheses generated by a developmental taxonomy that distinguishes between childhood and adolescent onset conduct disorders were tested. Hypotheses predicted that (1) individual and familial factors would be more strongly related to childhood onset conduct disorder, whereas ethnic minority status and exposure to deviant peers would be more strongly related to adolescent onset conduct disorder and (2) individuals with childhood onset disorder would be more likely to commit violent and victim oriented offenses than individuals with adolescent onset conduct disorder. The first hypothesis was strongly supported and the second hypothesis was partially supported. Implications for early identification of youth at risk for chronic offending are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Manual for the Youth Self Report and 1991 Profile. Burlington: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry.
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
Anderson, K. E., Lytton, H., & Romney, D. M. (1986). Mothers' interactions with normal and conduct-disordered boys: Who affects whom? Developmental Psychology, 22, 604-609.
Blumstein, A., & Cohen, J. (1987). Characterizing criminal careers. Science, 237, 985-991.
Brown, S. A., Gleghorn, A., Schuckit, M. A., Myers, M. G., & Mott, M. A. (1996). Conduct disorder among adolescent alcohol and drug abusers. Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 57, 314-324.
Bry, B. H. (1983). Predicting drug abuse: Review and reformulation. International Journal of the Addictions, 18, 223-233.
Buriel, R., Calzada, S., & Vasquez, R. (1982). The relationship of traditional Mexican American culture to adjustment and delinquency among three generations of Mexican American male adolescents. The Psychiatric Clinics of North America: Cultural Psychiatry, 18, 41-55.
Burnam, M. A., Telles, C., & Karno, M. (1987). Measurement of acculturation in a community population of Mexican Americans. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 9, 105-130.
Caspi, A., Elder, G. H., & Bem, D. J. (1987). Moving against the world: Life-course patterns of explosive children. Developmental Psychology, 23, 308-313.
Chen, A., & True, R. (1994). Experience of violence: Asian Americans. In L. Eron, J. Gentry, & P. Schlegel (Eds.), Reason to hope: A psychosocial perspective on violence and youth (pp. 133-144). Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Conley, D. J. (1994). Adding color to a black and white picture: Using qualitative data to explain racial disproportionality in the juvenile justice system. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 31, 135-148.
Cuellar, I., Harris, L. C., & Jasso, I. (1980). An acculturation scale for Mexican American normal and clinical populations. Hispanic Journal of Behavioral Sciences, 2, 199-217.
Dinges, G. G., Atlis, M. M., & Vincent, G. M. (1997). Cross-cultural perspectives on antisocial behavior. In D. M. Stoff & J. Breiling (Eds.), Handbook of antisocial behavior (pp. 474-495). New York: Wiley.
Farrington, D. P. (1986). Age and crime. In M. Tonry & N. Morris (Eds.), Crime and justice: An annual review of research (Vol. 7., pp. 189-250). Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
Garland, A. F., Hough, R. L., McCabe, K. M., Yeh, M., Wood, P. A., & Aarons, G. A. (2001). Prevalence of psychiatric diagnoses in youth across five sectors of care. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 40, 409-418.
Garmezy, N. (1985). Stress resistant children: The search for protective factors. In J. Stevenson (Ed.), Recent research in developmental psychopathology (pp. 213-233). Oxford, England: Pergamon.
Green, S. M., Loeber, R., & Lahey, B. B. (1991). Stability of mothers' recall of the age of onset of their child's attention and hyperactivity problems. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 30, 135-137.
Henry, G. T. (1990). Practical sampling. Newbury Park: Sage.
Hinshaw, S. P., Lahey, B. B., & Hart, E. L. (1993). Issues of taxonomy and comorbidity in the development of conduct disorder. Developmental Psychopathology, 5, 31-50.
Jensen, P., Rubio-Stipec, M., Canino, G., Bird, H. R., Dulcan, M. K., Schwab-Stone, M. E., & Lahey, B. B. (1999). Parent and child contributions to diagnosis of mental disorder: Are both informants always necessary? Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 38, 1569-1579.
Kazdin, A. E. (1995). Conduct disorder in childhood and adolescence (2nd ed.). Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
Kraemer, H. C., Kazdin, A. E., Offord, D. R., Kessler, R. C., Jensen, P. S., & Kupfer, D. J. (1997). Coming to terms with the terms of risk. Archives of General Psychiatry, 54, 337-343.
Krisberg, B., DeComo, R., & Herrera, N. (1992). National juvenile custody trends 1978–1989 (OJJDP Publication No. NCJ 131649). Washington DC: U.S. Department of Justice.
Lahey, B. B., Flagg, E. W., Bird, H. R., Schwab-Stone, M. E., Canino, G., Dulcan, M. K., Leaf, P. J., Davies, M., Brogan, D., Bourdon, K., Horwitz, S. M., Rubio-Stipec, M., Freeman, D. H., Lichtman, J. H., Shaffer, D., Goodman, S. H., Narrow, W. E., Weissman, M. M., Kandel, D. B., Jensen, P. S., Richters, J. E., & Regier, D. A. (1996). The NIMH Methods for the epidemiology of Child and Adolescent Mental Disorders Study: Background and methodology. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 35, 855-864.
Lahey, B. B., Goodman, S. H., Waldman, I. D., Bird, H., Canino, G., Jensen, P., Regier, D., Leaf, P. J., Gordon, R., & Applegate, B. (1999). Relation of age of onset to the type and severity of child and adolescent conduct problems. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 27, 247-260.
Lahey, B. B., Loeber, R., Quay, H., Applegate, B., Shaffer, D., Waldman, I., Hart, E., McBurnett, K., Frick, P. J., Jensen, P. S., Dulcan, M. K., Canino, G., & Bird, H. R. (1998). Validity of the DSM-IV subtypes of conduct disorder based on age of onset. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 37, 435-442.
Loeber, R. (1982). The stability of antisocial and delinquent child behavior: A review. Child Development, 53, 1431-1446.
Loeber, R. (1988). Natural histories of conduct problems, delinquency, and associated substance abuse: Evidence for developmental progressions. In B. B. Lahey & A. E. Kazdin (Eds.), Advances in clinical child psychology (Vol. 11, pp. 73-124). New York: Plenum.
Loeber, R. (1990). Development and risk factors of juvenile antisocial behavior and delinquency. Clinical Psychology Review, 10, 1-41.
Loeber, R., Farrington, D. P., Stouthamer-Loeber, M., & Van Kammen, W. (1998). Antisocial behavior and mental health problems: Explanatory factors in childhood and early adolescence. Mahwah, NJ: Erlbaum.
Loeber, R., Green, S. M., Keenan, K., & Lahey, B. B. (1995). Which boys fare worse? Early predictors of the onset of conduct disorder in a six-year longitudinal study. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 34, 499-509.
Loeber, R., & Stouthamer-Loeber, M. (1987). Prediction. In H. C. Quay (Ed.), Handbook of juvenile delinquency (pp. 325-382). New York: Wiley.
Loeber, R., Wung, P., Keenan, K., Giroux, B., Stouthamer-Loeber, M., Van Kammen, W. B., & Maughan, B. (1993). Developmental pathways in disruptive child behavior. Development and Psychopathology, 5, 103-133.
McCabe, K., Yeh, M., Hough, R. L., Landsverk, J., Hurlburt, M. S., Culver, S. W., & Reynolds, B. (1999). Racial/ethnic representation across five public sectors of care for youth. Journal of Emotional and Behavioral Disorders, 7, 72-82.
McCord, J. (1979). Some child-rearing antecedents of criminal behavior in adult men. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 9, 1477-1486.
Mendoza, R. H., & Martinez, J. L. (1981). The measurement of acculturation. In A. Baren, Jr. (Ed.), Explorations in chicano psychology (pp. 21-82). New York: Holt.
Moffitt, T. E. (1993). Adolescence-limited and life-course-persistent antisocial behavior: A developmental taxonomy. Psychological Review, 4, 674-701.
Myers, M. G., Brown, S. A., & Mott, M. A. (1995). Preadolescent conduct disorder behaviors predict relapse and progression of addiction for adolescent alcohol and drug users. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 19, 1528-1536.
National Center for Education Statistics. (1995). The pocket condition of education 1995 (NCES 95-817). Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Education.
Patterson, G. R. (1986). Performance models for antisocial boys. American Psychologist, 41, 432-444.
Pope, C. E., & Feyerherm, W. F. (1995). Minorities and the juvenile justice system (OJJDP Publication No. NCJ 145849). Washington, DC: U.S. Department of Justice.
Quinton, D., Rutter, M., & Gulliver, L. (1990). Continuities in psychiatric disorders from childhood to adulthood in the children of psychiatric patients. In L. N. Robins & M. Rutter (Eds.), Straight and devious pathways from childhood to adulthood (pp. 259-278). Cambridge: University Press.
Rutter, M. (1987). Psychosocial resilience and protective mechanisms. American Journal of Orthopsychiatry, 57, 316-331.
SANDAG: San Diego Association of Governments. (1995). Population Estimates by Age, Sex, and Ethnic Group, January 1, 1995.
Schwab-Stone, M., Fallon, T., Briggs, M., & Crowther, B. (1994). Reliability of diagnostic reporting for children aged 6–11 years: A test-retest study of the Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children—Revised. American Journal of Psychiatry, 15, 1048-1054.
Shaffer, D., Fisher, P., Dulcan, M. K., Davies, M., Piacentini, J., Schwab-Stone, M. E., Lahey, B. B., Bourdon, K., Jensen, P. S., Bird, H. R., Canino, G., & Regier, D. A. (1996). The NIMH Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children Version 2.3 (DISC-2.3): Description, acceptability, prevalence rates, and performance in the MECA study. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 35, 865-877.
Shaffer, D., Fisher, P., Lucas, C. P., Dulcan, M. K., & Schwab-Stone, M. E. (2000). NIMH Diagnostic Interview Schedule for Children Version IV (NIMH DISC-IV): Description, differences from previous versions, and reliability of some common diagnoses. Journal of the American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 39, 28-38.
Soriano, F. I., & Hough, R. L. (2000). New developments in acculturation measurement: An introduction to the Pan-Acculturation Scale. Unpublished manuscript, Child and Adolescent Services Research Center, Children's Hospital, San Diego, CA.
Stewart, D. G., Brown, S. A., & Myers, M. G. (1997). Antisocial behavior and psychoactive substance involvement among Hispanic and Non-Hispanic Caucasian adolescents in substance abuse treatment. Journal of Child and Adolescent Substance Abuse, 6, 1-22.
Straus, M. A., Hamby, S. L., Finkelhor, D., Moore, D. W., & Runyan, D. (1998). Identification of child maltreatment with the Parent-Child Conflict Tactics Scales: Development and psychometric data for a national sample of American parents. Child Abuse and Neglect, 22, 249-270.
Sue, S. (1998). In search of cultural competence in psychotherapy and counseling. American Psychologist, 53, 440-448.
Tolan, P. H. (1987). Implications of age of onset for delinquency risk. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 15, 47-65.
Wordes, M., Bynum, T. S., & Corley, C. J. (1994). Locking up youth: The impact of race on detention decisions. Journal of Research in Crime and Delinquency, 31, 149-165.
Yung, B. R., & Hammond, W. R. (1997). Antisocial behavior in minority groups: Epidemiological and cultural perspectives. In D. M. Stoff & J. Breiling (Eds.), Handbook of antisocial behavior (pp. 474-495). New York: Wiley.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCabe, K.M., Hough, R., Wood, P.A. et al. Childhood and Adolescent Onset Conduct Disorder: A Test of the Developmental Taxonomy. J Abnorm Child Psychol 29, 305–316 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010357812278
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1010357812278