Abstract
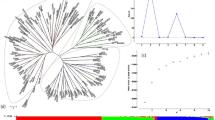
Twenty-eight mapped barley SSRs were used to examine changes in the level and pattern of variability in northern European spring barley over time. Comparing the most recently introduced cultivars with a group of 19 landraces and key progenitors termed `foundation genotypes' we observed a reduction in the spectrum of alleles at 28 loci over time, and highlighted chromosomal regions with limited SSR allelic variation. The 19 `foundation genotypes' contained 72% of the alleles present in all the cultivars sampled. The smallest number of genotypes required to encompass all of the alleles detected in this study was 44, several of which were recently introduced cultivars. The level of diversity within modern cultivars was lower (0.484) than in the `foundation genotypes' (0.597), although the values varied with the SSR locus. A total of 74 rare alleles (frequency <0.05) were detected in the cultivar sample, representing 34% of the total. Measures of genetic distance using SSRs, kinship coefficients and botanical descriptors were compared. Although the correlations between SSRs and kinship and SSRs and botanical descriptors were statistically significant (r=0.26, p<0.001 and r=0.09, p<0.001, respectively), SSR analysis provided greater resolution and allowed better discrimination between genotypes. Discussion of the results focuses on how this information can provide new opportunities in barley breeding.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allard R.W. 1996. Genetic basis of the evolution of adaptedness in plants. Euphytica 92: 1–11.
Autrique E., Nachit M.M., Monneveux P., Tanksley S.D. and Sorrells M.E. 1986. Genetic diversity in durum-wheat based on RFLPs, morphophysiological traits, and coefficient of parentage. Crop Sci. 36: 735–742.
Baum B.B. 1986. Classification of cultivated barley (Hordeum vulgare). 1. Historical aspects, and phenetic character analysis of some characters by information theory and by spatial autocorrelation. Can. J. Bot. 64: 2769–2773.
Becker J. and Heun M. 1995. Barley microsatellites: allelic variation and mapping. Plant Mol. Biol. 27: 835–845.
Borovkora I.G., Jin Y., Staffeman B.J., Kilian A., Blake T.K. and Kleinhofs A. 1997. Identification and mapping of a leaf rust resistance gene in barley line Q21861. Genome 40: 236–241.
Cao D. and Oard J.H. 1977. Pedigree and RAPD-based DNA analysis of commercial US rice cultivars. Crop Sci. 37: 1630–1635.
Davila J.A., de la Hoz M.P.S., Loarce Y. and Ferrer E. 1998. The use of random amplified microsatellite polymorphic DNA and coefficients of parentage to determine genetic relationships in barley. Genome 41: 477–486.
Ellis R.P., McNicol J.W., Baird E., Booth A., Lawrence P., Thomas B. and Powell W. 1997. The use of AFLPs to examine genetic relatedness in barley. Mol. Breed. 3: 359–369.
Fischbeck G. 1992. Barley cultivar development in Europe: success in the past and possible changes in the future. In: Munck L. (ed.), Barley Genetics VI (II). Munksgaard, Copenhagen, pp. 885–901.
Goldstein D.B., Ruiz-Linares A., Cavalli-Sforza L.L. and Feldman M.W. 1995. Genetic absolute dating based on microsatellites and the origin of modern humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 6723–6727.
Graner A., Jahoor A., Schondelmaier J., Siedler H., Pillen K., Fischbeck G. and Wenzel G. 1991. Construction of an RFLP map of barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 83: 250–256.
Graner A., Bauer E., Kellerman A., Kirchner S., Muraya J.K., Jahoor A. and Wenzel G. 1994a. Progress of RFLP map construction in winter barley. Barley Genet. Newsl. 23: 53–59.
Graner A., Ludwig W.F. and Melchinger A.E. 1994b. Relationships among European barley germplasm. 2. Comparison of RFLP and pedigree data. Crop Sci. 34: 1199–1205.
Jarman R.J., Pickett A.A. and Eade A. 1993-1995. Botanical descriptions of cereal varieties. National Institute of Agricultural Botany, Cambridge, UK.
Lee M. 1995. DNA markers and plant breeding programmes. Adv. Agron. 55: 265–344.
Melchinger A.E., Graner A., Singh M. and Messmer M.M. 1994. Relationships among European barley germplasm. 1. Genetic diversity among winter and spring cultivars revealed by RFLPs. Crop Sci. 34: 1191–1199.
MAFF (Ministry of Agriculture, Fisheries and Food). 1974. Plant varieties and seeds gazette number 119, December 1974, p17. MAFF/Plant Variety Rights Office, Cambridge, UK.
Nei M. 1987. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics. Columbia University Press, New York.
Powell W., Machray G. and Provan J. 1996b. Polymorphism revealed by simple sequence repeats Trends Plant Sci. 1: 215–222.
Powell W., Morgante M., Doyle J.J., McNicol J.W., Tingey S.V. and Rafalski J.A. 1996b. Genepool variation in genus Glycine subgenus soja revealed by polymorphic nuclear and chloroplast SSRs. Genetics 144: 793–803.
Rafalski A., Vogel M.J., Morgante M., Andre C. and Tingey S.V. 1996. Generating and using DNA markers in plants. In: Birren B. and Lai E. (eds.), Non-Mammalian Genome Analysis: A Practical Guide. Academic Press, London, pp. 75–134.
Ribaut J.M. and Hoisington D. 1998. Marker-assisted selection: new tools and strategies. Trends Plant Sci. 3: 236–239.
Russell J.R., Fuller J.D., Macaulay M., Hatz B.G., Jahoor A., Powell W. and Waugh R. 1997a. Direct comparison of levels of genetic variation among barley accessions detected by RFLPs, AFLPs, SSRs and RAPDs. Theor. Appl. Genet. 95: 714–722.
Russell J., Fuller J., Young G., Thomas B., Taramino G., Macaulay M., Waugh R. and Powell W. 1997b. Discriminating between barley genotypes using microsatellite markers. Genome 40: 442–450.
Saghai-Maroof M.A., Biyashev R.M., Yang G.P., Zhang Q. and Allard R.W. 1994. Extraordinarily polymorphic microsatellite DNA in barley: species diversity, chromosomal locations and population dynamics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 5466–5470.
Schut J.W., Qi X. and Stam P. 1997. Association between relationship measures based on AFLP markers, pedigree data and morphological traits in barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 95: 1161–1168.
Struss D. and Plieske J. 1998. The use of microsatellite markers for detection of genetic diversity in barley populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 97: 308–315.
Swanston J.S., Thomas W.T.B., Powell W., Young G.R., Lawrence P.E., Ramsay L. and Waugh R. 1999. Using molecular markers to determine barleys most suitable for malt whisky distilling. Mol. Breed. 5: 103–109.
Tanksley S.D. and McCouch S.R. 1997. Seed banks and molecular maps: unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 277: 1063–1066.
Tinker N.A. and Mather D.E. 1993. KIN: software for computing kinship coefficients. J. Hered. 84: 238.
Tinker N.A., Fortin M.E. and Mather D.E. 1993. Random amplified polymorphic DNA and pedigree relationships in spring barley. Theor. Appl. Genet. 85: 976–984.
Waugh R., Macaulay M., McLean K., Fuller J., Bonar N., Ramsay L. and Powell W. 1997. Development of a simple sequence repeat-based linkage map of barley. In: Annual Report of the Scottish Crop Research Institute for 1996/97. Scottish Crop Research Institute, Dundee, UK, pp. 82–84.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russell, J.R., Ellis, R.P., Thomas, W.T. et al. A retrospective analysis of spring barley germplasm development from `foundation genotypes' to currently successful cultivars. Molecular Breeding 6, 553–568 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011372312962
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1011372312962