Abstract
Purpose. Previous studies have established that chitosan hydrochloride and glutamate are potent absorption enhancers for large hydrophilic compounds across mucosal surfaces. However, these compounds lack solubility at neutral pH values. A partially quaternized and well-soluble derivative of chitosan, N-trimethyl chitosan chloride, was synthesized and the effects of this polymer on the transepithelial electrical resistance and permeability of intestinal epithelial cells were investigated in vitro.
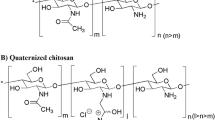
Methods. N-trimethyl chitosan chloride was synthesized by reductive methylation and characterized with NMR. The effect of this polymer (1.0−2.5% w/v) on the transepithelial electrical resistance of intestinal epithelial cells, using Caco-2 cell monolayers, was investigated. Permeation of the hydrophilic model compounds [l4C]-mannitol (MW 182.2), FITC-Dextran (MW 4400) and the peptide drug buserelin (MW 1299.5), in the presence of N-trimethyl chitosan chloride (1.5−2.5% w/v), was followed for 3 hours. The transport process of the fluorescent marker, FITC-Dextran 4400, across the cell monolayers was visualised with confocal laser scanning microscopy. Viability of the cells was checked with the trypan blue exclusion technique.
Results. N-trimethyl chitosan chloride was found to be a perfectly water-soluble, partially quaternized (about 12%) derivative of chitosan. This polymer (1.5−2.5% w/v) caused a pronounced and immediate reduction (25−85%) in the transepithelial electrical resistance of Caco-2 cells. Large increases in the transport rate of [!4C]-mannitol (32−60 fold), FITC-Dextran 4400 (167−373 fold) and buserelin (28−73 fold) were demonstrated. Confocal laser scanning microscopy confirmed that N-trimethyl chitosan chloride opens the tight junctions of intestinal epithelial cells to allow increased transport of hydrophilic compounds through the paracellular transport pathway. No deleterious effects to the cells could be demonstrated with trypan blue.
Conclusions. The potential use of N-trimethyl chitosan chloride as an absorption enhancer across mucosal surfaces could be an important contribution towards the development of effective delivery systems for hydrophilic drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Q. Li, E. T. Dunn, E. W. Grandmaison, and M. F. A. Goosen. J. Boiact. Compat. Polym. 7:370–397 (1992).
O. Skaugrud. Manuf. Chem. 60:31–35 (1989).
S. Hirano, H. Seino, Y. Akiyama, and I. Nonaka. Polym. Eng. Sci. 59:897–901 (1988).
K. Arai, T. Kinumaki, and T. Fujita. Bull. Tokai Reg. Fish Lab. 43:89–94 (1968).
S. M. Upadrashta, P. R. Katikaneni, and N. O. Nuessle. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 18:1701–1708 (1992).
G. C. Ritthidej, P. Chomto, S. Pummamgura, and P. Menasveta. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 20:2109–2134 (1994).
J. Knapczyk. Int. J. Pharm. 93:233–237 (1993).
J. Kristl, J. Smid-Korbar, E. Struc, M. Schara, and H. Rupprecht. Int. J. Pharm. 99:13–19 (1993).
A. Polk, B. Amsden, K. de Yao, T. Peng, and M. F. Goosen. J. Pharm. Sci. 83:178–185 (1994).
A. Berthold, K. Cremer, and J. Kreuter. J. Control. Rel. 39:17–25 (1996).
A. G. Nigalaye, P. Adusumilli, and S. Bolton. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 16:449–467 (1990).
B. Chithambara Thanoo, M. C. Sunny, and A. Jayahrishnan. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 44:283–286 (1992).
C.-M. Lehr, J. A. Bouwstra, E. H. Schacht, and H. E. Junginger. Int. J. Pharm. 78:43–48 (1992).
H. Takeuchi, H. Yamamoto, T. Niwa, T. Hino, and Y. Kawashima. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 42:1954–1956 (1994).
R. S. Geary and H. W. Schlameus. J. Control. Rel. 23:65–74 (1993).
T. J. Aspden, L. Illum, and O. Skaugrud. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. (in press).
J. Knapczyk. Int. J. Pharm. 88:9–14 (1992).
H. L. Lueßen, C.-O. Rental. A. F. Kotzé. C.-M. Lehr, A. G. de Boer, J. C. Verhoef, and H. E. Junginger. J. Control. Rel. 45:15–23.
H. L. Lueßen. B. J. de Leeuw, M. W. E. Langemeÿer, A. G. de Boer, J. C. Verhoef, and H. E. Junginger. Pharm. Res. 13:1668–1672 (1996).
L. Illum, N. F. Farraj, and S. S. Davis. Pharm. Res. 11:1186–1189 (1994).
P. Artursson, T. Lindmark, S. S. Davis, and L. Illum. Pharm. Res. 11:1358–1361 (1994).
A. Domard, M. Rinaudo, and C. Terrassin. Int. J. Macromol. 8:105–107 (1986).
G. Borchard, H. L. Lueßen, A. G. de Boer, J. C. Verhoef, C.-M. Lehr, and H. E. Junginger. J. Control. Rel. 39:131–138 (1996).
A. B. J. Noach, Y. Kurosaki, M. C. M. Blom-Roosemalen, A. G. de Boer, and D. D. Breimer. Int. J. Pharm. 90:229–237 (1993).
M. A. Hurni, A. B. J. Noach, M. C. M. Blom-Roosemalen, A. G. de Boer, J. F. Nagelkerke, and D. D. Breimer. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 267:942–950 (1993).
A. J. Hoogstraate, C. Cullander, F. Nagelkerke, S. Senel, J. Verhoef, H. E. Junginger, and H. E. Boddé. Pharm. Res. 11:83–93 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kotzé, A.R., Lueβen, H.L., de Leeuw, B.J. et al. N-Trimethyl Chitosan Chloride as a Potential Absorption Enhancer Across Mucosal Surfaces: In Vitro Evaluation in Intestinal Epithelial Cells (Caco-2). Pharm Res 14, 1197–1202 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012106907708
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012106907708