Abstract
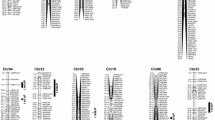
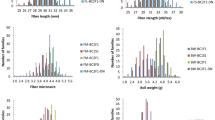
Cotton (Gossypium spp) is the world's leading natural fiber crop. Genetic manipulation continues to play a key role in the improvement of fiber quality properties. By use of DNA-based molecular markers and a polymorphic mapping population derived from an inter specific cross between TM-1 (G. hirsutum) and 3-79 (G. barbadense), thirteen quantitative trait loci (QTLs) controlling fiber quality properties were identified in 3-79, an extra long staple (ELS) cotton. Four QTLs influenced bundle fiber strength, three influenced fiber length, and six influenced fiber fineness. These QTLs were located on different chromosomes or linkage groups and collectively explained 30% to 60%of the total phenotypic variance for each fiber quality property in the F2 population. The effects and modes of action for the individual QTLs were characterized with 3-79 alleles in TM-1 genetic background. The results indicated more recessive than dominant, with much less additive effect in the gene mode. Transgressive segregation was observed for fiber fineness that could be beneficial to improvement of this trait. Molecular markers linked to fiber quality QTLs would be most effective in marker-assisted selection (MAS) of these recessive alleles in cotton breeding programs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agricultural Statistics Board 1999 ‘Annual Crop Summary.’ NASS, USDA Benedict, C.R., R.J. Kohel & H.L. Lewis, 1999. Cotton fiber quality, In: C.W. Smith & J.T. Cothren (Eds.), Cotton, pp. 269–288. John Wiley & Sons, NY.
Burr, B., S.V. Evola, F.A. Burr & J.S. Beckmann, 1983. The application of restrictionfragment length polymorphism to plant breeding. In: J.K. Setlow & A. Hollaender (Eds.), Genetic Engineering, vol. 5, Plenum Press, NY.
Deussen, H., 1992. Improved cotton fiber properties: The textile industry's key to success inglobal competition. Symposium: Cotton Fiber Cellulose: Structure, Function, and utilization, pp. 43–63. National Cotton Council America, Memphis, TN.
deVicente, M.C. & S.D. Tanksley, 1993. QTL analysis of transgressivesegregation in an interspecific tomato cross. Genetics 134: 585–596.
Edwards, M.D., C.W. Stuber & J.F. Wendel, 1987. Molecularmarker-facilitated investigations of quantitative trait loci in maize. I. Numbers, genomic distribution, and types of gene action. Genetics 116: 113–125.
Feinberg, A. & B. Vogelstein, 1984.Anal Biochem 137: 266–267.
Kohel, R.J., 1973. Genetic nomenclature in cotton. J Hered 64:291–195.
Kohel, R.J., 1999a. Cotton Improvement: A Perspective. Cotton World 1: (in press).
Kohel, R.J.,1999b. Cotton germplasm resources and the potential for improved fiber production and quality, In: A.S. Basra (Ed.), Cotton Fibers, pp. 167–182. The Haworth Press, Inc, NY.
Kohel, R.J., T.R. Richmond & C.F. Lewis,1970. Texas Marker-1. Description of a genetic standard for Gossypium hirsutum L. Crop Sci 10: 670–671.
Lander, E.S. & D. Botstein, 1989. Mapping Mendelian factors underlying quantitative traits using RFLP linkagemaps. Genetics 121: 185–199.
Lander, E.S., P. Green, J. Abrahamson, A. Barlow, M.J. Daly, S.E. Lincoln & L. Newburg, 1987. MAPMAKER: An interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1: 174–181.
Lazo, G.R., Y.H. Park & R.J. Kohel, 1994,Identification of RAPD markers linked to fiber strength in Gossypium hirsutum and G. barbadense interspecific crosses. Proc Biochemistry of Cotton. September 28–30, 1994. Galveston, Texas.
Park, Y.H. & R.J. Kohel, 1994. Effect ofconcentration of MgCl2 on random amplified DNA of cotton. BioTechniques 16: 652–656.
Paterson, A.H.,E.S. Lander, J.D. Hewitt, S. Peterson, S.E. Lincoln & S.D. Tanksley, 1988. Resolution of quantitative traits into Mendelian factors, using a complete linkage map of restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Nature (London) 335: 721–726.
Reinisch, A.J., J. Dong, C.L. Brubaker, D.M. Stelly, J.F. Wendel & A.H. Paterson, 1994. Adetailed RFLP map of cotton. Gossypium hirsutum x G. barbadense: Chromosome organization and evolution in a disomic polyploid genome. Genetics 138: 129–147.
Rick, C.M. & P.G. Smith, 1953. Novel variation in tomato specieshybrids. Am Nat 88: 359–373.
Shappley, Z.W., J.N. Jenkins, C.E. Watson Jr, A.L. Kahler & W.R. Meredith Jr, 1996. Establishment of molecular markers and linkage groups in two F2 populations of upland cotton. Theor Appl Genet 92: 915–919.
Stelly, S.M., 1993. Interfacing cytogenetics with the cotton genomemapping effort. Proc Beltwide Cotton Improv Conf, pp. 1545–1550.
Tanksley, S.D., J.C. Miller, A.H. Paterson & R. Bernatzky, 1988. Molecular mapping of plant chromosomes, In: J. Gustafson & R. Appels (Eds.), Chromosome Structure and Function, pp. 157–172. Plenum Press, NY.
Tanksley, S.D., N.D. Young, A.H. Paterson & M.W. Bonierbale, 1989. RFLP mapping in plant breeding: new tool for an old science. Biotechnology 7: 257–264.
Tanksley, S.D. & S.R. McCouch, 1997. Seed banks and molecular maps:unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 277: 1063–1066.
Yu, Z.H., J.F. Wang, R.E. Stall & C.E. Vallejos, 1995. Genomic localization of tomato genes that control a hypersensitive reaction to Xanthomonas campestris pv. vesicatoria (Doidge) Dye. Genetics 141: 675–682.
Yu, Z.H., Y.-H. Park, G.R. Lazo & R.J. Kohel, 1997. Molecular mapping of the cotton genome. Proc of 5th International Congress of Plant Molecular Biology. September 21–27, 1997. Singapore.
Yu, Z.H., Y.H. Park, G.R. Lazo & R.J. Kohel, 1998. Molecularmapping of the cotton genome: QTL analysis of fiber quality characteristics. Proc of Plant Animal Genome VI, Jan 18–22, 1998. San Diego California.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kohel, R.J., Yu, J., Park, YH. et al. Molecular mapping and characterization of traits controlling fiber quality in cotton. Euphytica 121, 163–172 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012263413418
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1012263413418