Abstract
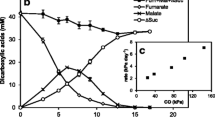
In vitro assays demonstrated that toluene-grown cells of Geobacter metallireducens catalyzed the addition of toluene to fumarate to form benzylsuccinate under anaerobic conditions. The specific in vitro rate of benzylsuccinate formationwas ca. 45% of the specific in vivo rate of toluene consumption. In addition, bssA and bssB, which code for the α and β subunits of benzylsuccinate synthase (BSS), respectively, were found to have sequences in G. etallireducens similar to the only sequences heretofore available (for three denitrifying strains). This is the first report of the presence of BSS in a ferriciron-reducing bacterium; BSS activity has previously been reported in denitrifying, sulfate-reducing, and anoxygenic phototrophic toluene degraders, as well as in a highly enriched methanogenic, toluene-degrading culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achong GR, Rodriguez AM& Spormann AM (2001) Benzylsuccinate synthase of Azoarcus sp. strain T: cloning, sequencing, transcriptional organization, and its role in anaerobic toluene and m-xylene mineralization. J. Bacteriol. 183: 6763-6770
Annweiler E, Materna A, Safinowski M, Kappler A, Richnow HH, Michaelis W& Meckenstock RU (2000) Anaerobic degradation of 2-methylnaphthalene by a sulfate-reducing enrichment culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66: 5329-5333
Beller HR& Edwards EA (2000) Anaerobic toluene activation by benzylsuccinate synthase in a highly enriched methanogenic culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66: 5503-5505
Beller HR& Spormann AM(1997a) Anaerobic activation of toluene and o-xylene by addition to fumarate in denitrifying strain T. J. Bacteriol. 179: 670-676
Beller HR& Spormann AM(1997b) Benzylsuccinate formation as a means of anaerobic toluene activation by sulfate-reducing strain PRTOL1. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63: 3729-3731
Beller HR& Spormann AM(1998) Analysis of the novel benzylsuccinate synthase reaction for anaerobic toluene activation based on structural studies of the product. J. Bacteriol. 180: 5454-5457
Beller HR& Spormann AM (1999) Substrate range of benzylsuccinate synthase from Azoarcus sp. strain T. FEMS Microbiol. Letters 178: 147-153
Biegert T, Fuchs G& Heider J (1996) Evidence that anaerobic oxidation of toluene in the denitrifying bacterium Thauera aromatica is initiated by formation of benzylsuccinate from toluene and fumarate. Eur. J. Biochem. 238: 661-668
Church GM& Gilbert W (1984) Genomic sequencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 81: 1991-1995
Coates JD, Bhupathiraju VK, Achenbach LA, McInerney MJ& Lovley DR (2001) Geobacter hydrogenophilus, Geobacter chapellei and Geobacter grbiciae, three new, strictly anaerobic, dissimilatory Fe(III)-reducers. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Micr. 51: 581-588
Coschigano PW, Wehrman TS& Young LY (1998) Identification and analysis of genes involved in anaerobic toluene metabolism by strain T1: putative role of a glycine free radical. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64: 1650-1656
Heider J, Spormann AM, Beller HR& Widdel F (1998) Anaerobic bacterial metabolism of hydrocarbons. FEMS Microbiol. Reviews 22: 459-473
Krieger CJ, Beller HR, Reinhard M& Spormann AM (1999) Initial reactions in anaerobic oxidation of m-xylene by the denitrifying bacterium Azoarcus sp. strain T. J. Bacteriol. 181: 6403-6410
Krieger CJ, Roseboom W, Albracht SPJ& Spormann AM (2001) A stable organic free radical in anaerobic benzylsuccinate synthase of Azoarcus sp. strain T. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 12924-12927
Kropp KG, Davidova IA& Suflita JM (2000) Anaerobic oxidation of n-dodecane by an addition reaction in a sulfate-reducing bacterial enrichment culture. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66: 5393-5398
Leuthner B, Leutwein C, Schulz H, Hörth P, Haehnel W, Schiltz E, Schägger H& Heider J (1998) Biochemical and genetic characterization of benzylsuccinate synthase from Thauera aromatica: a new glycyl radical enzyme catalysing the first step in anaerobic toluene metabolism. Mol. Microbiol. 28: 615-628
Lovley DR, Giovannoni SJ, White DC, Champine JE, Phillips EJP, Gorby YA& Goodwin S (1993) Geobacter metallireducens gen. nov. sp. nov., a microorganism capable of coupling the complete oxidation of organic compounds to the reduction of iron and other metals. Arch. Microbiol. 159: 336-344
Lovley DR, Greening RC& Ferry JG (1984) Rapidly growing rumen methanogenic organism that synthesizes coenzyme M and has a high affinity for formate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 48: 81-87
Lovley DR& Phillips EJP (1986) Organic matter mineralization with reduction of ferric iron in anaerobic sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 51: 683-689
Lovley DR& Phillips EJP (1988) Novel mode of microbial energy metabolism: organic carbon oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron or manganese. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 54: 1472-1480
Müller JA, Galushko AS, Kappler A& Schink B (1999) Anaerobic degradation of m-cresol by Desulfobacterium cetonicum is initiated by formation of 3-hydroxybenzylsuccinate. Arch. Microbiol. 172: 287-294
Müller JA, Galushko AS, Kappler A& Schink B (2001) Initiation of anaerobic degradation of p-cresol by formation of 4-hydroxybenzylsuccinate in Desulfobacterium cetonicum. J. Bacteriol. 183: 752-757
Rabus R& Heider J (1998) Initial reactions of anaerobic metabolism of alkylbenzenes in denitrifying and sulfate-reducing bacteria. Arch. Microbiol. 170: 377-384
Rabus R, Wilkes H, Behrends A, Armstroff A, Fischer T, Pierik AJ& Widdel F (2001) Anaerobic initial reaction of n-alkanes in a denitrifying bacterium: evidence for (1-methylpentyl)succinate as initial product and for involvement of an organic radical in n-hexane metabolism. J. Bacteriol. 183: 1707-1715
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke, NM, Olson BJ& Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 150: 76-85 (Erratum, 163: 279, 1987)
Zengler K, Heider J, Rossello-Mora R& Widdell F (1999) Phototrophic utilization of toluene under anoxic conditions by a new strain of Blastochloris sulfoviridis. Arch. Microbiol. 172: 204-212
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kane, S.R., Beller, H.R., Legler, T.C. et al. Biochemical and genetic evidence of benzylsuccinate synthase intoluene-degrading, ferric iron-reducing Geobacter metallireducens . Biodegradation 13, 149–154 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020454831407
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020454831407