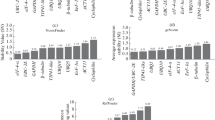
Abstract
Reverse transcription followed by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT Q-PCR) is useful for the systematic measurement of plant physiological changes in gene expression. The validity of using 18S rRNA and three housekeeping genes, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, actin, and tubulin, was tested as a reference of RT Q-PCR. Under various growth stages of etiolated seedlings, different cultivars, and various times after UV-irradiation treatment, expression level of 18S rRNA correlated with total RNA suggesting the uniformity of RT Q-PCR efficiencies among samples. Relative expressions of housekeeping genes varied among samples and independently of experimental conditions, up to two-fold, signifying generally constant fraction of mRNA in total RNA. Results indicate 18S rRNA was the most reliable reference gene for RT Q-PCR of total RNA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhatia P, Taylor WR, Greenberg AH, Wright JA (1994) Comparison of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and 28Sribosomal RNA gene expression as RNA loading controls for Northern blot analysis of cell lines of varying malignant potential. Anal. Biochem. 216: 223–226.
Chomczynski P, Sacchi N (1987) Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal. Biochem. 162: 156–159.
Koga-Ban Y, Niki T, Nagamura Y, Sasaki T, Minobe Y (1995) cDNA sequences of three kinds of b-tubulins from rice. DNA Res. 2: 21–26.
Koller A, Washburn MP, Lange BM, Andon NL, Deciu C, Haynes PA, Hays L, Schieltz D, Ulaszek R, Wei J, Wolters D, Yates III JR (2002) Proteomic survey of metabolic pathways in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99: 11969–11974.
McElroy D, Rothenberg M, Wu R (1990) Structural characterization of a rice actin gene. Plant Mol. Biol. 14: 163–171.
Rasmussen R, Morrison T, Herrmann M, Wittwer C (1998) Quantitative PCR by continuous fluorescence monitoring of a double strand DNA specific binding dye. Biochemica 2: 8–11.
Schmittgen TD, Zakrajsek BA (2000) Effect of experimental treatment on housekeeping gene expression: validation by real-time, quantitative RT-PCR. J. Biochem. Biophys. Meth. 46: 69–81.
Schmittgen TD, Zakrajsek BA, Mills AG, Gorn V, Singer MJ, Reed MW (2000) Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction to study mRNA decay: comparison of endpoint and real-time methods. Anal. Biochem. 285: 194–204.
Solanas M, Moral R, Escrich E (2001) Unsuitability of using ribosomal RNA as loading control for Nortnern blot analyses related to the imbalance between messenger and ribosomal RNA content in rat mammary tumors. Anal. Biochem. 288: 99–102.
Takaiwa F, Oono K, Sugiura M (1984) The complete nucleotide sequence of a rice 17S rRNA gene. Nucl. Acids Res. 12: 5441–5448.
Teare JM, Islam R, Flanagan R, Gallagher S, Davies MG, Grabau C (1997) Measurement of nucleic acid concentrations using the DyNA Quant and the GeneQuant. BioTechniques 22: 1170–1174.
Vandesompele J, de Paepe A, Speleman F (2002a) Elimination of primer-dimer artifacts and genomic coamplification using a two-step SYBR Green I real-time RT-PCR. Anal. Biochem. 303: 95–98.
Vandesompele J, de Preter K, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, de Paepe A, Speleman F (2002b) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol. 3: 1–11.
Zhong H, Simons JW (1999) Direct comparison of GAPDH, bactin, cyclophilin, and 28S rRNA as internal standards for quantifying RNA levels under hypoxia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 259: 523–526.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, BR., Nam, HY., Kim, SU. et al. Normalization of reverse transcription quantitative-PCR with housekeeping genes in rice. Biotechnology Letters 25, 1869–1872 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026298032009
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026298032009