Abstract
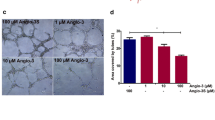
Integrins expressed on endothelial cells modulate cell migration and survival during angiogenesis. Integrins expressed on carcinoma cells potentiate metastasis by facilitating invasion and movement across blood vessels. We describe the activities of two synthetic low-molecular-weight peptidomimetics of the ligand amino acid sequence arg-gly-asp (RGD) in integrin-based functional assays in vitro. We also evaluate efficacy and potential mechanisms of action in models of both spontaneous and experimental metastasis. Broad-spectrum potency against the family of alpha v subunit-containing integrins was observed, with significantly less potency against α5β1 and αIIbβ3. Both endothelial and tumor cell migration mediated by αvβ3 was inhibited, whereas proliferation of endothelial cells but not tumor cells was diminished. Continuous infusion of compound by minipumps or oral administration twice daily significantly reduced metastatic tumor burden in the lungs of mice despite no reduction in growth of 435/HAL primary tumors, and only a slight reduction in tumor cells detected in circulating blood. Delaying treatment in this model until after extensive dissemination of tumor cells to the lungs had occurred, and after primary tumor resection, still produced significant efficacy. Conversely, administration of the agent for only the first 18 h after tumor-cell inoculation into the tail vein also resulted in decreased metastases observed after several weeks. These data suggest these compounds or their relatives have potential to interfere with both early and late steps of metastasis involving tumor and endothelial cell functions. Furthermore, the metastatic process can be effectively inhibited independently of primary tumor growth using integrin antagonists.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McLeod HL, McKay JA, Collie-Duguid ES, Cassidy J. Therapeutic opportunities from tumour biology in metastatic colon cancer. Eur J Cancer 2000; 36 (13 Spec No): 1706–12.
Heimann R, Hellman S. Clinical progression of breast cancer malignant behavior: what to expect and when to expect it. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18 (3): 591–9.
Lerner SP, Seale-Hawkins C, Carlton CE, Jr, Scardino PT. The risk of dying of prostate cancer in patients with clinically localized disease. J Urol 1991; 146 (4): 1040–5.
Naumov GN, MacDonald IC, Chambers AF, Groom AC. Solitary cancer cells as a possible source of tumour dormancy? Semin Cancer Biol 2001;11 (4): 271–6.
Brooks PC, Clark RA, Cheresh DA. Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science 1994; 264 (5158): 569–71.
Westlin WF. Integrins as targets of angiogenesis inhibition. Cancer J 2001; 7 (Suppl 3): S139–43.
Felding-Habermann B, O'Toole TE, Smith JW et al. Integrin activation controls metastasis in human breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98 (4): 1853–8.
Friedlander M, Brooks PC, Shaffer RW et al.. Definition of two angiogenic pathways by distinct alpha v integrins. Science 1995; 270 (5241): 1500–2.
Kim S, Bell K, Mousa SA, Varner JA. Regulation of angiogenesis in vivo by ligation of integrin alpha5beta1 with the central cell-binding domain of fibronectin. Am J pathol 2000; 156 (4): 1345–62.
Brooks PC, Stromblad S, Klemke R et al. Antiintegrin alpha v beta 3 blocks human breast cancer growth and angiogenesis in human skin. J Clin Invest 1995; 96 (4): 1815–22.
Munger JS, Huang X, Kawakatsu H et al. The integrin alpha v beta 6 binds and activates latent TGF beta 1: A mechanism for regulating pulmonary inflammation and fibrosis. Cell 1999; 96 (3): 319–28.
Pasche B. Role of transforming growth factor beta in cancer. J Cell Physiol 2001; 186 (2):153–68.
Mu D, Cambier S, Fjellbirkeland L et al. The integrin alpha(v)beta8 mediates epithelial homeostasis through MT1-MMP-dependent activation of TGF-beta1. J Cell Biol 2002; 157 (3): 493–507.
Trikha M, Raso E, Cai Y et al. Role of alphaII(b)beta3 integrin in prostate cancer metastasis. Prostate 1998; 35 (3): 185–92.
Mousa SA. Anti-integrin as novel drug-discovery targets: potential therapeutic and diagnostic implications. Curr Opin Chem Biol 2002; 6 (4): 534–41.
Carron CP, Meyer DM, Pegg JA et al. A peptidomimetic antagonist of the integrin alpha(v)beta3 inhibits Leydig cell tumor growth and the development of hypercalcemia of malignancy. Cancer Res 1998; 58 (9): 1930–5.
Reinmuth N, Liu W, Ahmad SA et al. Alphavbeta3 integrin antagonist S247 decreases colon cancer metastasis and angiogenesis and improves survival in mice. Cancer Res 2003; 63 (9): 2079–87.
Schmidt CM, Settle SL, Keene JL et al. Characterization of spontaneous metastasis in an aggressive breast carcinoma model using flow cytometry. Clin Exp Metast 1999; 17(6): 537–44.
Humphries MJ, Yamada KM, Olden K. Investigation of the biological effects of anti-cell adhesive synthetic peptides that inhibit experimental metastasis of B16-F10 murine melanoma cells. J Clin Invest 1988; 81 (3): 782–90.
Morris VL, Schmidt EE, Koop S, MacDonald IC, Grattan M, Khokha R, et al. Effects of the disintegrin eristostatin on individual steps of hematogenous metastasis. Exp Cell Res 1995; 219 (2): 571–8.
Mitjans F, Sander D, Adan J et al. An anti-alpha v-integrin antibody that blocks integrin function inhibits the development of a human melanoma in nude mice. J Cell Sci 1995; 108 (Pt 8): 2825–38.
Engleman VW, Nickols GA, Ross FP et al. A peptidomimetic antagonist of the alpha(v)beta3 integrin inhibits bone resorption in vitro and prevents osteoporosis in vivo. J Clin Invest 1997; 99 (9): 2284–92.
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Meth Meth 2001; 25 (4): 402–8.
Price JE, Polyzos A, Zhang RD, Daniels LM. Tumorigenicity and metastasis of human breast carcinoma cell lines in nude mice. Cancer Res 1990; 50 (3): 717–21.
Frisch SM, Vuori K, Ruoslahti E, Chan-Hui PY. Control of adhesion-dependent cell survival by focal adhesion kinase. J Cell Biol 1996; 134 (3): 793–9.
Condeelis JS, Wyckoff J, Segall JE. Imaging of cancer invasion and metastasis using green fluorescent protein. Eur J Cancer 2000; 36 (13 Spec No): 1671–80.
Wong NC, Mueller BM, Barbas CF, Ruminski P, Quaranta V, Lin EC, et al. Alphav integrins mediate adhesion and migration of breast carcinoma cell lines. Clin Exp Metast 1998; 16 (1): 50–61.
Liapis H, Flath A, Kitazawa S. Integrin alpha V beta 3 expression by bone-residing breast cancer metastases. Diagn Mol Pathol 1996; 5 (2): 127–35.
Pilch J, Habermann R, Felding-Habermann B. Unique ability of integrin alpha(v)beta 3 to support tumor cell arrest under dynamic flow conditions. J Biol Chem 2002; 277 (24): 21930–8.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shannon, K.E., Keene, J.L., Settle, S.L. et al. Anti-metastatic properties of RGD-peptidomimetic agents S137 and S247. Clin Exp Metastasis 21, 129–138 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CLIN.0000024764.93092.5f
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:CLIN.0000024764.93092.5f