Abstract
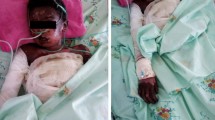
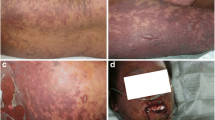
Toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) is an infrequent disease but with a high mortality rate. It is a mucocutaneous reaction resulting from hypersensitivity to a variety of agents including most anticonvulsants. Many patients with primary or metastatic intracranial tumours receive anticonvulsants for seizure prophylaxis despite their efficacy not having been clearly demonstrated. Moreover, several cases have been reported in the literature in which serious adverse drug reactions such as TEN and Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS) have occurred following anticonvulsants exposure. In some of these cases the effect of radiation therapy and the tapering of steroid dose on the pathogenesis of these reactions have been highlighted. We report, here, a case of TEN that appeared in a patient receiving phenytoin, and shortly after the end of cranial and thoracic irradiation therapy for brain metastases of non-small cell lung cancer. Clinical considerations about diagnosis of SJS and TEN are presented. The use of prophylactic anticonvulsants is also discussed as well as a review of the literature.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lyell A: Toxic epidermal necrolysis: an eruption resembling scalding of the skin. Br J Dermatol 68: 355-361, 1956
Revuz J, Penso D, Roujeau JC, Guillaume JC, Payne CR, Wechsler J, Touraine R: Toxic epidermal necrolysis: clinical findings and prognosis factors in 87 patients. Arch Dermatol 123: 1160-1165, 1987
Egan CA, Grant WJ, Morris SE, Saffle JR, Zone JJ: Plasmapheresis as an adjunct treatment in toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Am Acad Dermatol 40: 458-461, 1999
Renfro L, Grant-Kels JM, Daman LA: Drug-induced toxic epidermal necrolysis treated with cyclosporin. Int J Dermatol 28(7): 441-444, 1989
Heng MC, Allen SG: Efficacy of cyclophosphamide in toxic epidermal necrolysis. Clinical and pathophysiologic aspects. J Am Acad Dermatol 25: 778-786, 1991
Roujeau JC, Kelly JP, Naldi L, Rzany B, Stern RS, Anderson T, Auquier A, Bastuji-Garin S, Correia O, Locati F, Mockenhaupt M, Paoletti C, Shapiro S, F.R.C.P. (E), Shear N, Schöp E, Kaufman DW: Medication use and the risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis. N Engl J Med 333: 1600-1607, 1995
Schlienger RG, Shear NH: Antiepileptic drug hypersensitivity syndrome. Epilepsia 39(Suppl 7): S3-S7, 1998
Tennis P, Stern RS: Risk of serious cutaneous disorders after initiation of use of phenytoin, carbamazepine, or sodium valproate: a record linkage study. Neurology 49: 542-546, 1997
Stern RS, Chan HL: Usefulness of case report literature in determining drugs responsible for toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Am Acad Dermatol 21: 317-322, 1989
Bastuji-Garin S, Rzany B, Stern RS, Shear NH, Naldi L, Roujeau J-C: Clinical classification of cases of toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and erythema multiforme. Arch Dermatol 129: 92-96, 1993
Rzany B, Correia O, Kelly JP, Naldi L, Auquier A, Stern R: Risk of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis during first weeks of antiepileptic therapy: a case-control study. Study Group of the International Case-Control study on Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions. Lancet 353: 2190-2194, 1999
Mattson RH, Cramer JA, Collins JF: Department of Veterans Affairs Epilepsy Cooperative Study No. 264 Group. A comparison of valproate with carbamazepine for the treatment of complex partial seizures and secondarily generalised tonic-clonic seizures in adults. N Engl J Med 327: 765-771, 1992
Guberman AH, Besag FM, Brodie MJ, Dooley JM, Duchowny MS, Pellock JM, Richens A, Stern RS, Trevathan E: Lamotrigine-associated rash: risk/benefit considerations in adults and children. Epilepsia 40: 985-991, 1999
Yalcin B, Karaduman A: Stevens-Johnson syndrome associated with concomitant use of lamotrigine and valproic acid. J Am Acad Dermatol 43(5 Pt 2): 898-899, 2000
Duncan KO, Tigelaar RE, Bolognia JL: Stevens-Johnson syndrome limited to multiple sites of radiation therapy in a patient receiving phenobarbital. J Am Acad Dermatol 40: 493-496, 1999
Borg M, Probert J, Zwi L: Is phenytoin contraindicated in patients receiving cranial irradiation? Australas Radiol 39: 42-46, 1995
Cockey G, Amann S, Reents S, Lynch J: Stevens-Johnson syndrome resulting from whole-brain radiation and phenytoin. Am J Clin Oncol 19(1): 32-34, 1996
Delattre J, Safai B, Posner J: Erythema multiforme and Stevens-Johnson syndrome in patients receiving cranial irradiation and phenytoin. Neurology 38: 194-198, 1988
Hong-Xuan K, Delattre J, Poisson M: Stevens-Johnson syndrome in a patient receiving cranial irradiation and carbamazepine. Neurology 40: 1144-1145, 1990
Janinis J, Panagos G, Panousaki A, Skarlos D, Athamasiou E, Karpasitis N, Pirounaki M: Stevens-Johnson syndrome and epidermal necrolysis after administration of sodium phenytoin and cranial irradiation. Eur J Cancer 29A(3): 478-479, 1993
Maiche A, Teerenhovi L: Stevens-Johnson syndrome in patients receiving radiation therapy. Lancet 2(8445): 45, 1985
Rowe JE, Pina J, Sau P, Samlaska C, James W: Toxic epidermal necrolysis associated with diphenylhydantoin and cranial irradiation. Int J Dermatol 30: 747-749, 1991
Romero Maldonado N, Sendra Tello J, Raboso Garcia-Baquero E, Harto Castano A: Anticonvulsant hypersensitivity syndrome with fatal outcome. Eur J Dermatol 12: 503-505, 2002
Khafaga YM, Jamshed A, Allam AA, Mourad WA, Ezzat A, Al Eisa A, Gray AJ, Schultz H: Stevens-Johnson syndrome in patients on phenytoin and cranial radiotherapy. Acta Oncol 38: 111-116, 1999
Micali G, Linthicum K, Han N, West DP: Increased risk of erythema multiforme major with combination anticonvulsant and radiation therapies. Pharmacotherapy 19: 223-227, 1999
Errani A, Reggiani M, Schianchi S, Staffa M: Toxic epidermal necrolysis induced by barbiturates and radiotherapy. Br J Dermatol 131: 586-587, 1994
Mamon HJ, Wen PY, Burns AC, Loeffler JS: Allergic skin reactions to anticonvulsant medications in patients receiving cranial irradiation therapy. Epilepsia 40: 341-344, 1999
Trent JT, Bowes LE, Romanilli P, Kerdel FA: Toxic epidermal necrolysis of the scalp following anticonvulsants use and cranial irradiation. J Cutan Med Surg 5: 475-478, 2001
Eralp Y, Aydiner A, Tas F, Saip P, Topuz E: Stevens-Johnson syndrome in a patient receiving anticonvulsant therapy during cranial irradiation. Am J Clin Oncol 24: 347-350, 2001
Wen PY, Marks PW: Medical management of patients with brain tumors. Curr Opin Oncol 14: 299-307, 2002
Cohen N, Strauss G, Lew R, Silver D, Recht L: Should prophylactic anti-convulsants be administered to patients with newly-diagnosed cerebral metastasis? A retrospective analysis. J Clin Oncol 6: 1621-1624, 1988
Byrne TN, Cascino TC, Posner JB: Brain metastases from melanoma. J Neurooncol 1: 313-317, 1983
Glantz MJ, Cole BF, Friedberg MH, Lathi E, Choy H, Furie K, Akerley W, Wahlberg L, Lekos A, Louis S: A randomized, blinded, placebo-controlled trial of divalproex sodium prophylaxis in adults with newly diagnosed brain tumors. Neurology 46(4): 985-991, 1996
North JB, Penhall RK, Hanieh A, Frewin DB, Taylor WB: Phenytoin and postoperative epilepsy. A double-blind study. J Neurosurg 58: 672-677, 1983
Forsyth PA, Weaver S, Fulton D, Brasher PM, Sutherland G, Stewart D, Hagen NA, Barnes P, Cairncross JG, DeAngelis LM: Prophylactic anticonvulsants in patients with brain tumour. Can J Neurol Sci 30: 106-112, 2003
De Santis A, Villani R, Sinisi M, Stocchetti N, Perucca E: Add-on phenytoin fails to prevent early seizures after surgery for supratentorial brain tumors: a randomized controlled study. Epilepsia 43: 175-182, 2002
Foy PM, Chadwick DW, Rajgopalan N, Johnson AL, Shaw MD: Do prophylactic anticonvulsant drugs alter the pattern of seizures after craniotomy? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiat. 55: 753-757, 1992
Franceschetti S, Binelli S, Casazza M, Lodrini S, Panzica F, Pluchino F, Solero CL, Avanzini G: Influence of surgery and antiepileptic drugs on seizures symptomatic of cerebral tumours. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 103: 47-51, 1990
Glantz MJ, Cole BF, Forsyth PA, Recht LD, Wen PY, Chamberlain MC, Grossman SA, Cairncross JG: Practice parameter: anticonvulsant prophylaxis in patients with newly diagnosed brain tumors. Report of the quality standards subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology 54: 1886-1893, 2000
Kuijlen JM, Teernstra OP, Kessels AG, Herpers MJ, Beuls EA: Effectiveness of antiepileptic prophylaxis used with supratentorial craniotomies: a meta-analysis. Seizure 5: 291-298, 1996
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aguiar, D., Pazo, R., Durán, I. et al. Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis in Patients Receiving Anticonvulsants and Cranial Irradiation: A Risk to Consider. J Neurooncol 66, 345–350 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEON.0000014538.31561.bc
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/B:NEON.0000014538.31561.bc