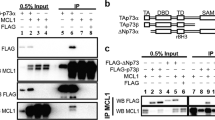
Abstract
The protein p73 is a structural and functional homologue of the p53 tumour-suppressor protein but, unlike p53, it is not induced in response to DNA damage1,2. The tyrosine kinase c-Abl is activated by certain DNA-damaging agents3 and contributes tothe induction of programmed cell death (apoptosis) by p53-dependent and p53-independent mechanisms4. Here we show that c-Abl binds to p73 in cells, interacting through its SH3 domain with the carboxy-terminal homo-oligomerization domain of p73. c-Abl phosphorylates p73 on a tyrosine residue at position 99 both in vitro and in cells that have been exposed to ionizing radiation. Our results show that c-Abl stimulates p73-mediated transactivation and apoptosis. This regulation of p73 by c-Abl in response to DNA damage is also demonstrated by a failure of ionizing-radiation-induced apoptosis after disruption of the c-Abl–p73 interaction. These findings show that p73 is regulated by a c-Abl-dependent mechanism and that p73 participates in the apoptotic response to DNA damage.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaghad, M. et al. Monoallelically expressed gene related to p53 at 1p36, a region frequently deleted in neuroblastoma and other human cancers. Cell 90, 809–819 (1997).
Jost, C. A., Marin, M. C. & Kaelin, W. G. J p73 is a human p53-related protein that can induce apoptosis. Nature 389, 191–193 (1997).
Kharbanda, S. et al. Activation of the c-Abl tyrosine kinase in the stress response to DNA-damaging agents. Nature 376, 785–788 (1995).
Yuan, Z.-M. et al. Regulation of DNA-damage-induced apoptosis by the c-Abl tyrosine kinase. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 94, 1437–1440 (1997).
Kharbanda, S. et al. c-Abl activation regulates induction of the SEK1/stress activated protein kinase pathway in the cellular response to 1-β-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 30278–30281 (1995).
Kharbanda, S. et al. Functional interaction of DNA-PK and c-Abl in response to DNA damage. Nature 386, 732–735 (1997).
Shafman, T. et al. Interaction between ATM protein and c-Abl in response to DNA damage. Nature 387, 520–523 (1997).
Baskaran, R. et al. Ataxia telangiectasia mutant protein activates c-Abl tyrosine kinase in response to ionizing radiation. Nature 387, 516–519 (1997).
Sawyers, C. L., McLaughlin, J., Goga, A., Havilik, M. & Witte, O. The nuclear tyrosine kinase c-Abl negatively regulates cell growth. Cell 77, 121–131 (1994).
Marin, M. C. et al. Viral oncoproteins discriminate between p53 and the p53 homolog p73. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 6316–6324 (1998).
Yuan, Z. M. et al. Role for the c-Abl tyrosine kinase in the growth arrest response to DNA damage. Nature 382, 272–274 (1996).
Tybulewicz, V. L. J., Crawford, C. E., Jackson, P. K., Bronson, R. T. & Mulligan, R. C. Neonatal lethality and lymphopenia in mice with a homozygous disruption of the c-abl proto-oncogene. Cell 65, 1153–1163 (1991).
Diller, L. et al. p53 functions as a cell cycle control protein in osteosarcomas. Mol. Cell. Biol. 10, 5772–5781 (1990).
Barak, Y., Gottlieb, E., Juven-Gershon, T. & Oren, M. Regulation of mdm2 expression by p53: alternative promoters produce transcripts with nonidentical translation potential. Genes Dev. 8, 1739–1749 (1994).
Zhu, J., Jiang, J., Zhou, W. & Chen, X. The potential tumor suppressor p73 differentially regulates cellular p53 target genes. Cancer Res. 58, 5061–5065 (1998).
Clarke, A. R. et al. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature 362, 849–852 (1993).
Lowe, S. W., Schmitt, E. M., Smith, S. W., Osborne, B. A. & Jacks, T. p53 is required for radiation-induced apotosis in mouse thymocytes. Nature 362, 847–849 (1993).
Lowe, S. W., Ruley, H. E., Jacks, T. & Housman, D. E. p53-dependent apoptosis modulates the cytotoxicity of anticancer agents. Cell 74, 957–967 (1993).
Kastan, M. B., Onyekwere, O., Sidransky, D., Vogelstein, B. & Craig, R. W. Participation of p53 protein in the cellular response to DNA damage. Cancer Res. 51, 6304–6311 (1991).
Luo, C. M. et al. High frequency and error-prone DNA recombination in ataxia telangiectasia cell lines. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 4497–4503 (1996).
Ren, R., Ye, Z.-S. & Baltimore, D. Abl protein-tyrosine kinase selects the Crk adapter as a substrate using SH3-binding sites. Genes Dev. 8, 783–795 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yuan, ZM., Shioya, H., Ishiko, T. et al. p73 is regulated by tyrosine kinase c-Abl in the apoptotic response to DNA damage. Nature 399, 814–817 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/21704
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/21704
This article is cited by
-
ABL1 kinase as a tumor suppressor in AML1-ETO and NUP98-PMX1 leukemias
Blood Cancer Journal (2023)
-
Enhanced pro-apoptosis gene signature following the activation of TAp63α in oocytes upon γ irradiation
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Anti-apoptotic HAX-1 suppresses cell apoptosis by promoting c-Abl kinase-involved ROS clearance
Cell Death & Disease (2022)
-
Hippo/YAP signaling pathway protects against neomycin-induced hair cell damage in the mouse cochlea
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)
-
The p53 family member p73 in the regulation of cell stress response
Biology Direct (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.