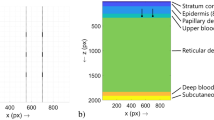
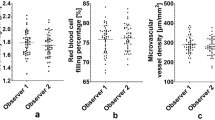
Abstract
THE microcirculation plays a central role in the regulation of the metabolic, haemodynamic and thermal state of the individual. Its physiological state varies over both long and short time periods and reflects the state of health of the individual; in particular it is the ultimatearbiter of the adequacy of tissue perfusion in the presence of vascular disease or injury. For these reasons it is of interest to both the physiologist and the clinician to be able to monitor the state of flow and distribution of flow in the compartments of the microvasculature rapidly, conveniently and with minimal interference with the many local and central reflex controls. At present such measurements depend on direct observation, plethysmography thermal or radioisotope techniques1, which are slow or cumbersome or grossly disturb the normal state of the subject. We report here the first stages in development of a noninvasive method for acquiring such information which has a rapid response and the potential ability to distinguish flow in the different microvascular compartments by the differences in flow velocities.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dahn, I., and Lasser, N. A., Scand. J. clin. Lab. Invest., 19 (Suppl. 99), 1–248 (1967).
Cummins, H. Z., Kable, N., and Yeh, Y., Phys. Rev. Lett., 12, 150 (1964).
Dubin, S. B., Lunacek, J. H., and Benedek, G. B., Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 57, 1164–1171 (1967).
Nossal, R., and Chen, S. H., Nature new Biol., 244, 253–254 (1973).
Schaefer, B. W., Banks, G., and Albert, S. S., Nature, 248, 162–164 (1974).
Tanaka, T., Riva, C., Ben-Sira, I., and Benedek, G. B., Assoc. Res. Vis. Opth. Abstr. April 24, 8 (1974).
Berge, P., Volachine, B., Billard, R., and Hamelin, A., C. r. hebd. Séanc. Acad. Sci., Paris, 265, 889–892 (1967).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
STERN, M. In vivo evaluation of microcirculation by coherent light scattering. Nature 254, 56–58 (1975). https://doi.org/10.1038/254056a0
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/254056a0
This article is cited by
-
The effect of subperichondrial dissection on nasal vascularity in septorhinoplasty operations
European Archives of Oto-Rhino-Laryngology (2024)
-
Development of modified laser Doppler flowmetry device for real-time monitoring of esophageal mucosal blood flow: a preclinical assessment with an animal model
Journal of Artificial Organs (2023)
-
Clinical outcome of the patients with femoropopliteal artery disease after endovascular therapy: focused on drug-coated-balloon-related distal embolism detected by laser doppler flowmetry
Cardiovascular Intervention and Therapeutics (2022)
-
Transmissive-detected laser speckle contrast imaging for blood flow monitoring in thick tissue: from Monte Carlo simulation to experimental demonstration
Light: Science & Applications (2021)
-
Laser speckle contrast imaging of forehead cutaneous blood flow during carotid endarterectomy as a potential non-invasive method for surrogate monitoring of cerebral perfusion
Journal of Clinical Monitoring and Computing (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.