Abstract
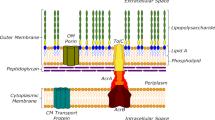
Increased expression of P-glycoprotein, a plasma membrane glycoprotein of relative molecular mass (Mr) 170,000 (170K), occurs in a wide variety of cell lines that exhibit pleiotropic resistance to unrelated drugs1–4. The presence of P-glycoprotein in human cancers refractory to chemotherapy suggests that tumour cells with multidrug resistance can arise during malignant progression5. We have discovered striking homology between P-glycoprotein and the HlyB protein, a 66K Eschericia coli membrane protein required for the export of haemolysin (protein of Mr 107K). P-glycoprotein can be viewed as a tandem duplication of the HlyB protein. The hydropathy profiles of the two proteins are similar and reveal an extensive transmembrane region resembling those found in pore-forming plasma membrane proteins. The C-terminal region of P-glycoprotein and the HlyB protein contain sequences homologous to the nucleotide-binding domains of a group of closely related bacterial ATP-binding proteins. We propose a model for multidrug resistance in which P-glycoprotein functions as an energy-dependent export pump to reduce intracellular levels of anticancer drugs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Juliano, R. L. & Ling, V. Biochim. biophys. Acta 455, 152–162 (1976).
Kartner, N., Riordan, J. R. & Ling, V. Science 221, 1285–1288 (1983).
Kartner, N., Evernden-Porelle, D., Bradley, G. & Ling, V. Nature 316, 820–823 (1985).
Gerlach, J. H., Kartner, N., Bell, D. R. & Ling, V. Cancer Surveys 5, 25–46 (1986).
Bell, D. R., Gerlach, J. H., Kartner, N., Buick, R. N. & Ling, V. J. clin. Oncol. 3, 311–315 (1985).
Felmlee, T., Pellet, S. & Welch, R. A. J. Bact. 163, 94–105 (1985)
Cavalieri, S. J., Bohach, G. A. & Snyder, I. S. Microbiol. Rev. 48, 326–343 (1984).
Hacker, J. & Hughes, C. Curr. Topics Microbiol. Immun. 118, 139–162 (1985).
Hartlein, M. et al. J. cell. Biochem. 22, 87–97 (1983).
Mackman, N., Nicaud, J. M., Gray, L. & Holland, I. B. Current Topics in Microbiol. Immun. 125, 159–181 (1986).
Eisenberg, D., Schwarz, E., Komaromy, M. & Wall, R. J. molec. Biol. 179, 125–142 (1984).
Eisenberg, D. A. Rev. Biochem. 53, 595–623 (1984).
Van der Bliek, A. M., Van der Velde-Koerts, T., Ling, V. & Borst, P. Molec. cell. Biol. 6, 1671–1678 (1986).
Higgins, C. F. et al. Nature 298, 723–727 (1982).
Gilson, E., Nikaido, H. & Hofnung, M. Nucleic Acids Res. 10, 7449–7458 (1982).
Gilson, E., Higgins, C. F., Hofnung, M. & Ames, G. F.-L. J. biol. Chem. 257, 9915–9918 (1982).
Surin, B. P., Rosenberg, H. & Cox, G. B. J. Bact. 161, 189–198 (1985).
Higgins, C. F., Hiles, I. D., Whalley, K. & Jamieson, D. J. EMBO J. 4, 1033–1040 (1985).
Ames, G. F.-L. A. Rev. Biochem. 55, 397–425 (1986).
Safa, A. R., Glover, C. J., Meyers, M. B., Biedler, J. L. & Felsted, R. L. J. biol. Chem. 261, 6137–6140 (1986).
Cornwell, M. M., Safa, A. R., Felsted, R. L., Gottesman, M. M. & Pastan, I. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 3847–3850 (1986).
Dano, K. Biochim. biophys. Acta 323, 466–483 (1973).
See, Y. P., Carlsen, S. A., Till, J. E. & Ling, V. Biochim. biophys. Acta 373, 242–252 (1974).
Skovsgaard, T. Cancer Res. 40, 1077–1083 (1980).
Inaba, M., Kobayashi, H., Sakurai, Y. & Johnson, R. K. Cancer Res. 39, 2200–2203 (1979).
Inaba, M., Fujikura, R. & Sakurai, Y. Biochem. Pharmacol. 30, 1863–1865 (1981).
Lalande, M. E., Ling, V. & Miller, R. G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 363–367 (1981).
Springer, W. & Goebel, W. J. Bact. 144, 53–59 (1980).
Carlsen, S. A., Till, J. E. & Ling, V. Biochim. biophys. Acta 455, 900–912 (1976).
Chlebowski, R. T., Block, J. B., Cundiff, D. & Dietrich, M. F. Cancer Treat. Rep. 66, 121–125 (1982).
Riordan, J. R. et al. Nature 316, 817–819 (1985).
Walton, J. R. & Smith, D. H. J. Bact. 98, 304–305 (1969).
Young, J. D.-E., Peterson, C. G. B., Venge, P. & Cohn, Z. A. Nature 321, 613–616 (1986).
Young, J. D.-E., Cohn, Z. A. & Podack, E. R. Science 233, 184–190 (1986).
Dayhofi, M. O. Atlas of Protein Sequence and Structure Vol. 5, Suppl. 3 (National Biomedical Research Foundation, Washington, 1978).
Elliott, E. M., Okayama, H., Sarangi, F. & Henderson, G. Molec. Cell Biol. 5, 236–241 (1985).
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. & Coulson, A. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5463–5467 (1977).
Fry, D. C., Kuby, S. A. & Mildvan, A. S. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 907–911 (1986).
Walker, J. E., Saraste, M., Runswick, M. J. & Gay, N. J. EMBO J. 1, 945–951 (1982).
Higgins, C. F. et al. Nature 323, 448–450 (1986).
Doolittle, R. F. et al. Nature 323, 451–453 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gerlach, J., Endicott, J., Juranka, P. et al. Homology between P-glycoprotein and a bacterial haemolysin transport protein suggests a model for multidrug resistance. Nature 324, 485–489 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/324485a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/324485a0
This article is cited by
-
P-gp expression in brown trout erythrocytes: evidence of a detoxification mechanism in fish erythrocytes
Scientific Reports (2013)
-
The ABC transporter gene family of Daphnia pulex
BMC Genomics (2009)
-
Toward a mechanical control of drug delivery. On the relationship between Lipinski’s 2nd rule and cytosolic pH changes in doxorubicin resistance levels in cancer cells: a comparison to published data
European Biophysics Journal (2009)
-
Use of arrays to investigate the contribution of ATP-binding cassette transporters to drug resistance in cancer chemotherapy and prediction of chemosensitivity
Cell Research (2007)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.