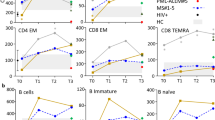
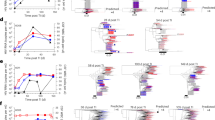
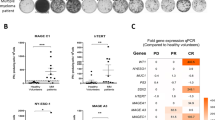
Abstract
A variety of clinical syndromes, including AIDS and neurological disorders, may follow as a consequence of infection with the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1)1–4. It is not yet clear, however, to what extent the destruction of lymphocytes and neural cells associated with these conditions is caused by adverse immune responses to HIV-1 or how much is due to cytopathic effects of the virus itself. Here we document the existence of HLA-restricted, HIV-1-specific cytoxic T lymphocytes in the cerebrospinal fluid of two AIDS patients manifesting neurologic disorders. These cytotoxic T lymphocytes showed dual specificity5, recognizing target cells coated with purified HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein (gp 120) or inactivated HIV-1 in the context of HLA antigens. Cytotoxic T-cell clones derived from one of the AIDS patients revealed restriction specificities representing both HLA class I and HLA class II antigens. Considerable phenotypic heterogeneity was observed amongst these clones, some expressing conventional combinations of cytotoxic T-cell surface markers, and others displaying unusual phenotypes. The presence of HIV-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes in AIDS patients, and in particular in their cerebrospinal fluid, suggests that these cytotoxic effectors may participate in the lymphoid cell and/or neurologic damage observed in such patients.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barré-Sinoussi et al. Science 220, 868–871 (1983).
Popovic, M., Sarngadharan, M. G., Read, E. & Gallo, R. C. Science 224, 497–500 (1984).
Levy, J. A. et al. Science 225, 840–842 (1984).
Hoo, D. D., Pomerantz, R. J. & Kaplan, J. C. New Engl. J. Med. 317, 278–286 (1987).
Zinkernagel, R. M. & Doherty, P. C. Adv. Immun. 27, 51–177 (1979).
Taylor, P. M., Davey, J., Howland, K., Rothbard, J. B. & Askonas, B. A. Immunogenelics 26, 267–272 (1987).
Biddison, W. E. J. clin. Immun. 2, 1–18 (1982).
Flomenberg, N. et al. Eur. J. Immun. 13, 905–911 (1983).
Reinherz, E. L. & Schlossman, S. F. Cell 19, 821–827 (1980).
Jacobsen, S. et al. J. Immun. 133, 754–757 (1984).
Yasukawa, M. & Zarling, J. M. J. Immun. 133, 422–427 (1984).
Brenner, M. B. et al. Nature 322, 145–149 (1986).
Moretta, L. et al. Eur. J. Immun. 17, 1229–1234 (1987).
Walker, B. D. et al. Nature 328, 345–348 (1987).
Plata, F. et al. Nature 328, 348–351 (1987).
Lyerly, H. K., Matthews, T. J., Langlois, A. J., Bolognesi, D. P. & Weinhold, K. J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 4601–4605 (1987).
Crowe, S., Mills, J. & McGrath, M. S. AIDS Res. hum. Retroviruses 3, 135–143 (1987).
Sethi, K. K. & Brandis, H. Z. Immun. Forsch. 150, 162–173 (1977).
Sethi, K. K., Stroehmann, I. & Brandis, H. Nature 286, 718–720 (1980).
Sethi, K. K., Stroehmann, I. & Brandis, H. Infect. Immunity 36, 657–661 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sethi, K., Näher, H. & Stroehmann, I. Phenotypic heterogeneity of cerebrospinal fluid-derived HIV-specific and HLA-restricted cytotoxic T-cell clones. Nature 335, 178–181 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/335178a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/335178a0
This article is cited by
-
Distinct roles of CD4+T cell subpopulations in retroviral immunity: lessons from the Friend virus mouse model
Retrovirology (2011)
-
HIV-1-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes and the control of HIV-1 replication
Springer Seminars in Immunopathology (1997)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.