Abstract
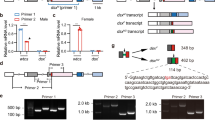
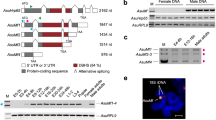
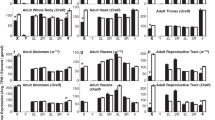
SOMATIC sexual differentiation in Drosophila melanogaster is accomplished by a hierarchy of genes1–5 of which one, Sex-lethal (Sxl)6,7, is required for the functional female-specific splicing of the transcripts of the immediately downstream regulatory gene, transformer (tra). The first exon of the tra primary transcript is spliced to one of two acceptor sites. Splicing to the upstream site yields a messenger RNA which is neither sex-specific nor func-tional, but that produced after splicing to the downstream acceptor site yields a functional female-specific mRNA. Here we address the question of how the Sxl gene product determines the alternative splicing of tra primary transcripts. One suggestion is that non-sex-specific splicing to the upstream acceptor is blocked in female flies by sex-specific factors8, but neither the identity of the female-specific factors nor the mechanism of the blockage has been specified. We have now performed co-transfection experiments in which Sxl complementary DNA and the tra gene are expressed in Drosophila Kc cells. Moreover, we find that female Sxl-encoded protein binds specifically to the tra transcript at or near the non-sex-specific acceptor site, implying that the female Sxl gene product is the trans-acting factor that regulates the alternative splicing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baker, B. S. Nature 340, 521–524 (1989).
Wolfner, M. F. Trends Genet. 4, 333–337 (1988).
Belote, J. M. Gene 82, 161–167 (1989).
Hodgkin, J. Cell 56, 905–906 (1989).
Bingbam, P. M., Chou, T-B., Mims, I. & Zachar, Z. Trends Genet. 4, 134–138 (1988).
Bell, L. R., Maine, E. M., Schedl, P. & Cline, T. W. Cell 55, 1037–1046 (1988).
Maine, E. M., Salz, H. K., Cline, T. W. & Schedl, P. Cell 43, 521–529 (1985).
Sosnowski, B. A., Belote, J. M. & McKeown, M. Cell 58, 449–459 (1989).
Boggs, R. T., Gregor, P., Idriss, S., Belote, J. M. & McKeown, M. Cell 50, 739–747 (1987).
McKeown, M., Belote, J. M. & Baker, B. S. Cell 48, 489–499 (1987).
Nagoshi, R. N., McKeown, M., Burtis, K. C. Belote, J. M. & Baker, B. S. Cell 53, 229–236 (1988).
McKeown, M., Belote, J. M. & Boggs, R. T. Cell 53, 887–895 (1988).
Miyake, T., Mae, N., Shiba, T. & Kondo, S. Molec. gen. Genet. 207, 29–37 (1987).
Ingolia, T. D., Craig, E. A. & McCarthy, B. J. Cell 21, 669–679 (1980).
Goralski, T. J., Edström, J-E. & Baker, B. S. Cell 56, 1011–1018 (1989).
Amrein, H., Gorman, M. & Nöthiger R. Cell 55, 1025–1035 (1988).
Studier, F. W. & Moffat, B. A. J. molec. Biol. 189, 113–130 (1986).
Laughon, A. & Scott, M. P. Nature 310, 25–31 (1984).
Salz, H. K. et al. Genes Dev. 3, 708–719 (1989).
Gorman, C. M., Moffat, L. F. & Howard, B. H. Molec. cell. Biol. 2, 1044–1051 (1982).
Nocera, P. P. D. & Dawid, I. B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 7095–7098 (1983).
Melton, D. A. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 7035–7056 (1984).
Inoue, K., Ohno, M., Sakamoto, H. & Shimura, Y. Genes Dev. 3, 1472–1479 (1989).
Zoller, M. J. & Smith, M. Meth. Enzym. 100, 468–500 (1983).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inoue, K., Hoshijima, K., Sakamoto, H. et al. Binding of the Drosophila Sex-lethal gene product to the alternative splice site of transformer primary transcript. Nature 344, 461–463 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/344461a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/344461a0
This article is cited by
-
Noncanonical function of the Sex lethal gene controls the protogyny phenotype in Drosophila melanogaster
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
A drug-inducible sex-separation technique for insects
Nature Communications (2020)
-
The study of the transformer gene from Bactrocera dorsalis and B. correcta with putative core promoter regions
BMC Genetics (2016)
-
The wright stuff: reimagining path analysis reveals novel components of the sex determination hierarchy in drosophila melanogaster
BMC Systems Biology (2015)
-
Characterization of the doublesex gene within the Culex pipiens complex suggests regulatory plasticity at the base of the mosquito sex determination cascade
BMC Evolutionary Biology (2015)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.