Abstract
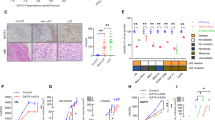
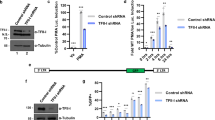
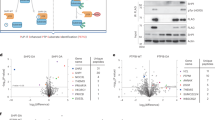
TRANSCRIPTION of lymphokine genes in activated T cells is inhibited by the immunosuppressive agents cyclosporin A and FK506, which act by blocking the phosphatase activity of calcineurin1–3. NFAT, a DNA-binding protein required for interleukin-2 gene transcription, is a potential target for calcineurin, cyclosporin A and FK5064–11. NFAT contains a subunit (NFATp) which is present in unstimulated T cells and which forms a complex with Fos and Jun proteins in the nucleus of activated T cells9,11. Here we report that NFATp is a DNA-binding phosphoprotein of relative molecular mass ∼ 120,000 and is a substrate for calcineurin in vitro. Purified NFATp forms DNA–protein complexes with recombinant Jun homodimers or Jun–Fos heterodimers; the DNA-binding domains of Fos and Jun are essential for the formation of the NFATp–Fos–Jun–DNA complex. The interaction between the lymphoid-specific factor NFATp and the ubiquitous transcription factors Fos and Jun provides a novel mechanism for combinatorial regulation of interleukin-2 gene transcription, which integrates the calcium-dependent and the protein-kinase C-dependent pathways of T-cell activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schreiber, S. L. & Crabtree, G. R. Immun. Today 13, 136–142 (1992).
Walsh, C. T., Zydowsky, L. D. & Mckeon, F. D. J. biol. Chem. 267, 13115–13118 (1992).
Sigal, N. H. & Dumont, F. J. Rev. Immun. 10, 519–560 (1992).
Shaw, J.-P. et al. Science 241, 202–205 (1988).
Mattila, P. S. et al. EMBO J. 9, 4425–4433 (1990).
Brabletz, T., Pietrowski, I. & Serfling, E. Nucleic Acids Res. 19, 61–67 (1991).
Banerji, S. S., Parsons, J. N. & Tocci, M. J. Molec. cell. Biol. 11, 4074–4087 (1991).
Flanagan, W. M., Corthesy, B., Bram, R. J. Crabtree, G. R. Nature 352, 803–807 (1991).
Jain, J., McCaffrey, P. G., Valge-Archer, V. E. & Rao, A. Nature 356, 801–804 (1992).
Clipstone, N. A. & Crabtree, G. R. Nature 357, 695–697 (1992).
MaCaffrey, P. G., Perrino, B. A., Soderling, T. R. & Rao, A. J. biol. Chem. 268, 3747–3752 (1993).
Hashimoto, Y., Perrino, B. A. & Soderling, T. R. J. biol. Chem. 265, 1924–1927 (1990).
Abate, C., Luk, D., Gagne, E., Roeder, R. G. & Curran, T. Molec. cell. Biol. 10, 5532–5535 (1990).
Jain, J., Valge-Archer, V. E. & Rao, A. J. Immun. 148, 1240–1250 (1992).
Abate, C., Patel, L., Rauscher, F. J. & Curran, T. Science 249, 1157–1161 (1990).
Xanthoudakis, S. & Curran, T. EMBO J. 11, 653–665 (1992).
Boise, L. H. et al. Molec. cell. Biol. 13, 1911–1919 (1993).
Abate, C., Luk, D. & Curran, T. Molec. cell. Biol. 11, 3624–3632 (1991).
Abate, C., Luk, D., Gentz, R., Rauscher, F. J. & Curran, T. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 87, 1032–1036 (1990).
Patel, L., Abate, C. & Curran, T. Nature 347, 572–575 (1990).
Kerppola, T. K. & Curran, T. Cell 66, 317–326 (1991).
Northrop, J. P., Ullman, K. S. & Crabtree, G. R. J. biol. Chem. 268, 2917–2923 (1993).
Cockerill, J. P., Shannon, M. F., Bert, A. G., Ryan, G. R. & Vadas, M. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 90, 2466–2470 (1993).
Miner, J. N. & Yamamoto, K. R. Genes Dev. 6, 2491–2501 (1992).
Kerppola, T. K., Luk, D. & Curran, T. Molec. cell. biol. 13, 3782–3791 (1993).
Bengal, E. et al. Cell 68, 507–519 (1992).
Li, L., Chambard, J-C., Karin, M. & Olson, E. N. Genes Dev. 6, 676–689 (1992).
Valge-Archer, V. E., de Villiers, J., Sinskey, A. J. & Rao, A. J. Immun. 145, 4355–4364 (1990).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jain, J., McCafffrey, P., Miner, Z. et al. The T-cell transcription factor NFATp is a substrate for calcineurin and interacts with Fos and Jun. Nature 365, 352–355 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/365352a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/365352a0
This article is cited by
-
Structure/epitope analysis and IgE binding activities of three cyclophilin family proteins from Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Longitudinal modeling of human neuronal aging reveals the contribution of the RCAN1–TFEB pathway to Huntington’s disease neurodegeneration
Nature Aging (2023)
-
Nano zinc supplementation in ruminant’s livestock, influence on physiological, immune functions and oxidative stability of West African dwarf goat bucks
Comparative Clinical Pathology (2023)
-
Palmitoylation targets the calcineurin phosphatase to the phosphatidylinositol 4-kinase complex at the plasma membrane
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Tacrolimus Decreases Cognitive Function by Impairing Hippocampal Synaptic Balance: a Possible Role of Klotho
Molecular Neurobiology (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.