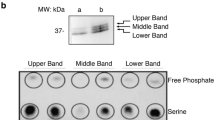
Abstract
THE engagement of CD28 with its ligand B7.1/CD80 results in potent costimulation of T-cell activation initiated through the CD3/T-cell receptor complex1,2. The biochemical basis of CD28 costimulatory function is poorly understood. The signalling pathways used by CD28 are unlike those used by the CD3/T-cell receptor in that they are resistant to cyclosporin A and independent of changes in cyclic AMP concentrations3. These differences suggest that each pathway provides unique biochemical informa-tion which is required for T-cell activation. We report here that CD28 becomes tyrosine-phosphorylated following interaction with B7.1/CD80, which induces formation of a complex with phospha-tidylinositol-3-OH kinase, mediated by the SH2 domains of the p85 subunit of the kinase. Phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase is a heterodimer of this 85K regulatory subunit and a 11 OK catalytic subunit, and is a common substrate for most receptor tyrosine kinases and some cytokine receptors4,5, binding through its SH2 domain to phosphotyrosine in the motif Tyr-X-X-Met in the CD28 sequence, which is highly conserved between human, mouse and rat6–8 and lies in the intracellular domain. We show that CD28 mutants that have their kinase-binding site deleted or the tyrosine at position 173 substituted by phenylalanine do not associate with the kinase after CD28 stimulation and cannot stimulate production of interleukin-2. Our results suggest that phosphatidylinositol-3-OH kinase is critical for signalling by CD28.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Linsley, P. S. et al. J. exp. Med. 173, 721–730 (1991).
Koulova, L., Clark, E. A., Shu, G. & Dupont, B. J. exp. Med. 173, 759–762 (1991).
June, C. H., Ledbetter, J. A., Gillespie, M. M., Lindsten, T. & Thompson, C. B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 1384–1388 (1987).
Otsu, M. et al. Cell 65, 91–104 (1991).
Hiles, I. D. et al. Cell 70, 419–429 (1992).
Aruffo, A. & Seed, B. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 8573–8577 (1987).
Gross, J. A., St John, T. & Allison, J. P. J. Immun. 144, 3201–3210 (1990).
Clark, G. J. & Dallman, M. J. Immunogenetics 35, 54–57 (1992).
Remillard, B. et al. J. biol. Chem. 266, 14167–14170 (1991).
Ward, S. G., Ley, S. C., MacPhee, C. & Cantrell, D. A. Eur. J. Immun. 22, 45–49 (1992).
Thompson, P. A., Gutkind, J. S., Robbins, K. C., Ledbetter, J. A. & Bolen, J. B. Oncogene 7, 719–725 (1992).
Ward, S. G., Westwick, J., Hall, N. D. & Sansom, D. M. Eur. J. Immun. 23, 2572–2577 (1993).
Gunning, P., Leavitt, J., Muscat, G., Ng, S. Y. & Kedes, L. Proc natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 4831–4835 (1987).
Couez, D. et al. Molec. Immun. 31, 47–57 (1994).
Rottapel, R. et al. Molec. cell. Biol. 11, 3043–3051 (1991).
McGlade, C. J. et al. Molec. cell. Biol. 12, 991–997 (1992).
Nunes, J. et al. Int. Immun. 5, 311–315 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pagès, F., Ragueneau, M., Rottapel, R. et al. Binding of phosphatidyl-inositol-3-OH kinase to CD28 is required for T-cell signalling. Nature 369, 327–329 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/369327a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/369327a0
This article is cited by
-
Iguratimod suppresses Tfh cell differentiation in primary Sjögren’s syndrome patients through inhibiting Akt/mTOR/STAT3 signaling
Arthritis Research & Therapy (2023)
-
A comparison of chimeric antigen receptors containing CD28 versus 4-1BB costimulatory domains
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2021)
-
Preclinical rationale and clinical efficacy of antiangiogenic therapy and immune checkpoint blockade combination therapy in urogenital tumors
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2019)
-
Predominant contribution of DGKζ over DGKα in the control of PKC/PDK‐1‐regulated functions in T cells
Immunology & Cell Biology (2017)
-
In the absence of its cytosolic domain, the CD28 molecule still contributes to T cell activation
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2015)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.