Abstract
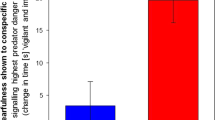
Although positive reciprocity (reciprocal altruism) has been a focus of interest in evolutionary biology, negative reciprocity (retaliatory infliction of fitness reduction) has been largely ignored. In social animals, retaliatory aggression is common, individuals often punish other group members that infringe their interests, and punishment can cause subordinates to desist from behaviour likely to reduce the fitness of dominant animals. Punishing strategies are used to establish and maintain dominance relationships, to discourage parasites and cheats, to discipline offspring or prospective sexual partners and to maintain cooperative behaviour.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Trivers, R. L. Q. Rev. Biol. 46, 35–57 (1971).
Packer, C. Nature 265, 441–445 (1977).
Axelrod, R. & Hamilton, W. D. Science 211, 1390–1396 (1981).
Nowak, M. A. & Sigmund, K. Nature 355, 250–253 (1992).
Dugatkin, L. A., Mesterton-Gibbons, M. & Houston, A. I. Trends Evol. Ecol. 7, 202–205 (1992).
Maynard Smith, J. & Price, G. R. Nature 246, 15–18 (1973).
Maynard Smith, J. J. theor. Biol. 47, 209–221 (1974).
Parker, G. A. J. theor. Biol. 47, 223–243 (1974).
Maynard Smith, J. & Parker, G. A. Anim. Behav. 24, 159–175 (1976).
Parker, G. A. & Rubenstein, D. Anim. Behav. 29, 221–240 (1981).
Hinde, R. A. Biological Bases of Human Social Behavior (McGraw Hill, New York, 1974).
Huntingford, F. & Turner, A. Animal Conflict (Chapman & Hall, London, 1987).
Bean, P. Punishment: A Philosophical and Criminological Enquiry (Robertson, Oxford, 1981).
Grotius De Jure Bellict Pacis (Innys, London, 1738).
Hamilton, W. D. Nature 228, 1218–1220 (1970).
Clutton-Brock, T. H. & Parker, G. A. Anim. Behav. (in the press).
Maynard Smith, J. Evolution and the Theory of Games (Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 1982).
Hammerstein, P. Anim. Behav. 29, 193–205 (1981).
de Waal, F. B. M. Chimpanzee Politics (Allen & Unwin, London, 1982).
Walters, J. R. & Seyfarth, R. M. in Primate Societies (eds Smuts, B. B., Cheney, D. L., Seyfarth, R. M., Wrangham, R. W. & Struhsaker, T. T.) 306–317 (Univ. Chicago Press, Chicago, 1987).
Silk, J. B. in Primate Social Conflict (eds Mason, W. A. & Mendoza, S. P.) 49–83 (State Univ. New York Press, New York, 1993).
Appleby, M. C. Behaviour 74, 294–309 (1980).
Hauser, M. D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 12137–12139 (1992).
Hauser, M. D. & Marler, P. Behavl Ecol. 4, 206–212 (1993).
Drukker, B., Nieuwenhuijsen, K., van der Werft ten Bosch, J. J., van Hooff, J. A. R. A. M. & Slob, A. K. Anim. Behav. 42, 171–182 (1991).
Cheney, D. L. & Seyfarth, R. M. Anim. Behav. 34, 722–731 (1986).
Cheney, D. L. & Seyfarth, R. M. Behaviour 110, 258–275 (1989).
Cheney, D. L. & Seyfarth, R. M. How Monkeys See the World (Univ. of Chicago Press, Chicago, 1990).
Aureli, F., Cossolino, R., Cordischi, C. & Scucchi, S. Anim. Behav. 44, 283–291 (1992).
Judge, P. J. Int. J. Primatol. 3, 301–302 (1982).
Judge, P. J. Am. J. Primatol. 23, 225–237 (1991).
Smuts, B. B. Nat. Hist. 2, 36–44 (1987).
Smuts, B. B. Sex and Friendship in Baboons (Aldine, Hawthorne, New York, 1985).
Wood Gush, D. G. M. The Behaviour of the Domestic Fowl (Heinemann Educational, London, 1971).
Rowell, T. E. Social Behavior of Monkeys (Penguin, Baltimore, 1972).
Mendoza, S. P. in Primate Social Conflict (eds Mason, W. A. & Mendoza, S. P.) 85–110 (State Univ. New York Press, New York, 1993).
Drummond, H. & Osorno, J. L. Anim. Behav. 44, 881–893 (1992).
de Waal, F. B. M. & Luttrell, L. M. Ethol. Sociobiol. 9, 101–118 (1988).
de Waal, F. B. M. in Coalitions and Alliances in Humans and Other Animals (eds Harcourt, A. H. & de Waal, F. B. M.) 233–257 (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 1992).
Fisher, J. in The Natural History of Aggression (eds Carthy, J. D. & Ebling, F. J.) 7–14 (Academic, London, 1964).
Andersson, M. in Producers and Scroungers (ed. Barnard, C. J.) 195–228 (Croom Helm, London, 1984).
Reiter, J., Stinson, N. L. & LeBoeuf, B. J. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 3, 337–367 (1978).
Clutton-Brock, T. H., Albon, S. D., Gibson, R. M. & Guinness, F. E. Anim. Behav. 27, 211–225 (1979).
Clutton-Brock, T. H., Green, D., Hiraiwa-Hasegawa, M. & Albon, S. D. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 23, 281–296 (1988).
Reiter, J., Panken, K. J. & LeBoeuf, B. J. Anim. Behav. 29, 670–687 (1981).
Mills, G. Kalahari Hyenas (Allen & Unwin, London, 1991).
Smuts, B. B. & Smuts, R. W. Adv. Stud. Behav. 22, 1–63 (1993).
Clutton-Brock, T. H., Guinness, F. E. & Albon, S. D. Red Deer: The Behavior and Ecology of Two Sexes (Univ. Chicago Press, Chicago, 1982).
Kummer, H. Social Organisation of Hamadryas Baboons (Karger, Basel, 1968).
Manson, J. H. Anim. Behav. 48, 473–475 (1994).
Manson, J. H. Anim. Behav. 44, 405–416 (1992).
Goodall, J. The Chimpanzees of Gombe (Belknap of Harvard Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1986).
Nadler, R. D. in The Orangutan: Its Biology and Conservation (ed. de Boer, L. E. M.) 231–248 (Junk, The Hague, 1982).
Nadler, R. D. in Human Sexual Aggression: Current Perspectives (eds Prentky, R. A. & Quinsey, V. L.) 154–162 (N.Y. Acad. Sci., New York, 1988).
Nadler, R. D. & Miller, L. C. Folia Primatol. 38, 233–239 (1982).
de Waal, F. B. M. in Animal Social Conflict (eds Mason, W. A. & Mendoza, S. P.) 114–144 (State Univ. New York Press, Albany, 1993).
Lindburg, D. G. in Perspectives on Primate Biology (ed. Seth. P. R.) (Today and Tomorrow, New Delhi, 1983).
Enomoto, T. Primates 22, 15–23 (1981).
Teas, J. Female Primates: Studies by Women Primatologists (ed. Small, M. F.) 237–247 (Liss, New York, 1984).
Le Boeuf, B. J. & Mesnick, S. Behaviour 116, 143–162 (1991).
Rajpurohit, L. S. & Sommer, V. Folia Primatol. 56, 17–27 (1991).
Trivers, R. L. Am. Zool. 14, 249–264 (1974).
Parker, G. A. & MacNair, M. R. Anim. Behav. 26, 97–110 (1978).
Nieuwenhuijsen, K., Slob, A. K. & van den Werft ten Bosch, J. J. Psychobiology 16, 357–371 (1988).
Horrocks, J. A. & Hunte, W. Am. Nat. 122, 417–421 (1983).
Horsfall, J. A. Anim. Behav. 32, 216–225 (1984).
Leonard, M. L., Horn, A. G. & Eden, S. F. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 23, 265–270 (1988).
Trivers, R. L. Social Evolution (Cummings, Menlo Park, 1985).
Brown, J. L. Helping and Communal Breeding in Birds (Princeton Univ. Press, Princeton, 1987).
Vehrencamp, S. L. Anim. Behav. 31, 667–682 (1983).
Schelling, T. The Strategy of Conflict (Harvard Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1960).
Thompson, E. & Faith, R. Am. Econ. Rev. 71, 366–380 (1981).
Yamagishi, T. J. Pers. Soc. Psych. 51, 100–116 (1986).
Axelrod, R. Am. Polit. Sci. Rev. 80, 1095–1111 (1986).
Boyd, R. & Richerson, P. J. Ethol. Sociobiol. 13, 171–195 (1992).
Axelrod, R. The Evolution of Cooperation (Basic Books, New York, 1984).
Oliver, P. Am. J. Sociol. 85, 1356–1375 (1980).
Hirschleifer, D. & Rasmusen, E. J. econ. Behav. Org. 12, 87–106 (1989).
Hirschleifer, D. & Martinez-Coll, J. J. Conflict Resolution 32, 367–398 (1988).
Strassman, J. E. & Mayer, D. C. Anim. Behav. 31, 431–438 (1983).
Reeve, H. K. & Gamboa, J. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 13, 63–74 (1983).
Reeve, H. K. & Gamboa, J. Behaviour 102, 147–167 (1987).
Reeve, H. K. Nature 358, 147–149 (1992).
Mulder, R. A. & Langmore, N. E. Anim. Behav. 45, 830–833 (1993).
Reeve, H. K. & Nonacs, P. Nature 359, 823–825 (1992).
de Waal, F. B. M. Peacemaking Among Primates (Harvard Univ. Press, Cambridge, 1989).
Cords, M. 13th Cong. Int. Primat Soc. (Kyoto, Japan, 1990).
Ehardt, C. L. & Bernstein, I. S. in Coalitions and Alliances in Humans and Other Animals (eds Harcourt, A. H. & de Waal, F. M. B.) 82–111 (Oxford Univ. Press, Oxford, 1992).
Hunte, W. & Horrocks, J. A. Behav. Ecol. Sociobiol. 20, 257–263 (1987).
Harrel, A. Int. J. Sport. 11, 290–298 (1980).
Hoebel, E. A. The Laws of Primitive Man: A Study of Comparative Legal Dynamics (Harvard Univ. Press., Cambridge, 1954).
Phillips, A. Ancient Israel's Criminal Law (Blackwells, Oxford, 1970).
Roberts, S. Order and Dispute: An Introduction to Legal Anthropology (Penguin, Harmondsworth, 1979).
Ratnieks, F. L. W. Am. Nat. 132, 217–236 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clutton-Brock, T., Parker, G. Punishment in animal societies. Nature 373, 209–216 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/373209a0
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/373209a0
This article is cited by
-
People punish defection, not failures to conform to the majority
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Punitiveness toward social distancing deviance in the COVID-19 pandemic: Findings from two national experiments
Journal of Experimental Criminology (2024)
-
Male cooperation improves their own and kin-group productivity in a group-foraging spider
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
The cognitive challenges of cooperation in human and nonhuman animals
Nature Reviews Psychology (2023)
-
Communicating emotions, but not expressing them privately, reduces moral punishment in a Prisoner’s Dilemma game
Scientific Reports (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.