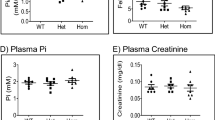
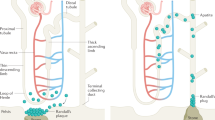
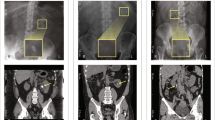
Abstract
KIDNEY stones (nephrolithiasis), which affect 12% of males and 5% of females in the western world, are familial in 45% of patients1,2 and are most commonly associated with hypercalciuria1. Three disorders of hypercalciuric nephrolithiasis (Dent's disease3, X-linked recessive nephrolithiasis (XRN)4, and X-linked recessive hypophosphataemic rickets (XLRH)5) have been mapped to Xpll.22 (refs 5–7). A microdeletion6 in one Dent's disease kindred allowed the identification of a candidate gene,CLCN5 (refs 8,9) which encodes a putative renal chloride channel. Here we report the investigation of 11 kindreds with these renal tubular disorders for CLCN5 abnormalities; this identified three nonsense, four missense and two donor splice site mutations, together with one intragenic deletion and one micro-deletion encompassing the entire gene. Heterologous expression of wild-type CLCN5 in Xenopus oocytes yielded outwardly rectifying chloride currents, which were either abolished or markedly reduced by the mutations. The common aetiology for Dent's disease, XRN and XLRH indicates that CLCN5 may be involved in other renal tubular disorders associated with kidney stones.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Coe, F. L., Parks, J. H. & Asplin, J. R. New Engl. J. Med. 327, 1141–1152 (1992).
Smith, L. H. J. Urol. 141, 707–710 (1989).
Wrong, O. M., Norden, A. G. W. & Feest, T. G. Q. J. Med. 87, 473–493 (1994).
Frymoyer, P. A. et al. New Engl. J. Med. 325, 681–686 (1991).
Bolino, A. et al. Eur. J. hum. Genet. 1, 269–279 (1993).
Pook, M. A. et al. Hum. molec. Genet. 2, 2129–2134 (1993).
Scheinman, S. J. et al. J. clin. Invest. 91, 2351–2357 (1993).
Fisher, S. E. et al. Hum. molec. Genet. 3, 2053–2059 (1994).
Fisher, S. E. et al. Genomics 29, 598–606 (1995).
Jentsch, T. J., Günther, W., Pusch, M. & Schwappach, B. J. Physiol., Lond. 482, 19S–25S (1995).
Steinmeyer, K., Ortland, C. & Jentsch, T. J. Nature 354, 301–304 (1991).
Steinmeyer, K. et al. EMBO J. 13, 737–743 (1994).
Meyer-Kleine, C., Steinmeyer, K., Ricker, K., Jentsch, T. J. & Koch, M. C. Am. J. hum. Genet. 57, 1325–1334 (1995).
Koch, M. C. et al. Science 257, 797–800 (1992).
Pusch, M., Ludewig, U., Rehfeldt, A. & Jentsch, T. J. Nature 373, 527–531 (1995).
Thiemann, A., Grūnder, S., Pusch, M. & Jentsch, T. J. Nature 356, 57–60 (1992).
Steinmeyer, K., Schwappach, B., Bens, M., Vandewalle, A. & Jentsch, T. J. J. biol. Chem. 270, 31172–31177 (1995).
Higgins, J. T., Gebler, B. & Frömter, E. Pflügers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 371, 87–97 (1977).
Green, J. R., Brown, N. H., DiDomenico, B. J., Kaplan, J. & Eide, D. J. Molec. gen. Genet. 241, 542–553 (1993).
Adachi, S. et al. J. biol. Chem. 269, 17677–17683 (1994).
Middleton, R. E., Pheasant, D. J. & Miller, C. Biochemistry 33, 13189–13198 (1994).
Friedman, P. A. & Gesek, F. A. Physiol. Rev. 75, 429–471 (1995).
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E. F. & Maniatis, T. A Laboratory manual 2nd edn. 7.19–7.22 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1989).
Pearce, S. H. S. et al. J. clin. Invest. 96, 2683–2692 (1995).
Thakker, R. V. et al. J. clin. Invest. 91, 2815–2821 (1993).
Krieg, P. A. & Melton, D. A. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 7057–7070 (1984).
Jentsch, T. J., Steinmeyer, K. & Schwarz, G. Nature 348, 510–514 (1990).
Brandt, S. & Jentsch, T. J. FEBS Lett. 377, 15–20 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lloyd, S., Pearce, S., Fisher, S. et al. A common molecular basis for three inherited kidney stone diseases. Nature 379, 445–449 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/379445a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/379445a0
This article is cited by
-
Prenatal diagnosis of dent disease type I with a nonsense pathogenic variant in CLCN5: a case study
BMC Medical Genomics (2024)
-
Inherited Fanconi syndrome
World Journal of Pediatrics (2023)
-
SCP2 variant is associated with alterations in lipid metabolism, brainstem neurodegeneration, and testicular defects
Human Genomics (2022)
-
Genetics and phenotypic heterogeneity of Dent disease: the dark side of the moon
Human Genetics (2021)
-
Case report: a Chinese girl with dent disease 1 and turner syndrome due to a hemizygous CLCN5 gene mutation and Isochromosome (Xq)
BMC Nephrology (2020)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.