Abstract
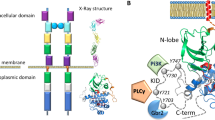
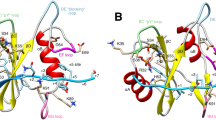
The crystal structure of the haematopoietic cell kinase Hck has been determined at 2.6/2.9 Å resolution. Inhibition of enzymatic activity is a consequence of intramolecular interactions of the enzyme's Src-homology domains SH2 and SH3, with concomitant displacement of elements of the catalytic domain. The conformation of the active site has similarities with that of inactive cyclin-dependent protein kinases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown, M. T. & Cooper, J. A. Regulation, substrates and functions of Src. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1287, 121–149 (1996).
Quintrell, N. et al. Identification of a human gene (HCK) that encodes a protein-tyrosine kinase and is expressed in hemopoietic cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7, 2267–2275 (1987).
Zeigler, S. F., March, J. D., Lewis, D. B. & Perlmutter, R. M. Novel protein-tyrosine kinase gene (hck) preferentially expressed in cells of hematopoietic origin. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7, 2276–2285 (1987).
Lowell, C. A., Soriano, P. & Varmus, H. E. Functional overlap in the src gene family: interaction of hck and fgr impairs natural immunity. Genes Dev. 8, 387–398 (1994).
Lowell, C. A., Niwa, M., Soriano, P. & Varmus, H. E. Deficiency of the Hck and Sre Tyrosine Kinases results in extreme levels of extramedullary hematopoiesis. Blood 87, 1780–1792 (1996).
Pawson, R. Protein modules and signalling networks. Nature 373, 573–580 (1995).
Cohen, G. B., Ren, R. & Baltimore, D. Modular binding domains in signal transduction proteins. Cell 80, 237–248 (1995).
Kuriyan, J. & Cowburn, D. Modular Peptide Binding Domains. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biomol. Struct. (in the press).
Cunningham, B. D., Threadgill, M. A., Groundwater, P. W., Dale, I. L. & Hickman, J. A. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a series of flavones designed as inhibitors of protein tyrosine kinases. Anti-cancer Drug Design 7, 365–384 (1992).
Waksman, F. et al. Crystal structure of the phosphotyrosine recognition domain SH2 of v-src complexed with tyrosine-phosphorylated peptides. Nature 358, 646–653 (1992).
Musacchio, A., Noble, M., Pauptit, R., Wierenga, R. & Saraste, M. Crystal structure of a Src-homology 3 (SH3) domain. Nature 359, 851–855 (1992).
Knighton, D. R. et al. Crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Science 253, 407–414 (1991).
Hubbard, S. R., Wei, L., Ellis, L. & Hendrickson, W. A. Crystal structure of the tyrosine kinase domain of the human insulin receptor. Nature 372, 746–754 (1994).
Yamaguchi, H. & Hendrickson, W. A. Structural basis for activation of the human lymphocyte kinase Lck upon tyrosine phosphorylation. Nature 384, 484–489 (1996).
Johnson, L. N., Noble, M. E. M. & Owen, D. J. Active and inactive protein kinases: structural basis for regulation. Cell 85, 149–158 (1996).
Adzhubei, A. A. & Sternberg, M. J. E. Left-handed polyproline II helices commonly occur in globular proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 229, 472–493 (1993).
Yu, H., Chen, J. K., Feng, S., Dalgarno, D. C., Brauer, A. W. & Schreiber, S. L. Structural basis for the binding of proline-rich peptides to SH3 domains. Cell 76, 933–945 (1994).
Musacchio, A., Saraste, M. & Wilmanns, M. High-resolution crystal structures of tyrosine kinase SH3 domains complexed with proline-rich peptides. Nature Struct. Biol. 1, 546–551 (1994).
Eck, M. J., Atwell, S. K., Shoelson, S. E. & Harrison, S. C. Crystal structure of the regulatory domains of the Src-family tyrosine kinase lck. Nature 368, 764–769 (1994).
Zheng, J. et al. 2.2 Å refined crystal structure of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase complexed with MnATP and a peptide inhibitor. Acta Crystallogr. D49, 362–365 (1993).
DeBondt, H. L. et al. Crystal structure of cyclin-dependent kinase 2. Nature 363, 595–602 (1993).
Waksman, G., Shoelson, S. E., Plant, N., Cowburn, D. & Kuriyan, J. Binding of a high affinity phosphotyrosyl peptide to the src SH2 domain: crystal structures of the complexed and peptide-free forms. Cell 72, 779–790 (1993).
Eck, M. J., Shoelson, S. E. & Harrison, S. C. Recognition of a high affinity phosphotyrosyl peptide by the Src homology 2 domain of p56lck. Nature 362, 87–91 (1993).
Songyang, Z. et al. SH2 domains recognize specific phosphopeptide sequences. Cell 72, 767–778 (1993).
Ladbury, J. E. et al. Measurement of the binding tyrosyl phosphopeptides to SH2 domains: a reappraisal. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 3199–3203 (1995).
Lim, W. A., Richards, D. M. & Fox, R. O. Structural determinants of peptide-binding orientation and of sequence specificity in SH3 domains. Nature 372, 375–379 (1994).
Lee, C. -H. et al. A single amino acid in the SH3 domain of Hck determines its high affinity and specificity in binding to HIV-1 Nef protein. EMBO J. 14, 5006–5015 (1995).
Lee, C. -H., Saksela, K., Mirza, U. A., Chait, B. T. & Kuriyan, J. Crystal structure of the conserved core of HIV-1 Nef complexed with a Src family SH3 domain. Cell 85, 931–942 (1996).
Erpel, T. A., Superti-Furga, G. & Courtneidge, S. A. Mutational analysis of the Src SH3 domain: the same residues of the ligand binding surface are important for intra- and inter-molecular interactions. EMBO J. 14, 963–975 (1995).
MacAuley, A. & Cooper, J. A. Structural differences between repressed and derepressed forms of p60c-src. Mol. Cell. Biol. 9, 2448–2656 (1989).
Juffrey, P. D. et al. Mechanism of CDK activation revealed by the structure of a cyclinA-CDK2 complex. Nature 376, 294–295 (1995).
Courtneidge, S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 4, 1471–1477 (1985).
Kmiecik, T. E. & Shalloway, D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell 49, 65–73 (1987).
Piwnica-Worms, H., Saunders, K. B., Roberts, T. M., Smith, A. E. & Cheng, S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-Src. Cell 49, 75–82 (1987).
Cartwright, C. A., Eckhart, W., Simon, S. & Kaplan, P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-Src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell 49, 83–91 (1987).
Cooper, J. A. & King, C. S. Dephosphorylation or antibody binding to the carboxy terminus stimulates pp60c-src. Mol. Cell. Biol. 6, 4467–4477 (1986).
Parsons, T. J. & Weber, M. J. Genetics of src. structure and functal organization of a protein tyrosine kinase. Curr. Top. Microb. Immunol. 147, 80–127 (1989).
Moarefi, I. et al. Activation of the Src-family tyrosine kinase Hck by SH3 domain displacement. Nature 385, 650–653 (1997).
Briggs, S. D., Bryant, S. S., Jove, R., Sanderson, S. D. & Smithgall, T. E. The Ras GTPase-activating protein (GAP) is an SH3 domain-binding protein and substrate for the Src-related tyrosine kinase, Hek. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 14718–14724 (1995).
Alexandropoulos, K. & Baltimore, D. Coordinate activation of c-Src by SH3- and SH2-binding sites on a novel p130Cas-related protein, Sin. Genes Dev. 10, 1341–1355 (1996).
Furey, W. & Swaminathan, S. in American Crystallographic Association Meeting Abstracts 73 (1990).
Jones, T. A., Zou, J. Y., Cowan, S. W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr. A47, 110–119 (1991).
Brünger, A. R. X-PLOR (Yale University, New Haven, CT, 1992).
Carson, M. Ribbons 2.0. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 958–961 (1991).
Nicholls, A., Sharp, K. A. & Honig, B. Protein folding and association: insights from the interfacial and thermodynamic properties of hydrocarbons. Proteins Struct. Funct. Genet. 11, 281–296 (1991).
Brünger, A. T. Crystallographic refinement by simulated annealing: application to a 2.8 Å resolution structure of aspartate aminotransferase. J. Mol. Biol. 203, 803–816 (1988).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sicheri, F., Moarefi, I. & Kuriyan, J. Crystal structure of the Src family tyrosine kinase Hck. Nature 385, 602–609 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/385602a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/385602a0
This article is cited by
-
Src family kinases, adaptor proteins and the actin cytoskeleton in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Cell Communication and Signaling (2021)
-
Novel mutations in the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 gene are associated with sheep body weight and fatness traits
Mammalian Genome (2021)
-
Exploring receptor tyrosine kinases-inhibitors in Cancer treatments
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics (2019)
-
Phosphorylation induced cochaperone unfolding promotes kinase recruitment and client class-specific Hsp90 phosphorylation
Nature Communications (2018)
-
Allosteric mechanisms underlie GPCR signaling to SH3-domain proteins through arrestin
Nature Chemical Biology (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.