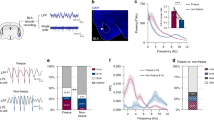
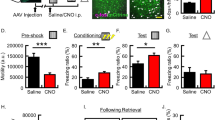
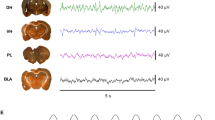
Abstract
Animals learn that a tone can predict the occurrence of an electric shock through classical conditioning. Mice or rats trained in this manner display fear responses, such as freezing behaviour, when they hear the conditioned tone. Studies using amygdalectomized rats have shown that the amygdala is required for both the acquisition and expression of learned fear responses1,2,3. Freezing to a conditioned tone is enhanced following damage to the dorsal part of the medial prefrontal cortex4, indicating that this area may be involved in fear reduction. Here we show that prefrontal neurons reduce their spontaneous activity in the presence of a conditioned aversive tone as a function of the degree of fear. The depression in prefrontal spontaneous activity is related to amygdala activity but not to the freezing response itself. These data indicate that, in the presence of threatening stimuli, the amygdala controls both fear expression and prefrontal neuronal activity. They suggest that abnormal amygdala-induced modulation of prefrontal neuronal activity may be involved in the pathophysiology of certain forms of anxiety disorder.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Davis,M. in The Amygdala: Neurobiological Aspects of Emotion, Memory, and Mental Dysfunction (ed. Aggleton, J. P.) 255–305 (Wiley-Liss, New York, 1992).
LeDoux,J. E. Emotion: clues from brain. Annu. Rev. Psychol. 46, 209–235 (1995).
Maren,S. & Fanselow,M. S. The amygdala and fear conditioning: has the nut been cracked? Neuron 16, 237–240 (1996).
Morgan,M. A. & LeDoux,J. E. Differential contribution of dorsal and ventral medial prefrontal cortex to acquisition and extinction of conditioned fear in rats. Behav. Neurosci. 109, 681–688 (1995).
Rescorla,R. A. Pavlovian conditioned inhibition. Psychol. Bull. 72, 77–94 (1969).
Campeau,S. et al. Elicitation and reduction of fear: behavioural and neuroendocrine indices and brain induction of the immediated-early gene c-fos. Neuroscience 78, 1087–1104 (1997).
Papini,M. R. & Bitterman,M. E. The two-test strategy in the study of inhibitory conditioning. J. Exp. Psychol. Anim. Behav. Process. 19, 342–352 (1993).
Thomas,E. & Yadin,E. Multiple unit activity in the septum during Pavlovian aversive conditioning: evidence for an inhibitory role for the septum. Exp. Neurol. 69, 50–60 (1980).
McDonald,A. J. Organization of amygdaloid projections to the prefrontal cortex and associated striatum in the rat. Neuroscience 44, 1–14 (1991).
LaBar,K. S. & LeDoux,J. E. Partial disruption of fear conditioning in rats with unilateral amygdala damage: correspondence with unilateral temporal lobectomy in humans. Behav. Neurosci. 110, 991–997 (1996).
Farb,C. R. & LeDoux,J. E. NMDA and AMPA receptors in the lateral nucleus of the amygdala are postsynaptic to auditory thalamic afferents. Synapse 27, 106–121 (1997).
LeDoux,J. E., Farb,C. & Ruggiero,D. A. Topographic organization of neurons in the acoustic thalamus that project to the amygdala. J. Neurosci. 10, 1043–1054 (1990).
Turner,B. H. & Herkenham,M. Thalamo-amygdaloid projections in the rat: a test of the amygdala's role in sensory processing. J. Comp. Neurol. 313, 295–325 (1991).
Garcia,R., Paquereau,J., Vouimba,R. M. & Jaffard,R. Conditioned fear stress enhances auditory-evoked potentials in the basolateral amygdala of the awake rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. (Suppl.) 9, 194 (1996).
Garcia,R., Paquereau,J., Vouimba,R. M. & Jaffard,R. Footshock stress but not contextual fear conditioning induces long-term enhancement of auditory-evoked potentials in the basolateral amygdala of the freely behaving rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 10, 457–463 (1998).
Rogan,M. T., Stäubli,U. V. & LeDoux,J. E. Fear conditioning induces associative long-term potentiation in the amygdala. Nature 390, 604–607 (1997).
Pérez-Jaranay,J. M. & Vives,F. Electrophysiological study of the response of medial prefrontal cortex neurons to stimulation of the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala in the rat. Brain Res. 564, 97–101 (1991).
McDonald,A. J. Organization of amygdaloid projections to the mediodorsal thalamus and prefrontal cortex: a fluorescence retrograde transport study in the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 262, 46–58 (1987).
Gonzales,C. & Chesselet,M. F. Amygdalo-nigral pathways: an anterograde study in the rat with phaseolus vulgaris leucoagglutinin (PHAL-L). J. Comp. Neurol. 297, 182–200 (1990).
Lindvall,O., Björklund,A., Moore,R. Y. & Stenevi,U. Mesencephalic dopamine neurons projecting to neocortex. Brain Res. 81, 325–331 (1974).
Fuxe,K., Hökfelt,T., Johansson,O., Lidbrink,P. & Ljungdahl,A. The origin of the dopamine nerve terminals in limbic and frontal cortex. Evidence for meso-cortico dopamine neurons. Brain Res. 82, 349–355 (1974).
Davis,M. et al. Stress-induced activation of prefrontal cortex dopamine turnover: blockade by lesions of the amygdala. Brain Res. 664, 207–210 (1994).
Goldstein,L. E., Rasmusson,A. M., Bunney,B. S. & Roth,R. H. Role of the amygdala in the coordination of behavioral, neuroendocrine, and prefrontal cortical monoamine responses to psychological stress in the rat. J. Neurosci. 16, 4787–4798 (1996).
Ferron,A., Thierry,A. M., Le Douarin,C. & Glowinski,J. Inhibitory influence of the mesocortical dopaminergic system on spontaneous activity or excitatory response induced from the thalamic mediodorsal nucleus in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. Brain Res. 302, 257–265 (1984).
Mantz,J., Milla,C., Glowinsky,J. & Thierry,A. M. Differential effects of ascending neurons containing dopamine and noradrenaline in the control of spontaneous activity and of evoked responses in the rat prefrontal cortex. Neuroscience 27, 517–526 (1988).
Schoenbaum,G., Chiba,A. A. & Gallagher,M. Neural encoding in orbitofrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala during olfactory discrimination learning. J. Neurosci. 19, 1876–1884 (1999).
Bechara,A., Damasio,H., Damasio,A. R. & Lee,G. P. Different contributions of the human amygdala and ventromedial prefrontal cortex to decision-making. J. Neurosci. 19, 5473–5481 (1999).
Herry,C., Vouimba,R. M. & Garcia,R. Plasticity in the thalamo-prefrontal cortical transmission in behaving mice. J. Neurophysiol. (in the press).
Schoenbaum,G., Chiba,A. A. & Gallagher,M. Orbitofrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala encode expected outcomes during learning. Nature Neurosci. 1, 155–159 (1998).
Franklin,K. B. J. & Paxinos,G. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates (Academic, San Diego, 1997).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the Fondation Fyssen (R.M.V.) and from NATO (R.G.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garcia, R., Vouimba, RM., Baudry, M. et al. The amygdala modulates prefrontal cortex activity relative to conditioned fear. Nature 402, 294–296 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/46286
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/46286
This article is cited by
-
Pre-scan state anxiety is associated with greater right amygdala-hippocampal response to fearful versus happy faces among trait-anxious Latina girls
BMC Psychiatry (2024)
-
Longitudinal recordings of single units in the basal amygdala during fear conditioning and extinction
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Manipulating fear associations via optogenetic modulation of amygdala inputs to prefrontal cortex
Nature Neuroscience (2017)
-
Cannabinoids and Glucocorticoids in the Basolateral Amygdala Modulate Hippocampal–Accumbens Plasticity After Stress
Neuropsychopharmacology (2016)
-
Stress and Fear Extinction
Neuropsychopharmacology (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.