Abstract
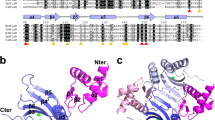
We have determined the high resolution NMR solution structure of the novel DNA binding domain of the Bacillus subtilis transition state regulator AbrB. Comparisons of the AbrB DNA binding domain with DNA binding proteins of known structure show that it is a member of a completely novel class of DNA recognition folds that employs a dimeric topology for cellular function. This new DNA binding conformation is referred to as the looped-hinge helix fold. Sequence homology investigations show that this DNA binding topology is found in other disparately related microbes. Structural analysis of the AbrB DNA binding domain together with bioanalytical and mutagenic data of full length AbrB allows us to construct a general model that describes the genetic regulation properties of AbrB.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$189.00 per year
only $15.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Strauch, M.A. and Hoch, J.A. Transition-state regulators: sentinels of Bacillus subtilis post-exponential gene expression. Mol. Microbiol. 7, 337–342 (1993).
Sonenshein, A.L., Losick R. & Hoch, J.A. Bacillus subtilis and other Gram-positive bacteria (American Society for Microbiology, Washington, D.C.; 1993).
Strauch, M.A. Regulation of Bacillus subtilis gene expression during the transition from exponential growth to stationary phase. Prog. Nucl. Acids Res. Mol. Biol. 46, 121–153 (1993).
Furbass R. & Marahiel, M.A. Mutant analysis of interaction of the Bacillus subtilis transcription regulator AbrB with the antibiotic biosynthesis gene tycA. FEBS Lett. 287,153–160 (1991).
Xu, K., Clark D. & Strauch, M.A. Analysis of abrB mutations, mutant proteins, and why abrB does not utilize a perfect consensus in the −35 region of its σA promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 2621–2626 ( 1996).
Fisher, S.H., Strauch, M.A., Atkinson, M.R. & L.V. Wray, Jr. Modulation of Bacillus subtilis catabolite repression by transition state regulatory protein AbrB. J. Bacteriol. 176,1903–1912 (1994).
Furbass, R., Gocht, M., Zuber, P. & Maraheil, M.A. Interaction of AbrB, a transcriptional regulator from Bacillus subtilis with the promoters of the transition-state activated genes tycA and spoVG . Mol. Gen. Genet. 225, 347– 354 (1991).
Slack, F.J., Mueller, J.P., Strauch, M.A., Mathiopoulos, C. & Sonenshein, A.L. Transcriptional regulation of Bacillus subtilis dipeptide transport operon. Mol. Microbiol. 5, 1915–1925 (1991).
Strauch, M.A. et al. The transition state transcription regulator abrB of Bacillus subtilis is a DNA binding protein. EMBO J. 8, 1615–1621 (1989).
Xu, K. & Strauch, M.A. In vitro selection of optimal AbrB-binding sites: comparison to known in vivo sites indicates flexibility in AbrB binding and recognition of three dimensional DNA structures. Mol. Microbiol. 19, 145–158 (1996).
Cavanagh, J., Fairbrother, W.J., Palmer, A.G. & Skelton, N.J. Protein NMR spectroscopy: principles and practice (Academic Press, Inc., San Diego; 1995).
Skelton, N.J., Aspiras, F., Ogez, J. & Schall, T.J. Proton NMR assignments and solution conformation of RANTES, a chemokine of the C-C type. Biochemistry 34, 5329– 5342 (1995).
Fairbrother, W.J., Reilly, D., Colby, T.J., Hesselgesser, J. & Horuk, R. The solution structure of melanoma growth stimulating activity. J. Mol. Biol. 242, 252–270 (1994).
Nilges, M. A calculation strategy for the structure determination of symmetric dimers by 1H NMR. Proteins 17, 297 –309 (1993).
Laskowski, R.A., Rullman, J.A.C., MacArthur, M.W., Kaptein, R., Thornton, J.M. AQUA and PROCHECK-NMR: programs for checking the quality of protein structure solved by NMR. J. Biol. NMR 8, 477–486 (1996).
Brunger, A.T. X-PLOR version 3.1: a system for X-ray crystallography and NMR (Yale University Press, New Haven; 1993).
Sibanda, B.L., Blundell, T.L. & Thornton, J.M. Conformation of β-hairpins in protein structures. J. Mol. Biol. 206, 759– 777 (1989).
Strauch, M.A. In vitro binding affinity of the Bacillus subtilis AbrB protein to six different DNA target regions. J. Bacteriol. 177, 4532–4536 (1995).
Grzesiek, S. et al. The solution structure of HIV-1 Nef reveals an unexpected fold and permits delineation of the binding surface for the SH3 domain of Hck tyrosine protein kinase. Nature Struct. Biol. 3 , 340–345 (1996).
Foster, M.P. et al. Chemical shift as a probe of molecular interfaces: NMR studies of DNA binding by the three amino-terminal zinc finger domains from transcription factor IIIA. J. Biol. NMR 12, 51– 71 (1998).
Madej, T., Gibrat, J-F. & Bryant, S.J. Threading a database of protein cores. Proteins 23, 356–359 ( 1995).
Holm, L. & Sander, C. Protein structure comparison by alignment of distance matrices. J. Mol. Biol. 223 , 123–138 (1993).
Veenstra, T.D. et al. Metal mediated sterol receptor-DNA complex association and dissociation determined by electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Nature Biotechnol. 16, 262–266 (1998).
Loo, J. Studying noncovalent protein complexes by electrospray ionization massspectrometry . Mass Spec. Rev. 16, 1– 23 (1997).
Strauch, M.A. et al. The transition state transcription regulator AbrB of Bacillus subtilis is autoregulated during vegetative growth. Mol. Microbiol. 3, 1203–1209 ( 1989)
O'Reilly, M. & Devine, K.M. Expression of AbrB, a transition state regulator from Bacillus subtilis, is growth phase dependent in a manner resembling that of Fis, the nucleoid binding protein from Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 179, 522–529 (1997).
Bagyan, I., Hobot J. & Cutting, S. A compartmentalized regulator of developmental gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 178, 4500–4507 (1996).
Kobayashi, K. et al. Analysis of a suppressor mutation ssb (kinC) of sur0B20 (spo0A) mutation in Bacillus subtilis reveals that kinC encodes a histidine protein kinase. J. Bacteriol. 177, 176–182 ( 1995).
The Institute for Genomic Research. Preliminary sequence data acquisition http://www.tigr.org
Huang, X. & Helmann, J.D. Identification of target promoters for the Bacillus subtilis σx factor using a consensus-directed search. J. Mol. Biol. 279, 165–173 (1998).
Shaka, A.J., Lee, C.J. & Pines, A. Iterative schemes for bilinear operators: application to spin decoupling. J. Mag. Res. 77, 274 –293 (1988).
Englander, S.W. & Kallenbach, N.R. Hydrogen exchange and structural dynamics of proteins and nucleic acids. Q. Rev. Biophys. 16, 521–655 (1984).
Vuister, G.W. & Bax, A. Quantitative J correlation: a new approach for measuring homonuclear three-bond J (HN-Hα) coupling constants in 15N-enriched proteins . J. Am. Chem. Soc. 115, 7772– 7777 (1993).
Archer, S.J., Ikura, M., Torchia, D.A. & Bax, A. An alternative 3D NMR technique for correlating backbone 15N with side chain Hβ resonances in larger proteins. J. Mag. Res. 95, 636–641 ( 1991).
Klein, W., Winkelmann, D., Hahn, M., Weber, T. & Marahiel, M.A. Molecular characterization of the transition state regulator AbrB from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1493, 82–90 (2000).
Vaughn, J.L., Feher, V.A., Bracken, C. & Cavanagh, J. The DNA-binding domain in the Bacillus subtilis transition-state regulator AbrB employs significant motion for promiscuous DNA recognition. J. Mol. Biol. in the press.
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Schaak, J. Osterhout, and R. Cunningham for helpful discussions. We are also indebted to K. Xu for providing purified wild type AbrB protein for the initial phases of this study. N. Skelton generously provided analytical scripts and insightful discussion. This work was supported by grants to J.C. from NIH and the Army Research Office.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaughn, J., Feher, V., Naylor, S. et al. Novel DNA binding domain and genetic regulation model of Bacillus subtilis transition state regulator AbrB. Nat Struct Mol Biol 7, 1139–1146 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/81999
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/81999
This article is cited by
-
Engineering of global transcription factors in Bacillus, a genetic tool for increasing product yields: a bioprocess overview
World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology (2023)
-
Applying a riboregulator as a new chromosomal gene regulation tool for higher glycogen production in Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2017)
-
Thermodynamic and molecular analysis of the AbrB-binding sites within the phyC-region of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB45
Molecular Genetics and Genomics (2012)
-
Mathematical Modelling of the Sporulation-Initiation Network in Bacillus Subtilis Revealing the Dual Role of the Putative Quorum-Sensing Signal Molecule PhrA
Bulletin of Mathematical Biology (2011)
-
Prokaryotic toxin–antitoxin stress response loci
Nature Reviews Microbiology (2005)