Abstract
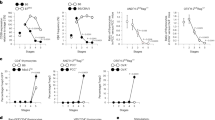
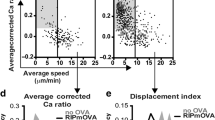
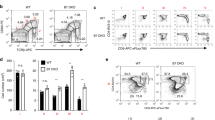
Despite accumulating evidence that regulatory T cells play a crucial role in preventing autoimmunity, the processes underlying their generation during immune repertoire formation are unknown. We show here that interactions with a single self-peptide can induce thymocytes that bear an autoreactive T cell receptor (TCR) to undergo selection to become CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Selection of CD4+CD25+ thymocytes appears to require a TCR with high affinity for a self peptide because thymocytes that bear TCRs with low affinity do not undergo selection into this pathway. Our findings indicate that specificity for self-peptides directs the selection of CD4+CD25+ regulatory thymocytes by a process that is distinct from positive selection and deletion.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sebzda, E. et al. Selection of the T cell repertoire. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17, 829–874 (1999).
Hogquist, K. A. et al. Identification of a naturally occurring ligand for thymic positive selection. Immunity 6, 389–399 (1997).
Nakano, N., Rooke, R., Benoist, C. & Mathis, D. Positive selection of T cells induced by viral delivery of neopeptides to the thymus. Science 275, 678–683 (1997).
Pawlowski, T., Elliott, J. D., Loh, D. Y. & Staerz, U. D. Positive selection of T lymphocytes on fibroblasts. Nature 364, 642–645 (1993).
Williams, C. B. et al. A kinetic threshold between negative and positive selection based on the longevity of the T cell receptor-ligand complex. J. Exp. Med. 189, 1531–1544 (1999).
Hogquist, K. A. et al. T cell receptor antagonist peptides induce positive selection. Cell 76, 17–27 (1994).
Jameson, S. C., Hogquist, K. A. & Bevan, M. J. Specificity and flexibility in thymic selection. Nature 369, 750–752 (1994).
Ashton-Rickardt, P. G. et al. Evidence for a differential avidity model of T cell selection in the thymus. Cell 76, 651–663 (1994).
Sebzda, E. et al. Positive and negative thymocyte selection induced by different concentrations of a single peptide. Science 263, 1615–1618 (1994).
Spain, L. M. & Berg, L. J. Developmental regulation of thymocyte susceptibility to deletion by “self”-peptide. J. Exp. Med. 176, 213–223 (1992).
Itoh, M. et al. Thymus and autoimmunity: production of CD25+CD4+ naturally anergic and suppressive T cells as a key function of the thymus in maintaining immunologic self-tolerance. J. Immunol. 162, 5317–5326 (1999).
Suri-Payer, E., Amar, A. Z., Thornton, A. M. & Shevach, E. M. CD4+CD25+ T cells inhibit both the induction and effector function of autoreactive T cells and represent a unique lineage of immunoregulatory cells. J. Immunol. 160, 1212–1218 (1998).
Takahashi, T. et al. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by CD25+CD4+ naturally anergic and suppressive T cells: induction of autoimmune disease by breaking their anergic/suppressive state. Int. Immunol. 10, 1969–1980 (1998).
Thornton, A. M. & Shevach, E. M. CD4+CD25+ immunoregulatory T cells suppress polyclonal T cell activation in vitro by inhibiting interleukin 2 production. J. Exp. Med. 188, 287–296 (1998).
Jordan, M. S., Riley, M. P., von Boehmer, H. & Caton, A. J. Anergy and suppression regulate CD4+ T cell responses to a self peptide. Eur. J. Immunol. 30, 136–144 (2000).
Kirberg, J. et al. Thymic selection of CD8+ single positive cells with a class II major histocompatibility complex-restricted receptor. J. Exp. Med. 180, 25–34 (1994).
Asano, M., Toda, M., Sakaguchi, N. & Sakaguchi, S. Autoimmune disease as a consequence of developmental abnormality of a T cell subpopulation. J. Exp. Med. 184, 387–396 (1996).
Riley, M. P. et al. Graded deletion and virus-induced activation of autoreactive CD4+ T Cells. J. Immunol. 165, 4870–4876 (2000).
Brandle, D. et al. Regulation of RAG-1 and CD69 expression in the thymus during positive and negative selection. Eur. J. Immunol. 24, 145–151 (1994).
Dutz, J. P., Ong, C. J., Marth, J. & Teh, H. S. Distinct differentiative stages of CD4+CD8+ thymocyte development defined by the lack of coreceptor binding in positive selection. J. Immunol. 154, 2588–2599 (1995).
Azzam, H. S. et al. CD5 expression is developmentally regulated by T cell receptor (TCR) signals and TCR avidity. J. Exp. Med. 188, 2301–2311 (1998).
Merkenschlager, M. et al. How many thymocytes audition for selection? J. Exp. Med. 186, 1149–1158 (1997).
Haberman, A. M., Moller, C., McCreedy, D. & Gerhard, W. U. A large degree of functional diversity exists among helper T cells specific for the same antigenic site of influenza hemagglutinin. J. Immunol. 145, 3087–3094 (1990).
Cerasoli, D. M., Riley, M. P., Shih, F. F. & Caton, A. J. Genetic basis for T cell recognition of a major histocompatibility complex class II-restricted neo-self peptide. J. Exp. Med. 182, 1327–1336 (1995).
Kouskoff, V. et al. A vector driving the expression of foreign cDNAs in the MHC class II-positive cells of transgenic mice. J. Immunol. Methods 166, 287–291 (1993).
Bevan, M. J., Hogquist, K. A. & Jameson, S. C. Selecting the T cell receptor repertoire. Science 264, 796–797 (1994).
Weber, S. et al. Specific low-affinity recognition of major histocompatibility complex plus peptide by soluble T-cell receptor. Nature 356, 793–796 (1992).
Hogquist, K. A., Jameson, S. C. & Bevan, M. J. Strong agonist ligands for the T cell receptor do not mediate positive selection of functional CD8+ T cells. Immunity 3, 79–86 (1995).
Girao, C., Hu, Q., Sun, J. & Ashton-Rickardt, P. G. Limits to the differential avidity model of T cell selection in the thymus. J. Immunol. 159, 4205–4211 (1997).
Laufer, T. M. et al. Unopposed positive selection and autoreactivity in mice expressing class II MHC only on thymic cortex. Nature 383, 81–85 (1996).
Schonrich, G., Momburg, F., Hammerling, G. J. & Arnold, B. Anergy induced by thymic medullary epithelium. Eur. J. Immunol. 22, 1687–1691 (1992).
Modigliani, Y. et al. Lymphocytes selected in allogeneic thymic epithelium mediate dominant tolerance toward tissue grafts of the thymic epithelium haplotype. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 7555–7559 (1995).
Seddon, B. & Mason, D. Peripheral autoantigen induces regulatory T cells that prevent autoimmunity. J. Exp. Med. 189, 877–882 (1999).
Shevach, E. M. Regulatory T cells in autoimmunity. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18, 423–449 (2000).
Caton, A. J. et al. Activation and negative selection of functionally distinct subsets of antibody-secreting cells by influenza hemagglutinin as a viral and a neo-self antigen. J. Exp. Med. 183, 13–26 (1996).
Cerasoli, D. M. et al. Low avidity recognition of a class II-restricted neo-self peptide by virus-specific T cells. Int. Immunol. 7, 935–945 (1995).
Shih, F. F., Cerasoli, D. M. & Caton, A. J. A major T cell determinant from the influenza virus hemagglutinin (HA) can be a cryptic self peptide in HA transgenic mice. Int. Immunol. 9, 249–261 (1997).
Kouskoff, V., Signorelli, K., Benoist, C. & Mathis, D. Cassette vectors directing expression of T cell receptor genes in transgenic mice. J. Immunol. Methods 180, 273–280 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank H. M. Guay and C. L. Iacocca for assistance; Jeffrey Faust for cell sorting; the University of Pennsylvania Flow Cytometry and Cell Sorting Facility for help with five-color flow cytometry; and M. P. Riley, J. A. Punt and T. M. Laufer for helpful discussions. Supported by National Institutes of Health grants AI24541, CA10815, 5T32AR07442 and 5T32EY07131.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jordan, M., Boesteanu, A., Reed, A. et al. Thymic selection of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells induced by an agonist self-peptide. Nat Immunol 2, 301–306 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/86302
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/86302
This article is cited by
-
Human thymic putative CD8αα precursors exhibit a biased TCR repertoire in single cell AIRR-seq
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Role of peripheral immune cells in spinal cord injury
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
Treg plasticity and human diseases
Inflammation Research (2023)
-
Proteomics reveals unique identities of human TGF-β-induced and thymus-derived CD4+ regulatory T cells
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Regulatory T cells in rheumatoid arthritis: functions, development, regulation, and therapeutic potential
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2022)