Abstract
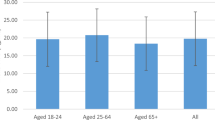
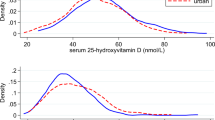
Although some evidence suggests a protective role of vitamin D against breast cancer, epidemiological findings are inconsistent. The current study investigated the relation of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25(OH)D) levels with mammographic density. Baseline serum samples from 182 premenopausal women including 67 Caucasians and 74 Asians from a nutritional trial were analyzed for 25(OH)D. Mammographic density was assessed using a computer-assisted method. Serum 25(OH)D was not associated with mammographic density after adjustment for confounders (body mass index (BMI), age at mammogram, Asian ethnicity, age at first birth, parity and age at menarche). 25(OH)D levels were significantly lower in Asians than in Caucasians, but no significant ethnic differences in mammographic density were observed after adjusting for BMI. Although the current results indicate that serum 25(OH)D levels were not associated with mammographic density among premenopausal women, a possible protective effect of vitamin D against breast cancer may be mediated through other pathways.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bérubé S, Diorio C, Masse B, Hebert-Croteau N, Byrne C, Cote G et al. (2005). Vitamin D and calcium intakes from food or supplements and mammographic breast density. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 14, 1653–1659.
Bérubé S, Diorio C, Verhoek-Oftedahl W, Brisson J (2004). Vitamin D, calcium, and mammographic breast densities. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 13, 1466–1472.
Boyd NF, Lockwood GA, Byng JW, Tritchler DL, Yaffe MJ (1998). Mammographic densities and breast cancer risk. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 7, 1133–1144.
Brisson J, Berube S, Diorio C, Sinotte M, Pollak M, Masse B (2007). Synchronized seasonal variations of mammographic breast density and plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin d. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 16, 929–933.
Byng JW, Boyd NF, Fishell E, Jong RA, Yaffe MJ (1994). The quantitative analysis of mammographic densities. Phys Med Biol 39, 1629–1638.
Cui Y, Rohan TE (2006). Vitamin D, calcium, and breast cancer risk: a review. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15, 1427–1437.
Knight JA, Vachon CM, Vierkant RA, Vieth R, Cerhan JR, Sellers TA (2006). No association between 25-hydroxyvitamin D and mammographic density. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 15, 1988–1992.
Lowe L, Hansen CM, Senaratne S, Colston KW (2003). Mechanisms implicated in the growth regulatory effects of vitamin D compounds in breast cancer cells. Recent results. Cancer Res 164, 99–110.
Maskarinec G, Takata Y, Franke AA, Williams AE, Murphy SP (2004). A 2-year soy intervention in premenopausal women does not change mammographic densities. J Nutr 134, 3089–3094.
Mishra G, McCormack V, Kuh D, Hardy R, Stephen A, dos Santos Silva I (2008). Dietary calcium and vitamin D intakes in childhood and throughout adulthood and mammographic density in a British birth cohort. Br J Cancer 99, 1539–1543.
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the National Institutes of Health grants R03CA130061 and S10RR020890. The original study was supported by NCI grant R01CA80843.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chai, W., Maskarinec, G. & Cooney, R. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels and mammographic density among premenopausal women in a multiethnic population. Eur J Clin Nutr 64, 652–654 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2010.36
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ejcn.2010.36
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Vitamin D and Reduction of Breast Cancer Risk
Current Breast Cancer Reports (2015)
-
Premenopausal plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D, mammographic density, and risk of breast cancer
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2015)
-
Plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 is associated with decreased risk of postmenopausal breast cancer in whites: a nested case–control study in the multiethnic cohort study
BMC Cancer (2014)
-
Mammographic density and serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels
Nutrition & Metabolism (2014)
-
A global representation of vitamin D status in healthy populations
Archives of Osteoporosis (2012)