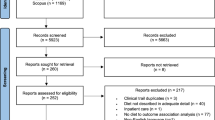
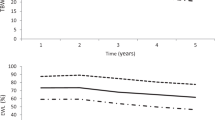
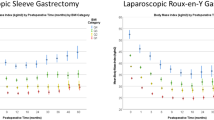
Abstract
Studies of lifestyle advice and dietary intervention show that although moderate, clinically significant weight loss is achievable and results in concomitant improvements in comorbidities, it is invariably transient and recidivism is almost universal. Pharmacotherapeutic options do show promise but are currently inadequate to address many obesity-associated comorbidities. Bariatric surgery consistently results in considerable improvement in weight, alongside a remarkable amelioration in comorbid conditions. Here we describe the physiology of energy balance and the putative mechanisms of change in weight set point following bariatric surgical procedures such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and adjustable gastric banding.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Flegal KM . Epidemiologic aspects of overweight and obesity in the United States. Physiol Behav 2005; 86: 599–602.
Bray GA . Obesity: a time bomb to be defused. Lancet 1998; 352: 160–161.
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ, Flegal KM . Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA 2006; 295: 1549–1555.
De Panfilis C, Cero S, Torre M, Salvatore P, Dall’Aglio E, Adorni A et al. Changes in body image disturbance in morbidly obese patients 1 year after laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Obes Surg 2007; 17: 792–799.
House of Commons Health Select Committee. Obesity—Third Report of Session 2003–2004 Vol 1, 27 May 2004.
Rennie KL, Jebb SA . Prevalence of obesity in Great Britain. Obes Rev 2005; 6: 11–12.
Yanovski S, Yanovski J . Obesity. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 591–602.
Padwal RS, Majumdar SR . Drug treatments for obesity: orlistat, sibutramine, and rimonabant. Lancet 2007; 369: 71–77.
Buchwald H, Avidor Y, Braunwald E, Jensen MD, Pories W, Fahrbach K et al. Bariatric surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA 2004; 292: 1724–1737.
Adams TD, Gress RE, Smith SC, Halverson RC, Simper SC, Rosamond WD et al. Long-term mortality after gastric bypass surgery. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 753–761.
Sjostrom L, Narbro K, Sjostrom CD, Karason K, Larsson B, Wedel H et al. Effects of bariatric surgery on mortality in Swedish obese subjects. N Engl J Med 2007; 357: 741–752.
Cummings DE, Overduin J, Foster-Schubert KE . Gastric bypass for obesity: mechanisms of weight loss and diabetes resolution. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 2608–2615.
Huerta S, Kohan D, Siddiqui A, Anthony T, Livingston EH . Assessment of comorbid conditions in veteran patients after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Am J Surg 2007; 194: 48–52.
McCloskey CA, Ramani GV, Mathier MA, Schauer PR, Eid GM, Mattar SG et al. Bariatric surgery improves cardiac function in morbidly obese patients with severe cardiomyopathy. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2007; 3: 503–507.
Titi M, Jenkins JT, Modak P, Galloway DJ . Quality of life and alteration in comorbidity following laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Postgrad Med J 2007; 83: 487–491.
Hawkins SC, Osborne A, Finlay IG, Alagaratnam S, Edmond JR, Welbourn R . Paid work increases and state benefit claims decrease after bariatric surgery. Obes Surg 2007; 17: 434–437.
Rubino F . Bariatric surgery: effects on glucose homeostasis. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care 2006; 9: 497–507.
Morton GJ, Cummings DE, Baskin DG, Barsh GS, Schwartz MW . Central nervous system control of food intake and body weight. Nature 2006; 443: 289–295.
Friedman JM, Halaas JL . Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature 1998; 395: 763–770.
Cummings DE . Ghrelin and the short- and long-term regulation of appetite and body weight. Physiol Behav 2006; 89: 71–84.
Purnell JQ, Cummings D, Weigle DS . Changes in 24-h area-under-the-curve ghrelin values following diet-induced weight loss are associated with loss of fat-free mass, but not with changes in fat mass, insulin levels or insulin sensitivity. Int J Obes (Lond) 2007; 31: 385–389.
Druce MR, Wren AM, Park AJ, Milton JE, Patterson M, Frost G et al. Ghrelin increases food intake in obese as well as lean subjects. Int J Obes (Lond) 2005; 29: 1130–1136.
le Roux CW, Batterham RL, Aylwin SJ, Patterson M, Borg CM, Wynne KJ et al. Attenuated peptide YY release in obese subjects is associated with reduced satiety. Endocrinology 2006; 147: 3–8.
Ugleholdt R, Zhu X, Deacon CF, Orskov C, Steiner DF, Holst JJ . Impaired intestinal proglucagon processing in mice lacking prohormone convertase 1. Endocrinology 2004; 145: 1349–1355.
Drucker DJ . The biology of incretin hormones. Cell Metab 2006; 3: 153–165.
Wynne K, Park AJ, Small CJ, Patterson M, Ellis SM, Murphy KG et al. Subcutaneous oxyntomodulin reduces body weight in overweight and obese subjects: a double-blind, randomized, controlled trial. Diabetes 2005; 54: 2390–2395.
Powley TL, Chi MM, Schier LA, Phillips RJ . Obesity: should treatments target visceral afferents? Physiol Behav 2005; 86: 698–708.
Sobocki J, Fourtanier G, Estany J, Otal P . Does vagal nerve stimulation affect body composition and metabolism? Experimental study of a new potential technique in bariatric surgery. Surgery 2006; 139: 209–216.
Gibbs J, Young RC, Smith GP . Cholecystokinin decreases food intake in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol 1973; 84: 488–495.
Moran TH . Cholecystokinin and satiety: current perspectives. Nutrition 2000; 16: 858–865.
Deitel M, Shikora SA . The development of the surgical treatment of morbid obesity. J Am Coll Nutr 2002; 21: 365–371.
Santry H, Gillen D, Lauderdale D . Trends in bariatric surgical procedures. JAMA 2005; 294: 1909–1917.
Biertho L, Steffen R, Ricklin T, Horber F, Pomp A, Inabnet W et al. Laparoscopic gastric bypass versus laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding: a comparative study of 1200 cases. J Am Coll Surg 2003; 197: 536–545.
Brolin RE, LaMarca LB, Kenler HA, Cody RP . Malabsorptive gastric bypass in patients with superobesity. J Gastrointest Surg 2002; 6: 195–203; discussion 204–205.
MacLean LD, Rhode BM, Nohr CW . Long- or short-limb gastric bypass? J Gastrointest Surg 2001; 5: 525–530.
Griffen WO, Young VL, Stevenson CC . A prospective comparison of gastric and jejunoileal bypass procedures for morbid obesity. Ann Surg 1977; 186: 500–509.
Pilkington TR, Gazet JC, Ang L, Kalucy RS, Crisp AH, Day S . Explanations for weight loss after ileojejunal bypass in gross obesity. Br Med J 1976; 1: 1504–1505.
Elliot K . Nutritional considerations after bariatric surgery. Crit Care Nurs Q 2003; 26: 133–138.
Yamamoto H, Mori T, Tsuchihashi H, Akabori H, Naito H, Tani T . A possible role of GLP-1 in the pathophysiology of early dumping syndrome. Dig Dis Sci 2005; 50: 2263–2267.
Pappas TN . Physiological satiety implications of gastrointestinal antiobesity surgery. Am J Clin Nutr 1992; 55: 571S–572S.
Howard L, Malone M, Michalek A, Carter J, Alger S, Van Woert J . Gastric bypass and vertical banded gastroplasty–a prospective randomized comparison and 5-year follow-up. Obes Surg 1995; 5: 55–60.
Kenler HA, Brolin RE, Cody RP . Changes in eating behavior after horizontal gastroplasty and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass. Am J Clin Nutr 1990; 52: 87–92.
Cummings DE, Weigle DS, Frayo RS, Breen PA, Ma MK, Dellinger EP et al. Plasma ghrelin levels after diet-induced weight loss or gastric bypass surgery. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 1623–1630.
Morinigo R, Casamitjana R, Moize V, Lacy AM, Delgado S, Gomis R et al. Short-term effects of gastric bypass surgery on circulating ghrelin levels. Obes Res 2004; 12: 1108–1116.
Stoeckli R, Chanda R, Langer I, Keller U . Changes of body weight and plasma ghrelin levels after gastric banding and gastric bypass. Obes Res 2004; 12: 346–350.
Vendrell J, Broch M, Vilarrasa N, Molina A, Gomez JM, Gutierrez C et al. Resistin, adiponectin, ghrelin, leptin, and proinflammatory cytokines: relationships in obesity. Obes Res 2004; 12: 962–971.
McLaughlin T, Abbasi F, Lamendola C, Frayo RS, Cummings DE . Plasma ghrelin concentrations are decreased in insulin-resistant obese adults relative to equally obese insulin-sensitive controls. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2004; 89: 1630–1635.
Korner J, Bessler M, Cirilo LJ, Conwell IM, Daud A, Restuccia NL et al. Effects of Roux-en-Y gastric bypass surgery on fasting and postprandial concentrations of plasma ghrelin, peptide YY, and insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 359–365.
le Roux CW, Vincent RP, Murphy KG, Borg CM, Ghatei MA, Bloom SR . Supraphysiological doses of PYY are associated with nausea. Ann Clin Biochem 2008; 45: 93–95.
le Roux CW, Aylwin SJ, Batterham RL, Borg CM, Coyle F, Prasad V et al. Gut hormone profiles following bariatric surgery favor an anorectic state, facilitate weight loss, and improve metabolic parameters. Ann Surg 2006; 243: 108–114.
Sloth B, Holst JJ, Flint A, Gregersen NT, Astrup A . Effects of PYY1-36 and PYY3-36 on appetite, energy intake, energy expenditure, glucose and fat metabolism in obese and lean subjects. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2007; 292: E1062–E1068.
Tichansky DS, Boughter Jr JD, Madan AK . Taste change after laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Surg Obes Relat Dis 2006; 2: 440–444.
Scruggs DM, Buffington C, Cowan Jr GS . Taste acuity of the morbidly obese before and after gastric bypass surgery. Obes Surg 1994; 4: 24–28.
le Roux CW, Neary NM, Halsey TJ, Small CJ, Martinez-Isla AM, Ghatei MA et al. Ghrelin does not stimulate food intake in patients with surgical procedures involving vagotomy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 4521–4524.
Abbott CR, Monteiro M, Small CJ, Sajedi A, Smith KL, Parkinson JR et al. The inhibitory effects of peripheral administration of peptide YY(3–36) and glucagon-like peptide-1 on food intake are attenuated by ablation of the vagal–brainstem–hypothalamic pathway. Brain Res 2005; 1044: 127–131.
Dixon AF, Dixon JB, O’Brien PE . Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding induces prolonged satiety: a randomized blind crossover study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2005; 90: 813–819.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tadross, J., le Roux, C. The mechanisms of weight loss after bariatric surgery. Int J Obes 33 (Suppl 1), S28–S32 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2009.14
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2009.14
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The Importance of the Microbiome in Bariatric Surgery: a Systematic Review
Obesity Surgery (2019)
-
Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass Is More Effective than Sleeve Gastrectomy in Improving Postprandial Glycaemia and Lipaemia in Non-diabetic Morbidly Obese Patients: a Short-term Follow-up Analysis
Obesity Surgery (2018)
-
The role of bariatric surgery to treat diabetes: current challenges and perspectives
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2017)