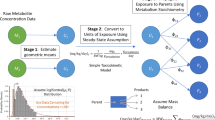
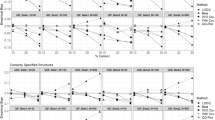
Abstract
A conceptual/computational framework for exposure reconstruction from biomarker data combined with auxiliary exposure-related data is presented, evaluated with example applications, and examined in the context of future needs and opportunities. This framework employs physiologically based toxicokinetic (PBTK) modeling in conjunction with numerical “inversion” techniques. To quantify the value of different types of exposure data “accompanying” biomarker data, a study was conducted focusing on reconstructing exposures to chlorpyrifos, from measurements of its metabolite levels in urine. The study employed biomarker data as well as supporting exposure-related information from the National Human Exposure Assessment Survey (NHEXAS), Maryland, while the MENTOR-3P system (Modeling ENvironment for TOtal Risk with Physiologically based Pharmacokinetic modeling for Populations) was used for PBTK modeling. Recently proposed, simple numerical reconstruction methods were applied in this study, in conjunction with PBTK models. Two types of reconstructions were studied using (a) just the available biomarker and supporting exposure data and (b) synthetic data developed via augmenting available observations. Reconstruction using only available data resulted in a wide range of variation in estimated exposures. Reconstruction using synthetic data facilitated evaluation of numerical inversion methods and characterization of the value of additional information, such as study-specific data that can be collected in conjunction with the biomarker data. Although the NHEXAS data set provides a significant amount of supporting exposure-related information, especially when compared to national studies such as the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES), this information is still not adequate for detailed reconstruction of exposures under several conditions, as demonstrated here. The analysis presented here provides a starting point for introducing improved designs for future biomonitoring studies, from the perspective of exposure reconstruction; identifies specific limitations in existing exposure reconstruction methods that can be applied to population biomarker data; and suggests potential approaches for addressing exposure reconstruction from such data.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ablonczy Z., Lukacs A., and Papp E. Application of the maximum entropy method to absorption kinetic rate processes. Biophys Chem 2003: 104 (1): 249–258.
Abramov S., Adamovich A., Inyukhin A., Moskovsky A., Roganov V., Shevchuk E., Shevchuk Y., and Vodomerov A. OpenTS: an outline of dynamic parallelization approach. Parallel Comput Technol 2005: 3606: 303–312.
ACM. Software from the Transactions on Mathematical Software (TOMS) 2006: http://www.netlib.org/toms/.
Albertini R., Bird M., Doerrer N., Needham L., Robison S., Sheldon L., and Zenick H. The use of biomonitoring data in exposure and human health risk assessments. Environ Health Perspect 2006: 114 (11): 1755–1762.
Allen B.C., Hack C.E., and Clewell H.J. Use of Markov chain Monte Carlo analysis with a physiologically-based pharmacokinetic model of methylmercury to estimate exposures in US women of childbearing age. Risk Anal 2007: 27 (4): 947–959.
Anderson E. LAPACK User's Guide. Software, Environments, Tools. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia, 1999: xxi: 407 p.
Armbruster B., Hamilton R.J., and Kuehl A.K. Spectrum reconstruction from dose measurements as a linear inverse problem. Phys Med Biol 2004: 49 (22): 5087–5099.
Aster R.C., Thurber C.H., and Borchers B. Parameter Estimation and Inverse Problems. International Geophysics Series. v. 90. Elsevier Academic Press, Amsterdam, Boston, 2005: xii: 301 p.
ATSDR. Toxicological Profile for Chlorpyrifos. Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry, Division of Toxicology, Atlanta, GA, 1997.
Bai J.P.F., Utis A., Crippen G., He H.D., Fischer V., Tullman R., Yin H.Q., Hsu C.P., Jiang L., and Hwang K.K. Use of classification regression tree in predicting oral absorption in humans. J Chem Inf Comput Sci 2004: 44 (6): 2061–2069.
Baker J.R., Edwards R.J., Lasker J.M., Moore M.R., and Satarug S. Renal and hepatic accumulation of cadmium and lead in the expression of CYP4F2 and CYP2E1. Toxicol Lett 2005: 159 (2): 182–191.
Balakin K.V., Ivanenkov Y.A., Savchuk N.P., Ivashchenko A.A., and Ekins S. Comprehensive computational assessment of ADME properties using mapping techniques. Curr Drug Discov Technol 2005: 2 (2): 99–113.
Balakrishnan S., Roy A., Ierapetritou M.G., Flach G.P., and Georgopoulos P.G. Uncertainty reduction and characterization for complex environmental fate and transport models: an empirical Bayesian framework incorporating the stochastic response surface method. Water Resour Res 2003: 39 (12): 1350.
Ballatori N. Transport of toxic metals by molecular mimicry. Environ Health Perspect 2002: 110 (Suppl. 5): 689–694.
Barr D.B., and Angerer J. Potential uses of biomonitoring data: a case study using the organophosphorus pesticides chlorpyrifos and malathion. Environ Health Perspect 2006: 114 (11): 1763–1769.
Barr D.B., Wilder L.C., Caudill S.P., Gonzalez A.J., Needham L.L., and Pirkle J.L. Urinary creatinine concentrations in the U.S. population: implications for urinary biologic monitoring measurements. Environ Health Perspect 2005: 113 (2): 192–200.
Beal S.L. Commentary on significance levels for covariate effects in NONMEM. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 2002: 29 (4): 403–410.
Bender R., and Heinemann L. Fitting nonlinear-regression models with correlated errors to individual pharmacodynamic data using SAS software. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 1995: 23 (1): 87–100.
Bischof C., Khademi P., Mauer A., and Carle A. ADIFOR 2.0: automatic differentiation of Fortran 77 programs. IEEE Comput Sci Eng 1996: 3 (3): 18–32.
Bischof C.H., Roh L., and Mauer-oats A.J. ADIC: an extensible automatic differentiation tool for ANSI-C. Software Pract Ex 1997: 27 (12): 1427–1456.
Blazewicz J., Lukasiak P., and Milostan M. Application of tabu search strategy for finding low energy structure of protein. Artif Intell Med 2005: 35 (1–2): 135–145.
Bois F., Maszle D., Revzan K., Tillier S., and Yuan Z. MCSim User Manual 2007: http://fredomatic.free.fr/mcsim.html.
Bois F.Y. Statistical analysis of Fisher et al. PBPK model of trichloroethylene kinetics. Environ Health Perspect 2000: 108: 275–282.
Bourne D.W. BOOMER, a simulation and modeling program for pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic data analysis. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 1989: 29 (3): 191–195.
Breiman L. Classification and Regression Trees. The Wadsworth Statistics/Probability Series. Wadsworth International Group, Belmont, CA, 1984: x: 358 p.
Bressler J.P., Olivi L., Cheong J.H., Kim Y., and Bannona D. Divalent metal transporter 1 in lead and cadmium transport. Ann NY Acad Sci 2004: 1012: 142–152.
Carrington C.D., and Bolger M.P. An exposure assessment for methylmercury from seafood for consumers in the United States. Risk Anal 2002: 22 (4): 689–699.
Castorina R., Bradman A., McKone T.E., Barr D.B., Harnly M.E., and Eskenazi B. Cumulative organophosphate pesticide exposure and risk assessment among pregnant women living in an agricultural community: a case study from the CHAMACOS cohort. Environ Health Perspect 2003: 111 (13): 1640–1648.
CDC. Third National Report on Human Exposure to Environmental Chemicals. NCEH Pub. no. 05-0570, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, GA, 2005: http://www.cdc.gov/exposurereport/.
Cherkassky V., and Gehring D. Comparison of adaptive methods for function estimation from samples. IEEE Trans Neural Netw 1996: 7 (4): 969–984.
Chow H.H., Tolle K.M., Roe D.J., Elsberry V., and Chen H.C. Application of neural networks to population pharmacokinetic data analysis. J Pharm Sci 1997: 86 (7): 840–845.
Christakos G., Bogaert P., and Serre M.L. Temporal GIS: Advanced Functions for Field-Based Applications. Springer, Berlin, New York, 2001: xii: 217 p.
Clarke C.J.S., and Janday B.S. The solution of the biomagnetic inverse problem by maximum statistical entropy. Inverse Probl 1989: 5 (4): 483.
Coello C.A.C., and Pulido G.T. Multiobjective structural optimization using a microgenetic algorithm. Structural and Multidisciplinary Optimization 2005: 30 (5): 388–403.
Conway G.R., Glass N.R., and Wilcox J.C. Fitting nonlinear models to biological data by Marquardt's algorithm. Ecology 1970: 51 (3): 503.
Covington T.R., Gentry P.R., Van Landingham C.B., Andersen M.E., Kester J.E., and Clewell H.J. The use of Markov chain Monte Carlo uncertainty analysis to support a public health goal for perchloroethylene. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 2007: 47 (1): 1–18.
CRAN. CRAN — The Comprehensive R Archive Network 2006: (http://cran.r-project.org/).
Deconinck E., Xu Q.S., Put R., Coomans D., Massart D.L., and Vander Heyden Y. Prediction of gastro-intestinal absorption using multivariate adaptive regression splines. J Pharm Biomed Anal 2005: 39 (5): 1021–1030.
Denison D.G.T., Mallick B.K., and Smith A.F.M. Bayesian MARS. Stat Comput 1998: 8 (4): 337–346.
Dennis J., Gay D., and Walsh R. An adaptive nonlinear least-squares algorithm. ACM Trans Math Softw 1981: 7 (3): 348–368.
Dirksen U., Moghadam K.A., Mambetova C., Esser C., Fuhrer M., and Burdach S. Glutathione S transferase theta 1 gene (GSTT1) null genotype is associated with an increased risk for acquired aplastic anemia in children. Pediatr Res 2004: 55 (3): 466–471.
Dokoumetzidis A., and Aarons L. Propagation of population pharmacokinetic information using a Bayesian approach: comparison with meta-analysis. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 2005: 32 (3–4): 401–418.
Drobna Z., Waters S.B., Walton F.S., LeCluyse E.L., Thomas D.J., and Styblo M. Interindividual variation in the metabolism of arsenic in cultured primary human hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2004: 201 (2): 166–177.
Egeghy P.P., Quackenboss J.J., Catlin S., and Ryan P.B. Determinants of temporal variability in NHEXAS-Maryland environmental concentrations, exposures, and biomarkers. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2005: 15 (5): 388–397.
Elzo M.A. Restricted maximum likelihood procedures for the estimation of additive and nonadditive genetic variances and covariances in multibreed populations. J Anim Sci 1994: 72 (12): 3055–3065.
Engl H.W., Hanke M., and Neubauer A. Regularization of Inverse Problems. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, Boston, 1996: viii: 321 p.
Farquharson C.G., and Oldenburg D.W. A comparison of automatic techniques for estimating the regularization parameter in non-linear inverse problems. Geophys J Int 2004: 156 (3): 411–425.
Flouris A., and Duffy J. Applications of artificial intelligence systems in the analysis of epidemiological data. Eur J Epidemiol 2006: 21 (3): 167.
Friedman J.H., and Meulman J.J. Multiple additive regression trees with application in epidemiology. Stat Med 2003: 22 (9): 1365–1381.
Friedman J.H., and Roosen C.B. An introduction to multivariate adaptive regression splines. Stat Methods Med Res 1995: 4 (3): 197–217.
Friedman J.H., and Stuetzle W. Projection pursuit regression. J Am Stat Assoc 1981: 76 (376): 817.
Gamboa F., and Gassiat E. Bayesian methods and maximum entropy for ill-posed inverse problems. Ann Stat 1997: 25 (1): 328–350.
Gamerman D., and Lopes H.F. Markov Chain Monte Carlo: Stochastic Simulation for Bayesian Inference. Taylor & Francis, Boca Raton, 2006: xvii: 323 p.
Garrick M.D., Dolan K.G., Horbinski C., Ghio A.J., Higgins D., Porubcin M., Moore E.G., Hainsworth L.N., Umbreit J.N., Conrad M.E., Feng L., Lis A., Roth J.A., Singleton S., and Garrick L.M. DMT1: a mammalian transporter for multiple metals. Biometals 2003: 16 (1): 41–54.
Gelman A. Bayesian Data Analysis. Texts in Statistical Science. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton, FL, 2004: xxv: 668 p.
Georgopoulos P.G., Balakrishnan S., Roy A., Isukapalli S., Sasso A., Chien Y.C., and Weisel C.P. A Comparison of Maximum Likelihood Estimation Methods for Inverse Problem Solutions Employing PBPK Modeling with Biomarker Data: Application to Tetrachloroethylene. CCL:2008.01, Computational Chemodynamics Laboratory, EOHSI, Piscataway, NJ, 2008: http://ccl.rutgers.edu/reports/MENTOR3P/CCL_2008-report_Bayesian.pdf.
Georgopoulos P.G., and Lioy P.J. From theoretical aspects of human exposure and dose assessment to computational model implementation: The MOdeling ENvironment for TOtal Risk studies (MENTOR). J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 2006: 9 (6): 457–483.
Georgopoulos P.G., Roy A., and Gallo M.A. Reconstruction of short-term multiroute exposure to volatile organic-compounds using physiologically-based pharmacokinetic models. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 1994: 4 (3): 309–328.
Gilks W.R., Richardson S., and Spiegelhalter D.J. Markov Chain Monte Carlo in Practice. Chapman & Hall, Boca Raton, FL, 1998: xvii: 486 p.
Glover F. Tabu search for nonlinear and parametric optimization (with links to genetic algorithms). Discrete Appl Math 1994: 49 (1–3): 231–255.
Glover F., Kelly J.P., and Laguna M. Genetic algorithms and tabu search — hybrids for optimization. Comput Oper Res 1995: 22 (1): 111–134.
Gobburu J.V.S., and Chen E.P. Artificial neural networks as a novel approach to integrated pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic analysis. J Pharm Sci 1996: 85 (5): 505–510.
Gosselin N.H., Brunet R.C., Carrier G., Bouchard M., and Feeley M. Reconstruction of methylmercury intakes in indigenous populations from biomarker data. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 2006: 16 (1): 19–29.
Goyer R.A. Toxic and essential metal interactions. Annu Rev Nutr 1997: 17: 37–50.
Haber L.T., Maier A., Gentry P.R., Clewell H.J., and Dourson M.L. Genetic polymorphisms in assessing interindividual variability in delivered dose. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 2002: 35 (2 Pt 1): 177–197.
Hansen P.C. Regularization tools: a Matlab package for analysis and solution of discrete ill-posed problems. Numer Algorithms 1994: 6 (1–2): 1–35.
Hashemi R.R., and Young J.F. The prediction of methylmercury elimination half-life in humans using animal data: a neural network/rough sets analysis. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2003: 66 (23): 2227–2252.
Hastie T., Tibshirani R., and Friedman J.H. The Elements of Statistical Learning: Data Mining, Inference, and Prediction: with 200 Full-Color Illustrations. Springer series in statistics. Springer, New York, 2001: xvi: 533 p.
Hays S.M., Becker R.A., Leung H.W., Aylward L.L., and Pyatt D.W. Biomonitoring equivalents: a screening approach for interpreting biomonitoring results from a public health risk perspective. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 2007: 47 (1): 96–109.
Hill Jr R.H., Head S.L., Baker S., Gregg M., Shealy D.B., Bailey S.L., Williams C.C., Sampson E.J., and Needham L.L. Pesticide residues in urine of adults living in the United States: reference range concentrations. Environ Res 1995: 71 (2): 99–108.
Hodgson E. In vitro human phase I metabolism of xenobiotics I: pesticides and related compounds used in agriculture and public health, May 2003. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 2003: 17 (4): 201–206.
Holmes C.C., and Denison D.G.T. Classification with Bayesian MARS. Machine Learn 2003: 50 (1–2): 159–173.
Holmes S.L., Ward R.C., Galambos J.D., and Strickler D.J. A method for optimization of pharmacokinetic models. Toxicol Methods 2000: 10 (1): 41–53.
Hovland P., Norris B., and Smith B. Making automatic differentiation truly automatic: coupling PETSc with ADIC. Future Generat Comput Syst 2005: 21 (8): 1426–1438.
Hristov D., Stavrev P., Sham E., and Fallone B.G. On the implementation of dose-volume objectives in gradient algorithms for inverse treatment planning. Med Phys 2002: 29 (5): 848–856.
ICRP. International Commission on Radiological Protection, 2003. http://www.icrp.org.
Isukapalli S.S., Lioy P.J., and Georgopoulos P.G. Mechanistic modeling of emergency events: assessing impact of hypothetical releases of anthrax. Risk Anal 2008 (in press).
Isukapalli S.S., Roy A., and Georgopoulos P.G. Efficient sensitivity/uncertainty analysis using the combined stochastic response surface method and automated differentiation: application to environmental and biological systems. Risk Anal 2000: 20 (5): 591–602.
Isukapalli S.S., Roy A., and Georgopoulos P.G. Stochastic response surface methods (SRSMs) for uncertainty propagation: application to environmental and biological systems. Risk Anal 1998: 18 (3): 351–363.
Jamshidian M. On algorithms for restricted maximum likelihood estimation. Comput Stat Data Anal 2004: 45 (2): 137–157.
Jitnah N., and Nicholson A. treeNets: a framework for anytime evaluation of belief networks. Qual Quant Pract Reason 1997: 1244: 350–364.
Johansen T.A., and Foss B.A. ORBIT — operating-regime-based modeling and identification toolkit. Control Eng Pract 1998: 6 (10): 1277–1286.
Kaltenbach M.L., and Vistelle R. KINFIT — a non-linear least-squares computer-program for the estimation of pharmacokinetic parameters after intravenous administration. Anticancer Res 1994: 14 (6A): 2375–2377.
Kazarlis S.A., Papadakis S.E., Theocharis J.B., and Petridis V. Microgenetic algorithms as generalized hill-climbing operators for GA optimization. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 2001: 5 (3): 204–217.
Kharche R.V., and Forth S.A. Source transformation for MATLAB automatic differentiation. Computational Science — ICCS 2006, Pt 4, Proceedings 2006, Springer, Berlin, Vol. 3994, pp. 558–565.
LeBlanc M., Moon J., and Kooperberg C. Extreme regression. Biostatistics 2006: 7 (1): 71–84.
Li G.Y., Wang S.W., Rabitz H., Wang S.Y., and Jaffe P. Global uncertainty assessments by high dimensional model representations (HDMR). Chem Eng Sci 2002: 57 (21): 4445–4460.
Lifeline Group. Physiological Parameters for PBPK Modeling Version 1.2 (P3M), 2004. http://www.thelifelinegroup.org/P3M.
Lingjaerde O.C., and Liestol K. Generalized projection pursuit regression. SIAM J Sci Comput 1998: 20 (3): 844–857.
Liu J., and Li M. Finding cancer biomarkers from mass spectrometry data by decision lists. J Comput Biol 2005: 12 (7): 971–979.
Lunn D.J., Best N., Thomas A., Wakefield J., and Spiegelhalter D. Bayesian analysis of population PK/PD models: general concepts and software. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 2002: 29 (3): 271–307.
MacIntosh D.L., Kabiru C., Echols S.L., and Ryan P.B. Dietary exposure to chlorpyrifos and levels of 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol in urine. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2001: 11 (4): 279–285.
Mage D.T., Allen R.H., Gondy G., Smith W., Barr D.B., and Needham L.L. Estimating pesticide dose from urinary pesticide concentration data by creatinine correction in the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES-III). J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2004: 14 (6): 457–465.
Marquardt D.W. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of nonlinear parameters. J Soc Indt Appl Math 1963: 11 (2): 431.
MathWorks Inc.. Matlab, Version 7. Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ, 2006: http://www.mathworks.com.
Mathworks. User's Guide to Genetic Algorithms and Direct Search Toolbox for Matlab, Version 2.0 2006a: http://www.mathworks.com.
Mathworks. User's Guide to Neural Networks Toolbox for Matlab, Version 2.0 2006b: http://www.mathworks.com.
Mathworks. User's Guide to Optimization Toolbox for Matlab, Version 3.0 2006c: http://www.mathworks.com.
Mathworks. User's Guide to Statistics Toolbox for Matlab, Version 5.0 2006d: http://www.mathworks.com.
Meeker J.D., Barr D.B., Ryan L., Herrick R.F., Bennett D.H., Bravo R., and Hauser R. Temporal variability of urinary levels of nonpersistent insecticides in adult men. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2005: 15 (3):271–281.
Merkwirth C. ENTOOL — Ensemble Toolbox for Statistical Learning (Matlab Toolbox) 2006: http://zti.if.uj.edu.pl/~merkwirth/entool.htm.
Messnarz B., Tilg B., Modre R., Fischer G., and Hanser F. A new spatiotemporal regularization approach for reconstruction of cardiac transmembrane potential patterns. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 2004: 51 (2): 273–281.
Meza M.M., Yu L., Rodriguez Y.Y., Guild M., Thompson D., Gandolfi A.J., and Klimecki W.T. Developmentally restricted genetic determinants of human arsenic metabolism: association between urinary methylated arsenic and CYT19 polymorphisms in children. Environ Health Perspect 2005: 113 (6): 775–781.
Mohammad-Djafari A., Giovannelli J.F., Demoment G., and Idier J. Regularization, maximum entropy and probabilistic methods in mass spectrometry data processing problems. Int J Mass Spectrom 2002: 215 (1–3): 175–193.
Moles C.G., Mendes P., and Banga J.R. Parameter estimation in biochemical pathways: a comparison of global optimization methods. Genome Res 2003: 13 (11): 2467–2474.
Moore M.R. A commentary on the impacts of metals and metalloids in the environment upon the metabolism of drugs and chemicals. Toxicol Lett 2004: 148 (3): 153–158.
Morales K.H., Ibrahim J.G., Chen C.J., and Ryan L.M. Bayesian model averaging with applications to benchmark dose estimation for arsenic in drinking water. J Am Stat Assoc 2006: 101 (473): 9–17.
Morgan M.K., Sheldon L.S., Croghan C.W., Jones P.A., Robertson G.L., Chuang J.C., Wilson N.K., and Lyu C.W. Exposures of preschool children to chlorpyrifos and its degradation product 3,5,6-trichloro-2-pyridinol in their everyday environments. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2005: 15 (4): 297–309.
Morozov V.A., and Stessin M. Regularization Methods for Ill-Posed Problems. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, 1993, 257 p.
Moscato P., Mendes A., and Berretta R. Benchmarking a memetic algorithm for ordering microarray data. Biosystems 2007: 88 (1–2): 56–75.
Muzic R.F., and Christian B.T. Evaluation of objective functions for estimation of kinetic parameters. Med Phys 2006: 33 (2): 342–353.
Nair S., and Gratzl M. Deconvolution of concentration recordings at live cell preparations via shape error optimization. Anal Chem 2005: 77 (9): 2875–2881.
Needham L.L., Calafat A.M., and Barr D.B. Uses and issues of biomonitoring. Int J Hyg Environ Health 2007: 210 (3–4): 229–238.
Nestorov I.S., Hadjitodorov S.T., Petrov I., and Rowland M. Empirical versus mechanistic modelling: comparison of an artificial neural network to a mechanistically based model for quantitative structure pharmacokinetic relationships of a homologous series of barbiturates. AAPS Pharmsci 1999: 1 (4): E17.
Netlib. Miscellaneous Approximation Algorithms from Netlib 2006: http://gams.nist.gov/serve.cgi/Package/A/.
NeuroDimension I. Documentation for NeuroSolutions by NeuroDimension Inc. 2006.
NIST. NIST Guide to Available Software: Unconstrained Optimization of a Smooth Multivariate Function, User Provides No Derivatives 2006: http://gams.nist.gov/serve.cgi/Class/G1b1a/.
Nolan R.J., Rick D.L., Freshour N.L., and Saunders J.H. Chlorpyrifos: pharmacokinetics in human volunteers. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 1984: 73 (1): 8–15.
Nordberg M., and Nordberg G.F. Toxicological aspects of metallothionein. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 2000: 46 (2): 451–463.
Nott D.J., Kuk A.Y.C., and Duc H. Efficient sampling schemes for Bayesian MARS models with many predictors. Stat Comput 2005: 15 (2): 93–101.
NRC. Human Biomonitoring for Environmental Chemicals, Committee on Human Biomonitoring for Environmental Toxicants, Board on Environmental Studies and Toxicology, Division on Earth and Life Studies. National Research Council, Washington DC, 2006: http://newton.nap.edu/catalog/11700.html.
Opara J., Primozic S., and Cvelbar P. Prediction of pharmacokinetic parameters and the assessment of their variability in bioequivalence studies by artificial neural networks. Pharm Res 1999: 16 (6): 944–948.
OptTek Systems Inc. OptQuest Engine, 2006. http://www.opttek.com/document.html.
Overgaard R.V., Jonsson N., Tornoe C.W., and Madsen H. Non-linear mixed-effects models with stochastic differential equations: implementation of an estimation algorithm. J Pharmacokinet Pharmacodyn 2005: 32 (1): 85–107.
Paige C.C. Computing the generalized singular value decomposition. SIAM J Sci Stat Comput 1986: 7 (4): 1126–1146.
Pang Y.H., MacIntosh D.L., Camann D.E., and Ryan B. Analysis of aggregate exposure to chlorpyrifos in the NHEXAS-Maryland investigation. Environ Health Perspect 2002: 110 (3): 235–240.
Patrick L. Toxic metals and antioxidants: Part II. The role of antioxidants in arsenic and cadmium toxicity. Altern Med Rev 2003: 8 (2): 106–128.
Pirkle J.L., Sampson E.J., Needham L.L., Patterson D.G., and Ashley D.L. Using biological monitoring to assess human exposure to priority toxicants. Environ Health Perspect 1995: 103 (Suppl. 3): 45–48.
Pohlheim H. GEATbx: Genetic and Evolutionary Algorithm Toolbox for Use with MATLAB Documentation, 2005. http://www.geatbx.com/docu.
Press W.H. Numerical Recipes Code CD-ROM. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England, 2002; 1 CD-ROM. http://www.nr.com/com/storefront.html.
Qu Q., Shore R., Li G., Jin X., Chen L.C., Cohen B., Melikian A.A., Eastmond D., Rappaport S.M., Li H., Rupa D., Waidyanatha S., Yin S., Yan H., Meng M., Winnik W., Kwok E.S., Li Y., Mu R., Xu B., Zhang X., and Li K. Validation and evaluation of biomarkers in workers exposed to benzene in China. Res Rep Health Eff Inst 2003: 115: 1–72; discussion 73–87.
Quackenboss J.J., Pellizzari E.D., Shubat P., Whitmore R.W., Adgate J.L, Thomas K.W., Freeman N.C., Stroebel C., Lioy P.J., Clayton A.C., and Sexton K. Design strategy for assessing multi-pathway exposure for children: the Minnesota Children's Pesticide Exposure Study (MNCPES). J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2000: 10 (2): 145–158.
Quig D. Cysteine metabolism and metal toxicity. Altern Med Rev 1998: 3 (4): 262–270.
Quinlan J.R. C4.5: Programs for Machine Learning. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers, San Mateo, CA, 1993.
Reddy M.B., Yang R.S.H., Clewell III H.J., and Andersen M.E. Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Modeling: Science and Applications. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ, 2005.
Ren S.J., and Kim H. Comparative assessment of multiresponse regression methods for predicting the mechanisms of toxic action of phenols. J Chem Inform Comput Sci 2003: 43 (6): 2106–2110.
RFSC. R: a Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing (RFSC), Vienna, Austria, 2006: http://www.R-project.org.
Rigas M.L., Okino M.S., and Quackenboss J.J. Use of a pharmacokinetic model to assess chlorpyrifos exposure and dose in children, based on urinary biomarker measurements. Toxicol Sci 2001: 61 (2): 374–381.
Ringrose T.J., and Forth S.A. Simplifying multivariate second-order response surfaces by fitting constrained models using automatic differentiation. Technometrics 2005: 47 (3): 249–259.
Robertson G.L., Lebowitz M.D., O’Rourke M.K., Gordon S., and Moschandreas D. The National Human Exposure Assessment Survey (NHEXAS) study in Arizona –– introduction and preliminary results. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 1999: 9 (5): 427–434.
Rose R.L., and Hodgson E. Pesticide metabolism and potential for metabolic interactions. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 2005: 19 (4): 276–277.
Roy A., and Georgopoulos P.G. Reconstructing week-long exposures to volatile organic compounds using physiologically based pharmacokinetic models. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 1998: 8 (3): 407–422.
Roy A., Weisel C.P., Ballo M.A., and Georgopoulos P.G. Studies of multiroute exposure/dose reconstruction using physiologically based pharmacokinetic models. Toxicol Ind Health 1996: 12 (2): 153–163.
Salford Systems. Treenet/MART 2006: http://www.salford-systems.com/treenet.php.
Serre M. BMElib, The Bayesian Maximum Entropy software 2006: http://www.unc.edu/depts/case/BMELIB/.
Sherrod P.H. DTREG User's Manual 2006: http://www.dtreg.com.
Silva Mdo C., Gaspar J., Duarte Silva I., Faber A., and Rueff J. GSTM1, GSTT1, and GSTP1 genotypes and the genotoxicity of hydroquinone in human lymphocytes. Environ Mol Mutagen 2004: 43 (4): 258–264.
Sohn M.D., McKone T.E., and Blancato J.N. Reconstructing population exposures from dose biomarkers: inhalation of trichloroethylene (TCE) as a case study. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2004: 14 (3): 204–213.
Sparacino G., Pillonetto G., Capello M., De Nicolao G., and Cobelli C. WINSTODEC: a stochastic deconvolution interactive program for physiological and pharmacokinetic systems. Comput Methods Programs Biomed 2002: 67 (1): 67–77.
Tahir M.A., Bouridane A., Kurugollu F., and Amira A. A novel prostate cancer classification technique using intermediate memory tabu search. EURASIP J Appl Signal Processing 2005: 2005 (1): 2241–2249.
Tan Y.M., Liao K.H., and Clewell III H.J. Reverse dosimetry: interpreting trihalomethanes biomonitoring data using physiologically based pharmacokinetic modeling. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 2007: 17 (7): 591–603.
Tan Y.M., Liao K.H., Conolly R.B., Blount B.C., Mason A.M., and Clewell H.J. Use of a physiologically based pharmacokinetic model to identify exposures consistent with human biomonitoring data for chloroform. J Toxicol Environ Health A 2006: 69 (18): 1727–1756.
Tang J., Cao Y., Rose R.L., Brimfield A.A., Dai D., Goldstein J.A., and Hodgson E. Metabolism of chlorpyrifos by human cytochrome P450 isoforms and human, mouse, and rat liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos 2001: 29 (9): 1201–1204.
Tarantola A. Inverse Problem Theory and Methods for Model Parameter Estimation. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia, PA, 2005: xii: 342 p.
Tenorio L. Statistical regularization of inverse problems. SIAM Rev 2001: 43 (2): 347–366.
Thomas D.J., Li J., Waters SB., Xing W., Adair B.M., Drobna Z., Devesa V., and Styblo M. Arsenic (+3 oxidation state) methyltransferase and the methylation of arsenicals. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 2007: 232 (1): 3–13.
Timchalk C., Kousba A., and Poet T.S. Monte Carlo analysis of the human chlorpyrifos-oxonase (PON1) polymorphism using a physiologically based pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic (PBPK/PD) model. Toxicol Lett 2002a: 135 (1–2): 51–59.
Timchalk C., Nolan R.J., Mendrala A.L., Dittenber D.A., Brzak K.A., and Mattsson J.L. A physiologically based pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic (PBPK/PD) model for the organophosphate insecticide chlorpyrifos in rats and humans. Toxicol Sci 2002b: 66 (1): 34–53.
Tomfohr J., Lu J., and Kepler T.B. Pathway level analysis of gene expression using singular value decomposition. BMC Bioinformatics 2005: 6: 225.
Tornoe C.W., Overgaard R.V., Agerso H., Nielsen H.A., Madsen H., and Jonsson E.N. Stochastic differential equations in NONMEM (R): implementation, application, and comparison with ordinary differential equations. Pharm Res 2005: 22 (8): 1247–1258.
Vankeerberghen P., Smeyersverbeke J., Leardi R., Karr C.L., and Massart D.L. Robust regression and outlier detection for nonlinear models using genetic algorithms. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst 1995: 28 (1): 73–87.
Venables W.N., and Ripley B.D. Modern Applied Statistics with S-PLUS. Statistics and Computing. Springer, New York, 1999: xi: 501 p.
Vogel C.R. Computational Methods for Inverse Problems. Frontiers in Applied Mathematics. Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, Philadelphia, 2002: xvi: 183 p.
Wang S.W., Georgopoulos P.G., Li G., and Rabitz H. Characterizing uncertainties in human exposure modeling through the random sampling-high dimensional model representation (RS-HDMR) methodology. Int J Risk Assess Manag 2005: 5: 387–406.
Wendlandt M., van Beek J.D., Suter U.W., and Meier B.H. Determination of orientational order in deformed glassy PMMA from solid-state NMR data. Macromolecules 2005: 38 (20): 8372–8380.
Whitmore R.W., Byron M.Z., Clayton C.A., Thomas K.W., Zelon H.S., Pellizzari E.D., Lioy P.J., and Quackenboss J.J. Sampling design, response rates, and analysis weights for the National Human Exposure Assessment Survey (NHEXAS) in EPA region 5. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 1999: 9 (5): 369–380.
Wilson N.K., Chuang J.C., Iachan R., Lyu C., Gordon S.M., Morgan M.K., Ozkaynak H., and Sheldon L.S. Design and sampling methodology for a large study of preschool children's aggregate exposures to persistent organic pollutants in their everyday environments. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2004: 14 (3): 260–274.
Wilson N.K., Chuang J.C., Lyu C., Menton R., and Morgan M.K. Aggregate exposures of nine preschool children to persistent organic pollutants at day care and at home. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2003: 13 (3): 187–202.
Winkler D.A. Neural networks in ADME and toxicity prediction. Drugs Future 2004: 29 (10): 1043–1057.
Wood T.C., Salavagionne O.E., Mukherjee B., Wang L.W., Klumpp A.F., Thomae B.A., Eckloff B.W., Schaid D.J., Wieben E.D., and Weinshilboum R.M. Human arsenic methyltransferase (AS3MT) pharmacogenetics — gene resequencing and functional genomics studies. J Biol Chem 2006: 281 (11): 7364–7373.
Yamashita F., Bando H., Takakura Y., and Hashida M. A deconvolution method for estimating the first-pass metabolism of orally administered drugs. Biol Pharm Bull 1995: 18 (12): 1787–1789.
Yang Y.C., Xu X., and Georgopoulos P.G. Evaluation of Stochastic Population and Bayesian Toxicokinetic Modeling Methods for Exposure and Dose Assessment Applications. CCL:2008.02, Computational Chemodynamics Laboratory, EOHSI, Piscataway, NJ, 2008: http://ccl.rutgers.edu/reports/MENTOR3P/CCL_2008-report_chloroform.pdf.
Yano Y., Yamaoka K., and Tanaka H. A nonlinear least squares program, MULTI(FILT), based on fast inverse Laplace transform for microcomputers. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 1989: 37 (4): 1035–1038.
Yap C.W., Xue Y., Li Z.R., and Chen Y.Z. Application of support vector machines to in silico prediction of cytochrome p450 enzyme substrates and inhibitors. Curr Top Med Chem 2006: 6 (15): 1593–1607.
Yjokley K., Tran H.T., Pekari K., Rappaport S., Riihimaki V., Rothman N., Waidyanatha S., and Schlosser P.M. Physiologically-based pharmacokinetic modeling of benzene in humans: a Bayesian approach. Risk Anal 2006: 26 (4): 925–943.
Yokel R.A., Lasley S.M., and Dorman D.C. The speciation of metals in mammals influences their toxicokinetics and toxicodynamics and therefore human health risk assessment. J Toxicol Environ Health B Crit Rev 2006: 9 (1): 63–85.
York T.P., Eaves L.J., and van den Oord E.J. Multivariate adaptive regression splines: a powerful method for detecting disease-risk relationship differences among subgroups. Stat Med 2006: 25 (8): 1355–1367.
Youssef H., Sait S.M., and Adiche H. Evolutionary algorithms, simulated annealing and tabu search: a comparative study. Eng Appl Artif Intell 2001: 14 (2): 167–181.
Acknowledgements
The United States Environmental Protection Agency (USEPA), through its Office of Research and Development (ORD), partially funded and collaborated in the research described here under University Partnership Agreement CR 83162501 to the Center for Exposure and Risk Modeling (CERM) of the Environmental and Occupational Health Sciences Institute. The research and this manuscript have been subjected to Agency review and approved for publication. USEPA has also supported this work through the Environmental Bioinformatics and Computational Toxicology Center (ebCTC – GAD R 832721-010). Additional support has been provided by the NIEHS sponsored UMDNJ Center for Environmental Exposures and Disease, Grant#: NIEHS P30ES005022. We acknowledge feedback and suggestions of numerous USEPA collaborators including C. Dary, R. Tornero-Velez, M. Morgan, M. Dellarco, F. Power, J.N. Blancato, and L. Sheldon.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Georgopoulos, P., Sasso, A., Isukapalli, S. et al. Reconstructing population exposures to environmental chemicals from biomarkers: Challenges and opportunities. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 19, 149–171 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2008.9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/jes.2008.9
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bayesian inference of chemical exposures from NHANES urine biomonitoring data
Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology (2022)
-
Source reconstruction of airborne toxics based on acute health effects information
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Exposure science and its places in environmental health sciences and risk assessment: why is its application still an ongoing struggle in 2014?
Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology (2015)
-
Polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) exposure and oxidative stress for a rural population from the North China Plain
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2015)
-
Regulatory toxicology in the twenty-first century: challenges, perspectives and possible solutions
Archives of Toxicology (2015)