Abstract
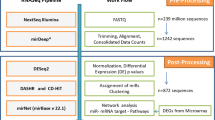
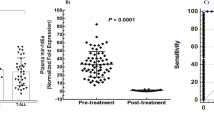
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) relevant to acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) in children are hypothesized to be largely unknown as most miRNAs have been identified in non-leukemic tissues. In order to discover these miRNAs, we applied high-throughput sequencing to pooled fractions of leukemic cells obtained from 89 pediatric cases covering seven well-defined genetic types of ALL and normal hematopoietic cells. This resulted into 78 million small RNA reads representing 554 known, 28 novel and 431 candidate novel miR genes. In all, 153 known, 16 novel and 170 candidate novel mature miRNAs and miRNA-star strands were only expressed in ALL, whereas 140 known, 2 novel and 82 candidate novel mature miRNAs and miRNA-star strands were unique to normal hematopoietic cells. Stem-loop reverse transcriptase (RT)-quantitative PCR analyses confirmed the differential expression of selected mature miRNAs in ALL types and normal cells. Expression of 14 new miRNAs inversely correlated with expression of predicted target genes (−0.49⩽Spearman's correlation coefficients (Rs)⩽−0.27, P⩽0.05); among others, low levels of novel sol-miR-23 associated with high levels of its predicted (antiapoptotic) target BCL2 (B-cell lymphoma 2) in precursor B-ALL (Rs −0.36, P=0.007). The identification of >1000 miR genes expressed in different types of ALL forms a comprehensive repository for further functional studies that address the role of miRNAs in the biology of ALL.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Bartel DP . MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004; 116: 281–297.
Ventura A, Jacks T . MicroRNAs and cancer: short RNAs go a long way. Cell 2009; 136: 586–591.
Bartel DP . MicroRNAs: target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009; 136: 215–233.
Winter J, Jung S, Keller S, Gregory RI, Diederichs S . Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat Cell Biol 2009; 11: 228–234.
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D et al. MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 2005; 435: 834–838.
Chen CZ, Lodish HF . MicroRNAs as regulators of mammalian hematopoiesis. Semin Immunol 2005; 17: 155–165.
Rosenfeld N, Aharonov R, Meiri E, Rosenwald S, Spector Y, Zepeniuk M et al. MicroRNAs accurately identify cancer tissue origin. Nat Biotechnol 2008; 26: 462–469.
Voorhoeve PM, le Sage C, Schrier M, Gillis AJ, Stoop H, Nagel R et al. A genetic screen implicates miRNA-372 and miRNA-373 as oncogenes in testicular germ cell tumors. Cell 2006; 124: 1169–1181.
Jongen-Lavrencic M, Sun SM, Dijkstra MK, Valk PJ, Lowenberg B . MicroRNA expression profiling in relation to the genetic heterogeneity of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2008; 111: 5078–5085.
Mi S, Lu J, Sun M, Li Z, Zhang H, Neilly MB et al. MicroRNA expression signatures accurately discriminate acute lymphoblastic leukemia from acute myeloid leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007; 104: 19971–19976.
Schotte D, Chau JC, Sylvester G, Liu G, Chen C, van der Velden VH et al. Identification of new microRNA genes and aberrant microRNA profiles in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 2009; 23: 313–322.
Schotte D, De Menezes RX, Akbari Moqadam F, Mohammadi Khankahdani L, Lange-Turenhout EA, Chen C et al. MicroRNAs characterize genetic diversity and drug resistance in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2011; 96: 703–711.
Schotte D, Lange-Turenhout EA, Stumpel DJ, Stam RW, Buijs-Gladdines JG, Meijerink JP et al. Expression of miR-196b is not exclusively MLL-driven but is especially linked to activation of HOXA genes in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Haematologica 2010; 95: 1675–1682.
Berezikov E, Cuppen E, Plasterk RH . Approaches to microRNA discovery. Nat Genet 2006; 38 (Suppl): S2–S7.
Bentwich I, Avniel A, Karov Y, Aharonov R, Gilad S, Barad O et al. Identification of hundreds of conserved and nonconserved human microRNAs. Nat Genet 2005; 37: 766–770.
Xie X, Lu J, Kulbokas EJ, Golub TR, Mootha V, Lindblad-Toh K et al. Systematic discovery of regulatory motifs in human promoters and 3′ UTRs by comparison of several mammals. Nature 2005; 434: 338–345.
Ahmed FE . Role of miRNA in carcinogenesis and biomarker selection: a methodological view. Expert Rev Mol Diagn 2007; 7: 569–603.
Whiteford N, Skelly T, Curtis C, Ritchie ME, Lohr A, Zaranek AW et al. Swift: primary data analysis for the Illumina Solexa sequencing platform. Bioinformatics 2009; 25: 2194–2199.
Stam RW, den Boer ML, Schneider P, Nollau P, Horstmann M, Beverloo HB et al. Targeting FLT3 in primary MLL-gene-rearranged infant acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 2005; 106: 2484–2490.
Den Boer ML, Harms DO, Pieters R, Kazemier KM, Gobel U, Korholz D et al. Patient stratification based on prednisolone-vincristine-asparaginase resistance profiles in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 3262–3268.
Weerkamp F, de Haas EF, Naber BA, Comans-Bitter WM, Bogers AJ, van Dongen JJ et al. Age-related changes in the cellular composition of the thymus in children. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005; 115: 834–840.
Berezikov E, Guryev V, van de Belt J, Wienholds E, Plasterk RH, Cuppen E . Phylogenetic shadowing and computational identification of human microRNA genes. Cell 2005; 120: 21–24.
Berezikov E, Liu N, Flynt AS, Hodges E, Rooks M, Hannon GJ et al. Evolutionary flux of canonical microRNAs and mirtrons in Drosophila. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 6–9; author reply -10.
Berezikov E, Thuemmler F, van Laake LW, Kondova I, Bontrop R, Cuppen E et al. Diversity of microRNAs in human and chimpanzee brain. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 1375–1377.
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, Zhou Z, Lee DH, Nguyen JT et al. Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 2005; 33: e179.
Edgar R, Domrachev M, Lash AE . Gene Expression Omnibus: NCBI gene expression and hybridization array data repository. Nucleic Acids Res 2002; 30: 207–210.
Den Boer ML, van Slegtenhorst M, De Menezes RX, Cheok MH, Buijs-Gladdines JG, Peters ST et al. A subtype of childhood acute lymphoblastic leukaemia with poor treatment outcome: a genome-wide classification study. Lancet Oncol 2009; 10: 125–134.
Croce CM . Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat Rev Genet 2009; 10: 704–714.
Basso K, Sumazin P, Morozov P, Schneider C, Maute RL, Kitagawa Y et al. Identification of the human mature B cell miRNome. Immunity 2009; 30: 744–752.
Cummins JM, He Y, Leary RJ, Pagliarini R, Diaz Jr LA, Sjoblom T et al. The colorectal microRNAome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 3687–3692.
Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 2007; 129: 1401–1414.
Creighton CJ, Benham AL, Zhu H, Khan MF, Reid JG, Nagaraja AK et al. Discovery of novel microRNAs in female reproductive tract using next generation sequencing. PLoS One 2010; 5: e9637.
Stark MS, Tyagi S, Nancarrow DJ, Boyle GM, Cook AL, Whiteman DC et al. Characterization of the melanoma miRNAome by deep sequencing. PLoS One 2010; 5: e9685.
Vaz C, Ahmad HM, Sharma P, Gupta R, Kumar L, Kulshreshtha R et al. Analysis of microRNA transcriptome by deep sequencing of small RNA libraries of peripheral blood. BMC Genomics 2010; 11: 288.
Zhang H, Yang JH, Zheng YS, Zhang P, Chen X, Wu J et al. Genome-wide analysis of small RNA and novel microRNA discovery in human acute lymphoblastic leukemia based on extensive sequencing approach. PLoS One 2009; 4: e6849.
Ramsingh G, Koboldt DC, Trissal M, Chiappinelli KB, Wylie T, Koul S et al. Complete characterization of the microRNAome in a patient with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2010; 116: 5316–5326.
Chiang HR, Schoenfeld LW, Ruby JG, Auyeung VC, Spies N, Baek D et al. Mammalian microRNAs: experimental evaluation of novel and previously annotated genes. Genes Dev 2010; 24: 992–1009.
Lan FF, Wang H, Chen YC, Chan CY, Ng SS, Li K et al. Hsa-let-7 g inhibits proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by down-regulation of c-Myc and up-regulation of p16(INK4A). Int J Cancer 2011; 128: 319–331.
Zhao C, Sun G, Li S, Lang MF, Yang S, Li W et al. MicroRNA let-7b regulates neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation by targeting nuclear receptor TLX signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2010; 107: 1876–1881.
Dong C, Ji M, Ji C . microRNAs and their potential target genes in leukemia pathogenesis. Cancer Biol Ther 2009; 8: 200–205.
Reed JC . Bcl-2: prevention of apoptosis as a mechanism of drug resistance. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 1995; 9: 451–473.
Coustan-Smith E, Kitanaka A, Pui CH, McNinch L, Evans WE, Raimondi SC et al. Clinical relevance of BCL-2 overexpression in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 1996; 87: 1140–1146.
Cirinna M, Trotta R, Salomoni P, Kossev P, Wasik M, Perrotti D et al. Bcl-2 expression restores the leukemogenic potential of a BCR/ABL mutant defective in transformation. Blood 2000; 96: 3915–3921.
Baek D, Villen J, Shin C, Camargo FD, Gygi SP, Bartel DP . The impact of microRNAs on protein output. Nature 2008; 455: 64–71.
Keene JD, Komisarow JM, Friedersdorf MB . RIP-Chip: the isolation and identification of mRNAs, microRNAs and protein components of ribonucleoprotein complexes from cell extracts. Nat Protoc 2006; 1: 302–307.
Tan LP, Seinen E, Duns G, de Jong D, Sibon OC, Poppema S et al. A high throughput experimental approach to identify miRNA targets in human cells. Nucleic Acids Res 2009; 37: e137.
Felli N, Fontana L, Pelosi E, Botta R, Bonci D, Facchiano F et al. MicroRNAs 221 and 222 inhibit normal erythropoiesis and erythroleukemic cell growth via kit receptor down-modulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2005; 102: 18081–18086.
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by The Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research (NWO-Vidi Grant; MLdB), the Quality of Life Foundation (MLdB/RP) and the Pediatric Oncology Foundation Rotterdam, KOCR (MLdB/RP). We thank Christel Kockx and Michael Moorhouse (core-facility high-throughput sequencing, Erasmus Center for Biomics, Rotterdam) for assistance with the Solexa high-throughput sequencing reactions and data extraction, respectively. We are grateful to Dr Eugene Berezikov (InteRNA genomics BV and the Hubrecht Institute, Utrecht) for the bioinformatic analysis of the small RNA sequence reads and helpful discussions. We thank Dr Leila Mohammadi Khankahdani (Department of Pediatric Oncology, Erasmus MC/Sophia Children's Hospital) for her help in the integration of miRNA and mRNA expression data.
Author contributions
DS performed research, analyzed data and wrote manuscript; FAM and EAML-T performed research, analyzed data and revised the manuscript; CC provided custom stem-loop based TaqMan assays for miRNA detection and revised the manuscript; WFJvIJ performed Solexa sequencing and revised the manuscript; RP and MLdB supervised research, analyzed data, wrote and revised the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Leukemia website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schotte, D., Moqadam, F., Lange-Turenhout, E. et al. Discovery of new microRNAs by small RNAome deep sequencing in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Leukemia 25, 1389–1399 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.105
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2011.105
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The association between genetic variation rs2292832 and the processing efficiency of pre-mir-149 affects the risk of breast cancer
Molecular Biology Reports (2023)
-
microRNA-155-5p initiates childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia by regulating the IRF4/CDK6/CBL axis
Laboratory Investigation (2022)
-
Next generation sequencing identifies novel diagnostic biomarkers for head and neck cancers
Oral Cancer (2019)
-
Changes in MiRNA-5196 Expression as a Potential Biomarker of Anti-TNF-α Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis and Ankylosing Spondylitis Patients
Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis (2018)
-
On the performance of pre-microRNA detection algorithms
Nature Communications (2017)