Abstract
The neurodevelopmental model of schizophrenia, which posits that the illness is the end state of abnormal neurodevelopmental processes that started years before the illness onset, is widely accepted, and has long been dominant for childhood-onset neuropsychiatric disorders. This selective review updates our 2005 review of recent studies that have impacted, or have the greatest potential to modify or extend, the neurodevelopmental model of schizophrenia. Longitudinal whole-population studies support a dimensional, rather than categorical, concept of psychosis. New studies suggest that placental pathology could be a key measure in future prenatal high-risk studies. Both common and rare genetic variants have proved surprisingly diagnostically nonspecific, and copy number variants (CNVs) associated with schizophrenia are often also associated with autism, epilepsy and intellectual deficiency. Large post-mortem gene expression studies and prospective developmental multi-modal brain imaging studies are providing critical data for future clinical and high-risk developmental brain studies. Whether there can be greater molecular specificity for phenotypic characterization is a subject of current intense study and debate, as is the possibility of neuronal phenotyping using human pluripotent-inducible stem cells. Biological nonspecificity, such as in timing or nature of early brain development, carries the possibility of new targets for broad preventive treatments.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rapoport JL, Addington AM, Frangou S, Psych MR . The neurodevelopmental model of schizophrenia: update 2005. Mol Psychiatry 2005; 10: 434–449.
Gur RC, Irani F, Seligman S, Calkins ME, Richard J, Gur RE . Challenges and opportunities for genomic developmental neuropsychology: examples from the Penn–Drexel collaborative battery. Clin Neuropsychol 2011; 25: 1029–1041.
Dickson H, Laurens KR, Cullen AE, Hodgins S . Meta-analyses of cognitive and motor function in youth aged 16 years and younger who subsequently develop schizophrenia. Psychol Med 2012; 42: 743–755.
Clarke MC, Tanskanen A, Huttunen M, Leon DA, Murray RM, Jones PB et al. Increased risk of schizophrenia from additive interaction between infant motor developmental delay and obstetric complications: evidence from a population-based longitudinal study. Am J Psychiatry 2011; 168: 1295–1302.
Johnstone EC, Ebmeier KP, Miller P, Owens DG, Lawrie SM . Predicting schizophrenia: findings from the Edinburgh High-Risk Study. Br J Psychiatry 2005; 186: 18–25.
Lawrie SM, Olabi B, Hall J, McIntosh AM . Do we have any solid evidence of clinical utility about the pathophysiology of schizophrenia? World Psychiatry 2011; 10: 19–31.
Polanczyk G, Moffitt TE, Arseneault L, Cannon M, Ambler A, Keefe RS et al. Etiological and clinical features of childhood psychotic symptoms: results from a birth cohort. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2010; 67: 328–338.
Hofman A, Jaddoe VW, Mackenbach JP, Moll HA, Snijders RF, Steegers EA et al. Growth, development and health from early fetal life until young adulthood: the Generation R Study. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol 2004; 18: 61–72.
Brown AS, Derkits EJ . Prenatal infection and schizophrenia: a review of epidemiologic and translational studies. Am J Psychiatry 2010; 167: 261–280.
Remington J, Klein J, Wilson C, Baker, DJ . Infectious Diseases of the Fetus and Newborn Infant, 6th edn. Elsevier Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, 2006.
Pedersen MG, Stevens H, Pedersen CB, Norgaard-Pedersen B, Mortensen PB . Toxoplasma infection and later development of schizophrenia in mothers. Am J Psychiatry 2011; 168: 814–821.
Mortensen PB, Norgaard-Pedersen B, Waltoft BL, Sorensen TL, Hougaard D, Torrey EF et al. Toxoplasma gondii as a risk factor for early-onset schizophrenia: analysis of filter paper blood samples obtained at birth. Biol Psychiatry 2007; 61: 688–693.
St Clair D, Xu M, Wang P, Yu Y, Fang Y, Zhang F et al. Rates of adult schizophrenia following prenatal exposure to the Chinese famine of 1959–1961. JAMA 2005; 294: 557–562.
Xu MQ, Sun WS, Liu BX, Feng GY, Yu L, Yang L et al. Prenatal malnutrition and adult schizophrenia: further evidence from the 1959–1961 Chinese famine. Schizophr Bull 2009; 35: 568–576.
Lumey LH, Stein AD, Susser E . Prenatal famine and adult health. Annu Rev Public Health 2011; 32: 237–262.
Nelson KB, Blair E . The placenta and neurologic and psychiatric outcomes in the child: study design matters. Placenta 2011; 32: 623–625.
Blair E, de Groot J, Nelson KB . Placental infarction identified by macroscopic examination and risk of cerebral palsy in infants at 35 weeks of gestational age and over. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2011; 205: 124.e1–7.
Bonnin A, Goeden N, Chen K, Wilson ML, King J, Shih JC et al. A transient placental source of serotonin for the fetal forebrain. Nature 2011; 472: 347–350.
McKay R . Developmental biology: remarkable role for the placenta. Nature 2011; 472: 298–299.
Passemard S, Sokolowska P, Schwendimann L, Gressens P . VIP-induced neuroprotection of the developing brain. Curr Pharm Des 2011; 17: 1036–1039.
Hoeffer CA, Klann E . mTOR signaling: at the crossroads of plasticity, memory and disease. Trends Neurosci 2010; 33: 67–75.
Nielsen LF, Schendel D, Grove J, Hvidtjorn D, Jacobsson B, Josiassen T et al. Asphyxia-related risk factors and their timing in spastic cerebral palsy. BJOG 2008; 115: 1518–1528.
Zeltser LM, Leibel RL . Roles of the placenta in fetal brain development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 15667–15668.
Johnson S, Marlow N . Preterm birth and childhood psychiatric disorders. Pediatr Res 2011; 69 (Part 2): 11R–18R.
van Os J, Kenis G, Rutten BP . The environment and schizophrenia. Nature 2010; 468: 203–212.
March D, Hatch SL, Morgan C, Kirkbride JB, Bresnahan M, Fearon P et al. Psychosis and place. Epidemiol Rev 2008; 30: 84–100.
Zammit S, Lewis G, Rasbash J, Dalman C, Gustafsson JE, Allebeck P . Individuals, schools, and neighborhood: a multilevel longitudinal study of variation in incidence of psychotic disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2010; 67: 914–922.
Lederbogen F, Kirsch P, Haddad L, Streit F, Tost H, Schuch P et al. City living and urban upbringing affect neural social stress processing in humans. Nature 2011; 474: 498–501.
Peen J, Schoevers RA, Beekman AT, Dekker J . The current status of urban–rural differences in psychiatric disorders. Acta Psychiatr Scand 2010; 121: 84–93.
Morgan C, Fisher H . Environment and schizophrenia: environmental factors in schizophrenia: childhood trauma--a critical review. Schizophr Bull 2007; 33: 3–10.
Cutajar MC, Mullen PE, Ogloff JR, Thomas SD, Wells DL, Spataro J . Schizophrenia and other psychotic disorders in a cohort of sexually abused children. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2010; 67: 1114–1119.
Habets P, Marcelis M, Gronenschild E, Drukker M, van Os J . Reduced cortical thickness as an outcome of differential sensitivity to environmental risks in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2011; 69: 487–494.
Arseneault L, Cannon M, Fisher HL, Polanczyk G, Moffitt TE, Caspi A . Childhood trauma and children's emerging psychotic symptoms: a genetically sensitive longitudinal cohort study. Am J Psychiatry 2011; 168: 65–72.
Salum GA, Polanczyk GV, Miguel EC, Rohde LA . Effects of childhood development on late-life mental disorders. Curr Opin Psychiatry 2010; 23: 498–503.
Polanczyk G, Laranjeira R, Zaleski M, Pinsky I, Caetano R, Rohde LA . ADHD in a representative sample of the Brazilian population: estimated prevalence and comparative adequacy of criteria between adolescents and adults according to the item response theory. Int J Methods Psychiatr Res 2010; 19: 177–184.
Polanczyk G, Caspi A, Houts R, Kollins SH, Rohde LA, Moffitt TE . Implications of extending the ADHD age-of-onset criterion to age 12: results from a prospectively studied birth cohort. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2010; 49: 210–216.
Polanczyk G, Bigarella MP, Hutz MH, Rohde LA . Pharmacogenetic approach for a better drug treatment in children. Curr Pharm Des 2010; 16: 2462–2473.
Moffitt TE, Caspi A, Taylor A, Kokaua J, Milne BJ, Polanczyk G et al. How common are common mental disorders? Evidence that lifetime prevalence rates are doubled by prospective versus retrospective ascertainment. Psychol Med 2010; 40: 899–909.
Canino G, Polanczyk G, Bauermeister JJ, Rohde LA, Frick PJ . Does the prevalence of CD and ODD vary across cultures? Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 2010; 45: 695–704.
Bauermeister JJ, Canino G, Polanczyk G, Rohde LA . ADHD across cultures: is there evidence for a bidimensional organization of symptoms? J Clin Child Adolesc Psychol 2010; 39: 362–372.
Arseneault L, Cannon M, Poulton R, Murray R, Caspi A, Moffitt TE . Cannabis use in adolescence and risk for adult psychosis: longitudinal prospective study. BMJ 2002; 325: 1212–1213.
Bourque F, van der Ven E, Malla A . A meta-analysis of the risk for psychotic disorders among first- and second-generation immigrants. Psychol Med 2010; 41: 897–910.
Veling W, Hoek H, Selten JP, Susser E . Age at migration and future risk of psychotic disorder among immigrants in the Netherlands: a 7-year incidence study. Am J Psychiatry 2011; 168: 1278–1285.
Meyer-Lindenberg A, Domes G, Kirsch P, Heinrichs M . Oxytocin and vasopressin in the human brain: social neuropeptides for translational medicine. Nat Rev Neurosci 2011; 12: 524–538.
Morgane PJ, Mokler DJ, Galler JR . Effects of prenatal protein malnutrition on the hippocampal formation. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2002; 26: 471–483.
Insel T. Rethinking schizophrenia. Nature 2010; 468: 187–193.
Greenstein D, Lerch J, Shaw P, Clasen L, Giedd J, Gochman P et al. Childhood onset schizophrenia: cortical brain abnormalities as young adults. J Child Psychol Psychiatry Allied Disciplines 2006; 47: 1003–1012.
Boos HB, Aleman A, Cahn W, Hulshoff Pol H, Kahn RS . Brain volumes in relatives of patients with schizophrenia: a meta-analysis. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2007; 64: 297–304.
Cannon TD, Thompson PM, van Erp TG, Toga AW, Poutanen VP, Huttunen M et al. Cortex mapping reveals regionally specific patterns of genetic and disease-specific gray-matter deficits in twins discordant for schizophrenia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2002; 99: 3228–3233.
Ettinger U, Picchioni M, Landau S, Matsumoto K, van Haren NE, Marshall N et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of the thalamus and adhesio-interthalamica in twins with schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2007; 64: 401–409.
Ettinger U, Schmechtig A, Toulopoulou T, Borg C, Orrells C, Owens S et al. Prefrontal and striatal volumes in monozygotic twins concordant and discordant for schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 2010; 38: 192–203.
Gogtay N, Greenstein D, Lenane M, Clasen L, Sharp W, Gochman P et al. Cortical brain development in nonpsychotic siblings of patients with childhood-onset schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2007; 64: 772–780.
Mattai AA, Weisinger B, Greenstein D, Stidd R, Clasen L, Miller R et al. Normalization of cortical gray matter deficits in nonpsychotic siblings of patients with childhood-onset schizophrenia. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 2011; 50: 697–704.
Walterfang M, McGuire PK, Yung AR, Phillips LJ, Velakoulis D, Wood SJ et al. White matter volume changes in people who develop psychosis. Br J Psychiatry 2008; 193: 210–215.
Walterfang M, Wood AG, Reutens DC, Wood SJ, Chen J, Velakoulis D et al. Morphology of the corpus callosum at different stages of schizophrenia: cross-sectional study in first-episode and chronic illness. Br J Psychiatry 2008; 192: 429–434.
Kyriakopoulos M, Frangou S . Recent diffusion tensor imaging findings in early stages of schizophrenia. Curr Opin Psychiatry 2009; 22: 168–176.
Ashtari M, Cottone J, Ardekani BA, Cervellione K, Szeszko PR, Wu J et al. Disruption of white matter integrity in the inferior longitudinal fasciculus in adolescents with schizophrenia as revealed by fiber tractography. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2007; 64: 1270–1280.
Kyriakopoulos M, Vyas NS, Barker GJ, Chitnis XA, Frangou S . A diffusion tensor imaging study of white matter in early-onset schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2008; 63: 519–523.
Douaud G, Smith S, Jenkinson M, Behrens T, Johansen-Berg H, Vickers J et al. Anatomically related grey and white matter abnormalities in adolescent-onset schizophrenia. Brain 2007; 130 (Part 9): 2375–2386.
Douad G . Longitudinal structural and diffusion imaging in adolescent-onset schizophrenia: a delayed brain maturation story? Proceedings of the 14th Annual Meeting of the Organization of Human Brain Mapping, 15–19 June 2008; Melbourne, Australia 2008.
Carpenter DM, Tang CY, Friedman JI, Hof PR, Stewart DG, Buchsbaum MS et al. Temporal characteristics of tract-specific anisotropy abnormalities in schizophrenia. NeuroReport 2008; 19: 1369–1372.
Rosenberger G, Kubicki M, Nestor PG, Connor E, Bushell GB, Markant D et al. Age-related deficits in fronto-temporal connections in schizophrenia: a diffusion tensor imaging study. Schizophr Res 2008; 102: 181–188.
Gogtay N, Lu A, Leow AD, Klunder AD, Lee AD, Chavez A et al. Three-dimensional brain growth abnormalities in childhood-onset schizophrenia visualized by using tensor-based morphometry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 15979–15984.
Bloemen OJ, de Koning MB, Schmitz N, Nieman DH, Becker HE, de Haan L et al. White-matter markers for psychosis in a prospective ultra-high-risk cohort. Psychol Med 2010; 40: 1297–1304.
Knickmeyer RC, Gouttard S, Kang C, Evans D, Wilber K, Smith JK et al. A structural MRI study of human brain development from birth to 2 years. J Neurosci 2008; 28: 12176–12182.
Gilmore JH, Kang C, Evans DD, Wolfe HM, Smith MD, Lieberman JA et al. Prenatal and neonatal brain structure and white matter maturation in children at high risk for schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2008; 167: 1083–1091.
Gilmore JH, Schmitt JE, Knickmeyer RC, Smith JK, Lin W, Styner M et al. Genetic and environmental contributions to neonatal brain structure: a twin study. Hum Brain Mapp 2010; 31: 1174–1182.
Frazier JA, Giedd JN, Hamburger SD, Albus KE, Kaysen D, Vaituzis AC et al. Brain anatomic magnetic resonance imaging in childhood-onset schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 1996; 53: 617–624.
Hazlett HC, Poe M, Gerig G, Smith RG, Provenzale J, Ross A et al. Magnetic resonance imaging and head circumference study of brain size in autism: birth through age 2 years. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2005; 62: 1366–1376.
Fornito A, Yoon J, Zalesky A, Bullmore ET, Carter CS . General and specific functional connectivity disturbances in first-episode schizophrenia during cognitive control performance. Biol Psychiatry 2011; 70: 64–72.
Schmitt A, Hasan A, Gruber O, Falkai P . Schizophrenia as a disorder of disconnectivity. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 2011; 261 (Suppl 2): 150–154.
Bullmore E, Sporns O . Complex brain networks: graph theoretical analysis of structural and functional systems. Nat Rev Neurosci 2009; 10: 186–198.
Lynall ME, Bassett DS, Kerwin R, McKenna PJ, Kitzbichler M, Muller U et al. Functional connectivity and brain networks in schizophrenia. J Neurosci 2010; 30: 9477–9487.
Liu Y, Liang M, Zhou Y, He Y, Hao Y, Song M et al. Disrupted small-world networks in schizophrenia. Brain 2008; 131 (Part 4): 945–961.
van den Heuvel MP, Mandl RC, Stam CJ, Kahn RS, Hulshoff Pol HE . Aberrant frontal and temporal complex network structure in schizophrenia: a graph theoretical analysis. J Neurosci Off J Soc Neurosci 2010; 30: 15915–15926.
Zalesky A, Fornito A, Seal ML, Cocchi L, Westin CF, Bullmore ET et al. Disrupted axonal fiber connectivity in schizophrenia. Biol Psychiatry 2011; 69: 80–89.
Alexander-Bloch AF, Gogtay N, Meunier D, Birn R, Clasen L, Lalonde F et al. Disrupted modularity and local connectivity of brain functional networks in childhood-onset schizophrenia. Front Syst Neurosci 2010; 4: 147.
Alexander-Bloch A, Lambiotte R, Roberts B, Giedd J, Gogtay N, Bullmore E . The discovery of population differences in network community structure: new methods and applications to brain functional networks in schizophrenia. NeuroImage 2011; 59: 3889–3900.
Shaw P, Lerch JP, Pruessner JC, Taylor KN, Rose AB, Greenstein D et al. Cortical morphology in children and adolescents with different apolipoprotein E gene polymorphisms: an observational study. Lancet Neurol 2007; 6: 494–500.
Nopoulos PC, Aylward EH, Ross CA, Mills JA, Langbehn DR, Johnson HJ et al. Smaller intracranial volume in prodromal Huntington's disease: evidence for abnormal neurodevelopment. Brain 2011; 134 (Part 1): 137–142.
Lenroot RK, Giedd JN . The changing impact of genes and environment on brain development during childhood and adolescence: initial findings from a neuroimaging study of pediatric twins. Dev Psychopathol 2008; 20: 1161–1175.
Pezawas L, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Drabant EM, Verchinski BA, Munoz KE, Kolachana BS et al. 5-HTTLPR polymorphism impacts human cingulate–amygdala interactions: a genetic susceptibility mechanism for depression. Nat Neurosci 2005; 8: 828–834.
Meyer-Lindenberg A, Weinberger DR . Intermediate phenotypes and genetic mechanisms of psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 2006; 7: 818–827.
Honea RA, Meyer-Lindenberg A, Hobbs KB, Pezawas L, Mattay VS, Egan MF et al. Is gray matter volume an intermediate phenotype for schizophrenia? A voxel-based morphometry study of patients with schizophrenia and their healthy siblings. Biol Psychiatry 2008; 63: 465–474.
Raznahan A, Greenstein D, Lee Y, Long R, Clasen L, Gochman P et al. Catechol-o-methyl transferase (COMT) val158met polymorphism and adolescent cortical development in patients with childhood-onset schizophrenia, their non-psychotic siblings, and healthy controls. NeuroImage 2011; 57: 1517–1523.
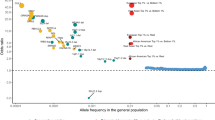
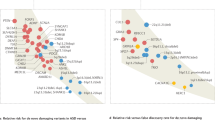
Moreno-De-Luca D, Mulle JG, Kaminsky EB, Sanders SJ, Myers SM, Adam MP et al. Deletion 17q12 is a recurrent copy number variant that confers high risk of autism and schizophrenia. Am J Hum Genet 2010; 87: 618–630.
Stone JL, O’Donovan MC, Gurling H, Kirov GK, Blackwood DH, Corvin A et al. Rare chromosomal deletions and duplications increase risk of schizophrenia. Nature 2008; 455: 237–241.
Levinson DF, Duan J, Oh S, Wang K, Sanders AR, Shi J et al. Copy number variants in schizophrenia: confirmation of five previous findings and new evidence for 3q29 microdeletions and VIPR2 duplications. Am J Psychiatry 2011; 168: 302–316.
Mulle JG, Dodd AF, McGrath JA, Wolyniec PS, Mitchell AA, Shetty AC et al. Microdeletions of 3q29 confer high risk for schizophrenia. Am J Hum Genet 2010; 87: 229–236.
Stefansson H, Rujescu D, Cichon S, Ingason A, Steinberg S, Fossdal R et al. Large recurrent microdeletions associated with schizophrenia. Nature 2008; 455: 232–236.
Kirov G, Rujescu D, Ingason A, Collier DA, O’Donovan MC, Owen MJ . Neurexin 1 (NRXN1) deletions in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 2009; 35: 851–854.
McCarthy SE, Makarov V, Kirov G, Addington AM, McClellan J, Yoon S et al. Microduplications of 16p11.2 are associated with schizophrenia. Nat Genet 2009; 41: 1223–1227.
Ingason A, Rujescu D, Cichon S, Sigurdsson E, Sigmundsson T, Pietilainen OP et al. Copy number variations of chromosome 16p13.1 region associated with schizophrenia. Mol Psychiatry 2011; 16: 17–25.
Abdolmaleky HM, Cheng KH, Russo A, Smith CL, Faraone SV, Wilcox M et al. Hypermethylation of the reelin (RELN) promoter in the brain of schizophrenic patients: a preliminary report. Am J Med Genet B 2005; 134: 60–66.
Stefansson H, Ophoff RA, Steinberg S, Andreassen OA, Cichon S, Rujescu D et al. Common variants conferring risk of schizophrenia. Nature 2009; 460: 744–747.
Rees E, Moskvina V, Owen MJ, O’Donovan MC, Kirov G . De novo rates and selection of schizophrenia-associated copy number variants. Biol Psychiatry 2011; 70: 1109–1114.
Walsh T, McClellan JM, McCarthy SE, Addington AM, Pierce SB, Cooper GM et al. Rare structural variants disrupt multiple genes in neurodevelopmental pathways in schizophrenia. Science 2008; 320: 539–543.
Lee Y, Mattai A, Long R, Rapoport J . Microduplications disrupting the MYT1L gene (2p25.3) are associated with schizophrenia. Psychiatric Genet (in press).
O’Tuathaigh CM, Desbonnet L, Waddington JL . Neuregulin-1 signaling in schizophrenia: ‘Jack of all trades’ or master of some? Expert Rev Neurother 2009; 9: 1–3.
Cirulli ET, Goldstein DB . Uncovering the roles of rare variants in common disease through whole-genome sequencing. Nat Rev Genet 2010; 11: 415–425.
Girirajan S, Rosenfeld JA, Cooper GM, Antonacci F, Siswara P, Itsara A et al. A recurrent 16p12.1 microdeletion supports a two-hit model for severe developmental delay. Nat Genet 2010; 42: 203–209.
Kuang SQ, Guo DC, Prakash SK, McDonald ML, Johnson RJ, Wang M et al. Recurrent chromosome 16p13.1 duplications are a risk factor for aortic dissections. PLoS Genet 2011; 7: e1002118, 1–10.
Dolmetsch R, Geschwind DH . The human brain in a dish: the promise of iPSC-derived neurons. Cell 2011; 145: 831–834.
Qiang L, Fujita R, Yamashita T, Angulo S, Rhinn H, Rhee D et al. Directed conversion of Alzheimer's disease patient skin fibroblasts into functional neurons. Cell 2011; 146: 359–371.
Marchetto MC, Carromeu C, Acab A, Yu D, Yeo GW, Mu Y et al. A model for neural development and treatment of Rett syndrome using human induced pluripotent stem cells. Cell 2010; 143: 527–539.
Cheung AY, Horvath LM, Grafodatskaya D, Pasceri P, Weksberg R, Hotta A et al. Isolation of MECP2-null Rett syndrome patient hiPS cells and isogenic controls through X-chromosome inactivation. Hum Mol Genet 2011; 20: 2103–2115.
Yoo AS, Sun AX, Li L, Shcheglovitov A, Portmann T, Li Y et al. MicroRNA-mediated conversion of human fibroblasts to neurons. Nature 2011; 476: 228–231.
Brennand KJ, Simone A, Jou J, Gelboin-Burkhart C, Tran N, Sangar S et al. Modelling schizophrenia using human induced pluripotent stem cells. Nature 2011; 473: 221–225.
Berry-Kravis E, Hessl D, Coffey S, Hervey C, Schneider A, Yuhas J et al. A pilot open label, single dose trial of fenobam in adults with fragile X syndrome. J Med Genet 2009; 46: 266–271.
Harris LW, Lockstone HE, Khaitovich P, Weickert CS, Webster MJ, Bahn S . Gene expression in the prefrontal cortex during adolescence: implications for the onset of schizophrenia. BMC Med Genomics 2009; 2: 28.
Huttenlocher PR . Synaptogenesis in human cerebral cortex. In: Dawson G, Fischer K (eds). Human Behavior and the Developing Brain. Guilford Press: New York, 1994, pp 137–152.
Petanjek Z, Judas M, Simic G, Rasin MR, Uylings HB, Rakic P et al. Extraordinary neoteny of synaptic spines in the human prefrontal cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2011; 108: 13–13.
Kang HJ, Kawasawa YI, Cheng F, Zhu Y, Xu X, Li M et al. Spatio-temporal transcriptome of the human brain. Nature 2011; 478: 483–489.
Colantuoni C, Lipska BK, Ye T, Hyde TM, Tao R, Leek JT et al. Temporal dynamics and genetic control of transcription in the human prefrontal cortex. Nature 2011; 478: 519–523.
Zhang YE, Landback P, Vibranovski MD, Long M . Accelerated recruitment of new brain development genes into the human genome. PLoS Biol 2011; 9: e1001179.
Kleinman JE, Law AJ, Lipska BK, Hyde TM, Ellis JK, Harrison PJ et al. Genetic neuropathology of schizophrenia: new approaches to an old question and new uses for postmortem human brains. Biol Psychiatry 2011; 69: 140–145.
Lewis DA, Gonzalez-Burgos G . Neuroplasticity of neocortical circuits in schizophrenia. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008; 33: 141–165.
Beneyto M, Lewis DA . Insights into the neurodevelopmental origin of schizophrenia from postmortem studies of prefrontal cortical circuitry. Int J Dev Neurosci 2011; 29: 295–304.
Henn F . Dopamine: a marker of psychosis and final common driver of schizophrenia psychosis. Am J Psychiatry 2011; 168: 1239–1240.
Howes OD, Kapur S . The dopamine hypothesis of schizophrenia: version III--the final common pathway. Schizophr Bull 2009; 35: 549–562.
Howes O, Bose S, Turkheimer F, Valli I, Egerton A, Valmaggia L et al. Dopamine synthesis capacity before onset of psychosis: a prospective 18F-DOPA PET imaging study. Am J Psychiatry 2011; 168: 1311–1317.
Fung SJ, Webster MJ, Sivagnanasundaram S, Duncan C, Elashoff M, Weickert CS . Expression of interneuron markers in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex of the developing human and in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 2010; 167: 1479–1488.
Hyde TM, Lipska BK, Ali T, Mathew SV, Law AJ, Metitiri OE et al. Expression of GABA signaling molecules KCC2, NKCC1, and GAD1 in cortical development and schizophrenia. J Neurosci 2011; 31: 11–11.
Marin O . Interneuron dysfunction in psychiatric disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 2012; 13: 107–120.
Voineagu I, Wang X, Johnston P, Lowe JK, Tian Y, Horvath S et al. Transcriptomic analysis of autistic brain reveals convergent molecular pathology. Nature 2011; 474: 380–384.
Brennand KJ, Gage FH . Modeling psychiatric disorders through reprogramming. Dis Model Mech 2011; 5: 26–32.
Meyer-Lindenberg A . The future of fMRI and genetics research. NeuroImage 2011; doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2011.10.063.
Mitchell KJ, Porteous DJ . Rethinking the genetic architecture of schizophrenia. Psychol Med 2011; 41: 19–32.
Mitchell KJ . The genetics of neurodevelopmental disease. Curr Opin Neurobiol 2011; 21: 197–203.
Mitchell KJ . The miswired brain: making connections from neurodevelopment to psychopathology. BMC Biol 2011; 9: 23.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rapoport, J., Giedd, J. & Gogtay, N. Neurodevelopmental model of schizophrenia: update 2012. Mol Psychiatry 17, 1228–1238 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2012.23
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2012.23
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Psychosis superspectrum I: Nosology, etiology, and lifespan development
Molecular Psychiatry (2024)
-
Neurodevelopmental trajectories, polygenic risk, and lipometabolism in vulnerability and resilience to schizophrenia
BMC Psychiatry (2023)
-
Moving from risk to resilience in psychosis research
Nature Reviews Psychology (2023)
-
Behavioral and cellular responses to circadian disruption and prenatal immune activation in mice
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Neurodevelopmental disturbances in schizophrenia: evidence from genetic and environmental factors
Journal of Neural Transmission (2023)