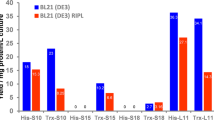
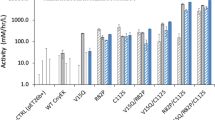
Abstract
We have designed stable pKD1 derivatives for efficient secretion of recombinant human serum albumin (rHSA) by industrial strains of Kluyveromyces yeasts. A comparison of this multi–copy expression system with isogenic cassettes integrated at chromosomal loci demonstrated that high level secretion of rHSA is a function of gene dosage in K. lactis. Various signal sequences could be used, and the secretion levels were independent of the presence of the native pro peptide. The mitotic stability of the pKD1–based expression vectors was found to be species and strain dependent and was influenced by promoter strength and culture conditions. Vector stability was drastically enhanced when the HSA gene was expressed from an inducible promoter: 90% of the transformed cells still harbored the vector after 100 generations of non–selective growth in uninduced culture conditions. Secretion levels in the range of several grams per liter of correctly folded and processed rHSA were obtained at the pilot scale, thus making the industrial production of pharmaceutical–grade, Kluyveromyces–derived rHSA economically feasible.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sellers, E.M. and Kocg-Weser, M.D. 1977. In: Albumin: Structure, Function and Uses, p. 159–182. Rosenoer, V.M., Oratz, M., Rothschild, M.A. (Eds.). Pergamon Press Inc., Oxford.
Jeans, E.R.A., Marshall, P.J. and Lowe, C.R. 1985. Plasma protein fractionation. Trends Biotechnol. 3: 267–270.
Brown, J.R. In: Albumin Structure, Function and Uses. p. 27–51. Rosenoer, V.M., Oratz, M., Rothschild, M.A. (Eds.). Pergamon Press Inc., Oxford.
Latta, M., Knapp, M., Sarmientos, P., Bréfort, G., Becquart, J., Guerrier, L., Jung, G. and Mayaux, J.F. 1987. Synthesis and purification of mature human serum albumin from E. coli. Bio/Technology 5: 1309–1314.
Saunders, C.W., Schmidt, B.J., Mallonee, R.L. and Guyer, M.S. 1987. Secretion of human serum albumin from B. subtilis. J. Bacteriol. 169: 2917–2925.
Schekman, R. and Novick, P. 1982. In: The Molecular Biology of the Yeast Saccharomyces: Metabolism and Gene Expression, p. 361–398. Strathern, J., Jones, E., and Broach, J. (Eds.). Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Judah, J.D. and Quinn, P.S. 1978. Calcium ion-dependent vesicle fusion in the conversion of proalbumin to albumin. Nature 271: 384–385.
Steiner, D.F., Quinn, P.S., Chan, S.J., Marsh, J. and Trager, H.S. 1980. Processing mechanisms in the biosynthesis of proteins. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 343: 1–16.
Bathurst, I.C., Brennan, S.O., Carrell, R.W., Cousens, L.S., Brake, A.J. and Barr, P.J., 1987. Kex2 protease has the properties of a human proalbumin converting enzyme. Science 235: 348–351.
Egel-Mitani, M., Flygenring, H.P. and Hansen, M.T. 1990. A novel aspartyl protease allowing KEX2-independent MFα propheromone processing in yeast. Yeast 6: 127–137.
Sleep, D., Belfield, G.P. and Goodey, A.R. 1990. The secretion of human serum albumin from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae using five different leader sequences. Bio/Technology 8: 42–46.
Etcheverry, T., Forrester, W. and Hitzeman, R. 1986. Regulation of the chelatin promoter during the expression of human serum albumin or yeast phosphoglycerate kinase in yeast. Bio/Technology 4: 726–730.
Kalman, M., Cserpan, I., Bajszar, G., Dobi, A., Horvath, E., Pazman, C. and Simoncsits, A. 1990. Synthesis of a gene for human serum albumin and its expression in S. cerevisiae. Nuc. Acids Res. 18: 6075–6081.
Stark, M.J.R., Boyd, A., Mileham, A.J. and Romanos, M.A. 1990. The plasmid-encoded killer system of Kluyveromyces lactis: a review. Yeast 6: 1–29.
Van den Berg, J.A., Van der Laken, K.J., Van Ooyen, A.J.J., Renniers, T.C.H.M., Rietveld, K. and Schaap, A., Brake, A.J., Bishop, R.J., Schultz, K., Moyer, D., Richman, M. and Shuster, J.R. 1990. Kluyveromyces as a host for heterologous gene expression: expression and secretion of prochymosin. Bio/Technology 8: 135–139.
Wésolowski-Louvel, M., Tanguy-Rougeau, C. and Fukuhara, H. 1988. A nuclear gene required for the expression of the linear DNA-associated killer system in the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. Yeast 4: 71–81.
Tanguy-Rougeau, C., Wésolowski-Louvel, M. and Fukuhara, H., 1988. The Kluyveromyces lactis KEX1 gene encodes a subtilisin-type serine proteinase. FEBS Lett. 234: 464–470.
Chen, X.J., Wésolowski-Louvel, M., Tanguy-Rougeau, C., Bianchi, M.M., Fabiani, L., Saliola, M., Falcone, C., Frontali, L. and Fukuhara, H. 1988. A gene-cloning system lor Kluyveromyces lactis and isolation of a chromosomal gene required for killer toxin production. J. Basic Microbiol. 28: 211–220.
Falcone, C., Saliola, M., Chen, X.J., Frontali, L. and Fukuhara, H. 1986. Analysis of a 1.6-μm circular plasmid from the yeast Kluyveromyces drosophilarum: structure and molecular dimorphism. Plasmid 15: 248–252.
Chen, X.J., Saliola, M., Falcone, C., Bianchi, M.M., Wésolowski-Louvel, M. and Fukuhara, H. 1986. Sequence organization of the circular plasmid pKD1 from the yeast Kluyveromyces drosophilarum. Nucl. Acids Res. 14: 4471–4481.
Bianchi, M.M., Falcone, C., Chen, X.J., Wésolowski-Louvel, M., Frontali, L. and Fukuhara, H. 1989. Transformation of the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis by new vectors derived from the 1.6 μm circular plasmid pKD1. Curr. Genet. 12: 185–192.
Chen, X.J., Bianchi, M.M., Suda, K. and Fukuhara, H. 1989. The host range of the pKD1-derived plasmids in yeast. Curr. Genet. 16: 95–98.
Sor, F. and Fukuhara, H. 1985.Structure of a linear plasmid of the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis: compact organization of the killer genome. Curr. Genet. 9: 147–155.
Hitzeman, R.A., Hagie, F.E., Hayflick, J.S., Chen, C.Y., Seeburg, P.H. and Derynck, R. 1983. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for 3-phosphoglycerate kinase. Nuc. Acids Res. 10: 7791–7808.
Kozak, M. 1984. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start in eukaryotic mRNA. Nuc. Acids Res. 12: 857–879.
Hamilton, R., Watanabe, C.K. and de Boer, H. A. 1987. Compilation and comparison of the sequence context around the AUG startcodons in Saccharomyces cerevisiae mRNAs. Nuc. Acid Res. 15: 3581–3593.
Kozak, M. 1986. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell 44: 283–292.
Stark, M.J.R. and Boyd, A. 1986. The killer toxin of Kluyveromyces lactis: characterization of the toxin subunits and identification of the genes which encodes them. EMBO J. 5: 1995–2002.
Tschopp, J.F., Sverlow, G., Kosson, R., Craig, W. and Grinna, L. 1987. High-level secretion of glycosylated invertase in the methylo-trophic yeast, Pichia pastoris. Bio/Technology 5: 1305–1308.
Ferrero, I., Goffrini, P. and Wésolowski-Louvel, M. 1991. Phospho-glucose isomerase gene is involved in the Rag phenotype of the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. Mol. Gen. Genet. In press.
Rothstein, R.J. 1983. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods in Enzymol. 101: 202–211.
Wésolowski-Louvel, M., Goffrini, P. and Ferrero, I., 1988. The RAG2 gene of the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis codes for a putative phosphoglu-cose isomerase. Nuc. Acid Res. 16: 8714.
Bitter, G.A. and Egan, K.M. 1984. Expression of heterologous genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae from vectors utilizing the glyceraldehy-3-phosphate gene promoter. Gene 32: 263–274.
Breuning, K.D., Dhalems, U., Das, S. and Hollenberg, C.P. 1984. Analysis of a eukaryotic β-galactosidase gene: the N-terminal end of the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis protein shows homology to the Escherichia coli lacZ gene product. Nuc. Acids Res. 5: 2327–2341.
Leonardo, J.M., Bhairi, S.M. and Dickson, R.C. 1987. Identification of upstream activator sequences that regulate induction of the β-ga-lactosidase gene in Kluyveromyces lactis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7: 4369–4376.
Das, S., Breuning, K.D. and Hollenberg, C.P. 1985. A positive regulatory element is involved in the induction of the β-galactosidase gene from Kluyveromyces lactis. EMBO J. 4: 793–798.
Fleer, R., Chen, X.J., Amellal, N., Yeh, P., Fournier, A., Guinet, F., Gault, N., Faucher, D., Folliard, F., Fukuhara, H. and Mayaux, J.-F. 1991. High level secretion of correctly processed recombinant human interleukin-1β in Kluyveromyces lactis. Gene. In press.
Wray, L.V., Witte, M.M., Dickson, R.C. and Riley, M.I. 1987. Characterization of a positive regulatory gene, LAC9, that controls induction of the lactose-galactose regulon of Kluyveromyces lactis: Structural and functional relationships to GAL4 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7: 1111–1121.
Sleep, D., Belfield, G.P., Ballance, D.J., Steven, J., Jones, S., Evans, L.R., Moir, P.D. and Goodey, A.R. 1991. Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains that overexpress heterologous proteins. Bio/Technology 9: 183–187.
Rhône-Poulenc Santé 1989. Method for the microbiological preparation of human serum albumin and other heterologous proteins from yeast. Europ. Patent Appl. N° 89 10480.
Ito, H., Fukuda, Y., Murata, K. and Kimura, A. 1983. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J. Bacteriol. 153: 163–168.
Fournier, A., Fleer, R., Yeh, P. and Mayaux, J.-F. 1990. The primary structure of the 3-phosphoglycerate kinase (PGK) gene from Kluyveromyces lactis. Nuc. Acids Res. 18: 365.
Lue, N.F., Chasman, D.I., Buchman, A.R. and Kornberg, R. 1987. Interaction of GAL4 and GAL80 gene regulatory proteins in vivo. Mol. Cell. Biol. 7: 3446–3451.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fleer, R., Yeh, P., Amellal, N. et al. Stable Multicopy Vectors for High–Level Secretion of Recombinant Human Serum Albumin by Kluyveromyces Yeasts. Nat Biotechnol 9, 968–975 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1091-968
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1091-968
This article is cited by
-
High level production of stable human serum albumin in Pichia pastoris and characterization of the recombinant product
Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering (2022)
-
Surface Display of Human Serum Albumin on Bacillus subtilis Spores for Oral Administration
Current Microbiology (2012)
-
The extremely high level expression of human serum albumin in the milk of transgenic mice
Transgenic Research (2012)
-
Heterologous expression of glucose oxidase in the yeast Kluyveromyces marxianus
Microbial Cell Factories (2010)
-
Gene copy number and polyploidy on products formation in yeast
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2010)