Abstract
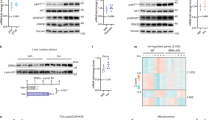
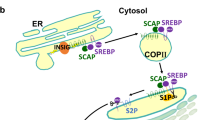
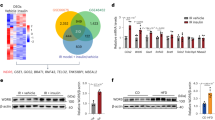
Insulin receptor substrate 2 (IRS-2) is the main mediator of insulin signalling in the liver, controlling insulin sensitivity. Sterol regulatory element binding proteins (SREBPs) have been established as transcriptional regulators of lipid synthesis. Here, we show that SREBPs directly repress transcription of IRS-2 and inhibit hepatic insulin signalling. The IRS-2 promoter is activated by forkhead proteins through an insulin response element (IRE). Nuclear SREBPs effectively replace and interfere in the binding of these transactivators, resulting in inhibition of the downstream PI(3)K/Akt pathway, followed by decreased glycogen synthesis. These data suggest a molecular mechanism for the physiological switching from glycogen synthesis to lipogenesis and hepatic insulin resistance that is associated with hepatosteatosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
White, M.F. The IRS-signalling system: a network of docking proteins that mediate insulin action. Mol. Cell Biochem. 182, 3–11 (1998).
Rother, K.I. et al. Evidence that IRS-2 phosphorylation is required for insulin action in hepatocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 17491–17497 (1998).
Kido, Y. et al. Tissue-specific insulin resistance in mice with mutations in the insulin receptor, IRS-1, and IRS-2. J. Clin. Invest. 105, 199–205 (2000).
Brown, M.S., Ye, J., Rawson, R.B. & Goldstein, J.L. Regulated intramembrane proteolysis: a control mechanism conserved from bacteria to humans. Cell 100, 391–398 (2000).
Shimano, H. Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBPs): transcriptional regulators of lipid synthetic genes. Prog. Lipid Res. 40, 439–452 (2001).
Horton, J.D., Goldstein, J.L. & Brown, M.S. SREBPs: activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J. Clin. Invest. 109, 1125–1131 (2002).
Kerouz, N.J., Horsch, D., Pons, S. & Kahn, C.R. Differential regulation of insulin receptor substrates-1 and -2 (IRS-1 and IRS-2) and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase isoforms in liver and muscle of the obese diabetic (ob/ob) mouse. J. Clin. Invest. 100, 3164–3172 (1997).
Shimomura, I. et al. Decreased IRS-2 and increased SREBP-1c lead to mixed insulin resistance and sensitivity in livers of lipodystrophic and ob/ob mice. Mol. Cell 6, 77–86 (2000).
Yahagi, N. et al. Absence of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 (SREBP-1) ameliorates fatty livers but not obesity or insulin resistance in Lep(ob)/Lep(ob) mice. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 19353–19357 (2002).
Shimano, H. et al. Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 as a key transcription factor for nutritional induction of lipogenic enzyme genes. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 35832–35839 (1999).
Liang, G. et al. Diminished hepatic response to fasting/refeeding and liver X receptor agonists in mice with selective deficiency of sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c. J. Biol. Chem 277, 9520–9528 (2002).
Zhang, J. et al. Insulin inhibits transcription of IRS-2 gene in rat liver through an insulin response element (IRE) that resembles IREs of other insulin-repressed genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98, 3756–3761 (2001).
Vassen, L., Wegrzyn, W. & Klein-Hitpass, L. Human insulin receptor substrate-2 (IRS-2) is a primary progesterone response gene. Mol. Endocrinol. 13, 485–494 (1999).
Nakae, J., Kitamura, T., Silver, D.L. & Accili, D. The forkhead transcription factor Foxo1 (Fkhr) confers insulin sensitivity onto glucose-6-phosphatase expression. J. Clin. Invest. 108, 1359–1367 (2001).
Hall, R.K. et al. Regulation of phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-1 gene expression by insulin. The role of winged helix/forkhead proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 30169–30175 (2000).
Ayala, J.E. et al. Conservation of an insulin response unit between mouse and human glucose-6-phosphatase catalytic subunit gene promoters: transcription factor FKHR binds the insulin response sequence. Diabetes 48, 1885–1889 (1999).
Kops, G.J. et al. Direct control of the Forkhead transcription factor AFX by protein kinase B. Nature 398, 630–634 (1999).
Biggs, W.H., 3rd, Meisenhelder, J., Hunter, T., Cavenee, W.K. & Arden, K.C. Protein kinase B/Akt-mediated phosphorylation promotes nuclear exclusion of the winged helix transcription factor FKHR1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 7421–7426 (1999).
Hirota, K. et al. Hepatocyte nuclear factor-4 is a novel downstream target of insulin via FKHR as a signal-regulated transcriptional inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 13056–13060 (2003).
Tang, E.D., Nunez, G., Barr, F.G. & Guan, K.L. Negative regulation of the forkhead transcription factor FKHR by Akt. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 16741–16746 (1999).
Puigserver, P. et al. Insulin-regulated hepatic gluconeogenesis through FOXO1–PGC-1α interaction. Nature 423, 550–555 (2003).
Yamamoto, T. et al. SREBP-1 interacts with HNF-4α and interferes with PGC-1 recruitment to suppress hepatic gluconeogenic genes. J. Biol. Chem. DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M310333200 (2004).
Tobe, K. et al. Increased expression of the sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 gene in insulin receptor substrate-2(−/−) mouse liver. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 38337–38340 (2001).
Matsuzaka, T. et al. Insulin-independent induction of SREBP-1c expression in the livers of streptozotocin-treated mice. Diabetes 53, 560–569 (2004).
Shimano, H. et al. Overproduction of cholesterol and fatty acids causes massive liver enlargement in transgenic mice expressing truncated SREBP-1a. J. Clin. Invest. 98, 1575–1584 (1996).
Shimano, H. et al. Isoform 1c of sterol regulatory element binding protein is less active than isoform 1a in livers of transgenic mice and in cultured cells. J. Clin. Invest. 99, 846–854 (1997).
He, T.C. et al. A simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 2509–2514 (1998).
Murakami, K. et al. A novel insulin sensitizer acts as a coligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-α (PPAR-α) and PPAR-γ: effect of PPAR-α activation on abnormal lipid metabolism in liver of Zucker fatty rats. Diabetes 47, 1841–1847 (1998).
Vassen, L., Wegrzyn, W. & Klein-Hitpass, L. Human insulin receptor substrate-2: gene organization and promoter characterization. Diabetes 48, 1877–1880 (1999).
Daitoku, H., Yamagata, K., Matsuzaki, H., Hatta, M. & Fukamizu, A. Regulation of PGC-1 promoter activity by protein kinase B and the forkhead transcription factor FKHR. Diabetes 52, 642–649 (2003).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to M.S. Brown and J.L. Goldstein for continuous support of the SREBP projects. We also thank H. Kurose for technical support with the adenoviral vectors, and A.H. Hasty for critical reading of the manuscript. We acknowledge S. Ishibashi, T. Gotoda, J. Osuga and K. Murakami for helpful discussions. This work was supported by grants-in-aid from the Ministry of Science, Education, Culture and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information Figures
Supplementary Information, Fig. S1 (PDF 659 kb)
Supplementary Information, Fig. S2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ide, T., Shimano, H., Yahagi, N. et al. SREBPs suppress IRS-2-mediated insulin signalling in the liver. Nat Cell Biol 6, 351–357 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1111
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1111
This article is cited by
-
The prognostic significance of insulin resistance in COVID-19: a review
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders (2024)
-
Emerging roles of TFE3 in metabolic regulation
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
The COVID-19-diabetes mellitus molecular tetrahedron
Molecular Biology Reports (2022)
-
Alterations in cellular and organellar phospholipid compositions of HepG2 cells during cell growth
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
TNF-Receptor-1 inhibition reduces liver steatosis, hepatocellular injury and fibrosis in NAFLD mice
Cell Death & Disease (2020)