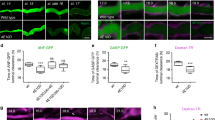
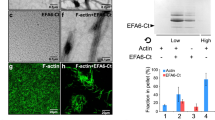
Abstract
The exocyst is a multiprotein complex essential for tethering secretory vesicles to specific domains of the plasma membrane for exocytosis1,2,3. Here, we report that the exocyst component Exo70 interacts with the Arp2/3 complex, a key regulator of actin polymerization4,5. We further show that the exocyst–Arp2/3 interaction is regulated by epidermal growth factor (EGF) signalling. Inhibition of Exo70 by RNA interference (RNAi) or antibody microinjection blocks the formation of actin-based membrane protrusions and affects various aspects of cell motility. We propose that Exo70, in addition to functioning in exocytosis, also regulates actin at the leading edges of migrating cells, therefore coordinating cytoskeleton and membrane traffic during cell migration.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Novick, P. & Guo, W. Ras family therapy: Rab, Rho and Ral talk to the exocyst. Trends Cell Biol. 12, 247–249 (2002).
Lipschutz, J. & Mostov, K. Exocytosis: the many masters of the exocyst. Curr. Biol. 12, R212–R214 (2002).
Hsu, S-C, TerBush, D., Abraham, M. & Guo, W. The exocyst complex in polarized exocytosis. Int. Rev. Cytol. 233, 243–265 (2004).
Pollard, T. D., Borisy, G. G. Cellular motility driven by assembly and disassembly of actin filaments. Cell 112, 453–465 (2003).
Ridley, A. J. et al. Cell migration: integrating signals from front to back. Science 302, 1704–1709 (2003).
Bretscher, M. S. Getting membrane flow and the cytoskeleton to cooperate in moving cells. Cell 87, 601–606 (1996).
Wang, S. et al. The mammalian exocyst, a complex required for exocytosis, inhibits tubulin polymerization. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 35958–35966 (2004).
Xu, K. F. et al. Interaction of BIG2, a brefeldin A-inhibited guanine nucleotide-exchange protein, with exocyst protein Exo70. Proc. Natl Acad. Sc.i USA 102, 2784–2789 (2005).
Rosse, C. et al. RalB mobilizes the exocyst to drive cell migration. Mol. Cell Biol. 26, 727–734 (2006).
Sugihara, K. et al. The exocyst complex binds the small GTPase RalA to mediate filopodia formation. Nature Cell Biol. 4, 73–78 (2002).
Takaya, A., Ohba, Y., Kurokawa, K. & Matsuda, M. RalA activation at nascent lamellipodia of epidermal growth factor-stimulated Cos7 cells and migrating Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 2549–2557 (2004).
Welch, M. D., DePace, A. H., Verma, S., Iwamatsu, A. & Mitchison, T. J. The human Arp2/3 complex is composed of evolutionarily conserved subunits and is localized to cellular regions of dynamic actin filament assembly. J. Cell Biol. 138, 375–384 (1997).
Machesky, L. M. et al. Mammalian actin-related protein 2/3 complex localizes to regions of lamellipodial protrusion and is composed of evolutionarily conserved proteins. Biochem. J. 328, 105–112 (1997).
Machesky, L. M. & Insall, R. H. Scar1 and the related Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein, WASP, regulate the actin cytoskeleton through the Arp2/3 complex. Curr. Biol. 8, 1347–1356 (1998).
Marchand, J. B., Kaiser, D. A., Pollard, T. D. & Higgs, H. N. Interaction of WASP/Scar proteins with actin and vertebrate Arp2/3 complex. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 76–82 (2001).
Inoue, M., Chang, L., Hwang, J., Chiang, S. H. & Saltiel, A. R. The exocyst complex is required for targeting of Glut4 to the plasma membrane by insulin. Nature 422, 629–633 (2003).
Nobes, C. D. & Hall, A. Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell 81, 53–62 (1995).
Acknowledgements
We thank T. Svitkina, M. Welch, B. Goode, S. Zigmond, M. Chou, J. Peterson and C. Yang for reagents and numerous constructive discussions during the research. This work is supported by the National Institutes of Health (NIH), the American Cancer Society (ACS), the American Heart Association (AHA) and the Pew Scholars Program for Biomedical Sciences to W.G.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary figures S1, S2 and Supplementary materials (PDF 291 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zuo, X., Zhang, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Exo70 interacts with the Arp2/3 complex and regulates cell migration. Nat Cell Biol 8, 1383–1388 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1505
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1505