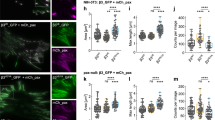
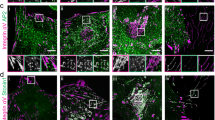
Abstract
Integrin-mediated adhesion regulates membrane binding sites for Rac1 within lipid rafts. Detachment of cells from the substratum triggers the clearance of rafts from the plasma membrane through caveolin-dependent internalization. The small GTPase Arf6 and microtubules also regulate Rac-dependent cell spreading and migration, but the mechanisms are poorly understood. Here we show that endocytosis of rafts after detachment requires F-actin, followed by microtubule-dependent trafficking to recycling endosomes. When cells are replated on fibronectin, rafts exit from recycling endosomes in an Arf6-dependent manner and return to the plasma membrane along microtubules. Both of these steps are required for the plasma membrane targeting of Rac1 and for its activation. These data therefore define a new membrane raft trafficking pathway that is crucial for anchorage-dependent signalling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
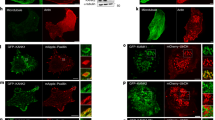
References
del Pozo, M. A. et al. Integrins regulate Rac targeting by internalization of membrane domains. Science 303, 839–842 (2004).
del Pozo, M. A. et al. Phospho-caveolin-1 mediates integrin-regulated membrane domain internalization. Nature Cell Biol. 7, 901–908 (2005).
Palazzo, A. F., Eng, C. H., Schlaepfer, D. D., Marcantonio, E. E. & Gundersen, G. G. Localized stabilization of microtubules by integrin- and FAK-facilitated Rho signaling. Science 303, 836–839 (2004).
Vasanji, A., Ghosh, P. K., Graham, L. M., Eppell, S. J. & Fox, P. L. Polarization of plasma membrane microviscosity during endothelial cell migration. Dev. Cell 6, 29–41 (2004).
Golub, T. & Pico, C. Spatial control of actin-based motility through plasmalemmal PtdIns(4,5)P2-rich raft assemblies. Biochem. Soc. Symp. 72, 119–127 (2005).
Simons, K. & Toomre, D. Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 1, 31–39 (2000).
Hancock, J. F. Lipid rafts: contentious only from simplistic standpoints. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 456–462 (2006).
Manes, S. et al. Membrane raft microdomains mediate front–rear polarity in migrating cells. EMBO J. 18, 6211–6220 (1999).
Gaus, K., Le Lay, S., Balasubramanian, N. & Schwartz, M. A. Integrin-mediated adhesion regulates membrane order. J. Cell Biol. 174, 725–734 (2006).
Donaldson, J. G. Multiple roles for Arf6: sorting, structuring, and signaling at the plasma membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 41573–41576 (2003).
D'Souza-Schorey, C. & Chavrier, P. ARF proteins: roles in membrane traffic and beyond. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 347–358 (2006).
Sabe, H. Requirement for Arf6 in cell adhesion, migration, and cancer cell invasion. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 134, 485–489 (2003).
Radhakrishna, H., Al-Awar, O., Khachikian, Z. & Donaldson, J. G. ARF6 requirement for Rac ruffling suggests a role for membrane trafficking in cortical actin rearrangements. J. Cell Sci. 112, 855–866 (1999).
Cheung, H. T. & Terry, D. S. Effects of nocodazole, a new synthetic microtubule inhibitor, on movement and spreading of mouse peritoneal macrophages. Cell Biol. Int. Rep. 4, 1125–1129 (1980).
Gundersen, G. G. & Bulinski, J. C. Selective stabilization of microtubules oriented toward the direction of cell migration. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 85, 5946–5950 (1988).
Krendel, M., Zenke, F. T. & Bokoch, G. M. Nucleotide exchange factor GEF-H1 mediates cross-talk between microtubules and the actin cytoskeleton. Nature Cell Biol. 4, 294–301 (2002).
Le, P. U. & Nabi, I. R. Distinct caveolae-mediated endocytic pathways target the Golgi apparatus and the endoplasmic reticulum. J. Cell Sci. 116, 1059–1071 (2003).
Prigozhina, N. L. & Waterman-Storer, C. M. Protein kinase D-mediated anterograde membrane trafficking is required for fibroblast motility. Curr. Biol. 14, 88–98 (2004).
Presley, J. F. et al. ER-to-Golgi transport visualized in living cells. Nature 389, 81–85 (1997).
Pelkmans, L., Kartenbeck, J. & Helenius, A. Caveolar endocytosis of simian virus 40 reveals a new two-step vesicular-transport pathway to the ER. Nature Cell Biol. 3, 473–483 (2001).
Sabharanjak, S., Sharma, P., Parton, R. G. & Mayor, S. GPI-anchored proteins are delivered to recycling endosomes via a distinct cdc42-regulated, clathrin-independent pinocytic pathway. Dev. Cell 2, 411–423 (2002).
Ullrich, O., Reinsch, S., Urbe, S., Zerial, M. & Parton, R. G. Rab11 regulates recycling through the pericentriolar recycling endosome. J. Cell Biol. 135, 913–924 (1996).
Yamashiro, D. J. & Maxfield, F. R. Acidification of endocytic compartments and the intracellular pathways of ligands and receptors. J. Cell Biochem. 26, 231–246 (1984).
Weigert, R., Yeung, A. C., Li, J. & Donaldson, J. G. Rab22a regulates the recycling of membrane proteins internalized independently of clathrin. Mol. Biol. Cell 15, 3758–3770 (2004).
D'Souza-Schorey, C. & Chavrier, P. ARF6 targets recycling vesicles to the plasma membrane: insights from an ultrastructural investigation. J. Cell Biol. 140, 603–616 (1998).
Zhang, Q., Calafat, J., Janssen, H. & Greenberg, S. ARF6 is required for growth factor- and rac-mediated membrane ruffling in macrophages at a stage distal to rac membrane targeting. Mol. Cell. Biol. 19, 8158–8168 (1999).
Song, J., Khachikian, Z., Radhakrishna, H. & Donaldson, J. G. Localization of endogenous ARF6 to sites of cortical actin rearrangement and involvement of ARF6 in cell spreading. J. Cell Sci. 111, 2257–2267 (1998).
Price, L. S., Leng, J., Schwartz, M. A. & Bokoch, G. M. Activation of Rac and Cdc42 by integrins mediates cell spreading. Mol. Biol. Cell 9, 1863–1871 (1998).
del Pozo, M. A., Price, L. S., Alderson, N. B., Ren, X. D. & Schwartz, M. A. Adhesion to the extracellular matrix regulates the coupling of the small GTPase Rac to its effector PAK. EMBO J. 19, 2008–2014 (2000).
Santy, L. C. & Casanova, J. E. Activation of ARF6 by ARNO stimulates epithelial cell migration through downstream activation of both Rac1 and phospholipase D. J. Cell Biol. 154, 599–610 (2001).
Goldfinger, L. E., Ptak, C., Jeffery, E. D., Shabanowitz, J., Hunt, D. F., Ginsberg, M. H. RLIP76 (RalBP1) is an R-Ras effector that mediates adhesion-dependent Rac activation and cell migration. J. Cell Biol. 174, 877–888 (2006).
Santy, L. C. Characterization of a fast cycling ADP-ribosylation factor 6 mutant. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 40185–40188 (2002).
Schmoranzer, J., Kreitzer, G. & Simon, S. M. Migrating fibroblasts perform polarized, microtubule-dependent exocytosis towards the leading edge. J. Cell Sci. 116, 4513–4519 (2003).
Ren, Y., Li, R., Zheng, Y. & Busch, H. Cloning and characterization of GEF-H1, a microtubule-associated guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rac and Rho GTPases. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 34954–34960 (1998).
Kawasaki, Y. et al. Asef, a link between the tumor suppressor APC and G-protein signaling. Science 289, 1194–1197 (2000).
Torgersen, M. L., Skretting, G., van Deurs, B. & Sandvig, K. Internalization of cholera toxin by different endocytic mechanisms. J. Cell Sci. 114, 3737–3747 (2001).
Nabi, I. R. & Le, P. U. Caveolae/raft-dependent endocytosis. J. Cell Biol. 161, 673–677 (2003).
Nichols, B. J. A distinct class of endosome mediates clathrin-independent endocytosis to the Golgi complex. Nature Cell Biol. 4, 374–378 (2002).
Caroni, P. New EMBO members' review: actin cytoskeleton regulation through modulation of PI(4,5)P2 rafts. EMBO J. 20, 4332–4336 (2001).
Pletjushkina, O. J. et al. Induction of cortical oscillations in spreading cells by depolymerization of microtubules. Cell Motil. Cytoskel. 48, 235–244 (2001).
Rosania, G. R. & Swanson, J. A. Microtubules can modulate pseudopod activity from a distance inside macrophages. Cell Motil. Cytoskel. 34, 230–245 (1996).
Grande-Garcia, A. et al. Caveolin-1 regulates cell polarization and directional migration through Src kinase and Rho GTPases. J. Cell Biol. 177, 683–694 (2007).
Etienne-Manneville, S. Actin and microtubules in cell motility: which one is in control? Traffic 5, 470–477 (2004).
Moissoglu, K., Slepchenko, B. M., Meller, N., Horwitz, A. F. & Schwartz, M. A. In vivo dynamics of Rac–membrane interactions. Mol. Biol. Cell 17, 2770–2779 (2006).
Santy, L. C., Ravichandran, K. S. & Casanova, J. E. The DOCK180/Elmo complex couples ARNO-mediated Arf6 activation to the downstream activation of Rac1. Curr. Biol. 15, 1749–1754 (2005).
Cotton, M. et al. Endogenous ARF6 interacts with Rac1 upon angiotensin II stimulation to regulate membrane ruffling and cell migration. Mol. Biol. Cell 18, 501–511 (2007).
Prag, S. et al. Activated ezrin promotes cell migration through recruitment of the GEF Dbl to lipid rafts and preferential downstream activation of Cdc42. Mol. Biol. Cell 18, 2935–2948 (2007).
Ren, M. et al. Hydrolysis of GTP on rab11 is required for the direct delivery of transferrin from the pericentriolar recycling compartment to the cell surface but not from sorting endosomes. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 6187–6192 (1998).
Choi, S. et al. ARF6 and EFA6A regulate the development and maintenance of dendritic spines. J. Neurosci. 26, 4811–4819 (2006).
Acknowledgements
We thank Robert Nabi (University of British Colombia, Vancouver, Canada) for generously providing anti-AMF antibody; Richard Kahn (Emory University School of Medicine, Atlanta GA) for antibodies to Arfs 1, 3, 4 and 5; Jennifer Lippincott-Schwartz (NICHHD, NIH, Bethesda, MD) for VSVG-GEP; and Vivek Malhotra (University of California, San Diego, CA) for PKD constructs. Anti-tubulin antibody was obtained from the Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank. This work was supported by a US Public Health Service grant RO1 GM47214 to M.A.S.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
N.B. designed and carried out experiments, analysed data and wrote the manuscript. D.W.S. carried out experiments. J.D.C. and J.E.C. provided reagents and advice. M.A.S. designed experiments, analysed data and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
Supplementary figures S1, S2, S3, S4, S5, S6 and S7 (PDF 3618 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balasubramanian, N., Scott, D., Castle, J. et al. Arf6 and microtubules in adhesion-dependent trafficking of lipid rafts. Nat Cell Biol 9, 1381–1391 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1657
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb1657
This article is cited by
-
CNK2 promotes cancer cell motility by mediating ARF6 activation downstream of AXL signalling
Nature Communications (2023)
-
A mobile endocytic network connects clathrin-independent receptor endocytosis to recycling and promotes T cell activation
Nature Communications (2018)
-
A cell-based high-throughput screening assay system for inhibitor compounds of antigen presentation by HLA class II molecule
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Integrin-Dependent Regulation of Small GTPases: Role in Cell Migration
Journal of the Indian Institute of Science (2017)
-
Basigin-mediated redistribution of CD98 promotes cell spreading and tumorigenicity in hepatocellular carcinoma
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2015)