Abstract
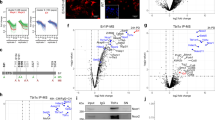
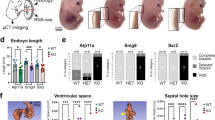
The placenta and cardiovascular system are the first organ systems to form during mammalian embryogenesis. We show here that a single gene is critical for development of both. The Hand1 gene, previously called Hxt, eHAND and Thingl, encodes a basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factor that starts to be expressed during pre-implantation development. After implantation, Handl expression is restricted to placental trophoblast cells and later to embryonic cardiac and neural crest cells1–3. We generated Hand1-null mutant mice by gene targetting. Homozygous mutant embryos arrested by embryonic day (E) 7.5 of gestation with defects in trophoblast giant cell differentiation. This early mortality could be rescued by aggregation of mutant embryos with wild-type tetraploid embryos, which contribute wild-type cells to the trophoblast, but not the embryo. By E10.5, however, the Hand1-null fetuses derived from tetraploid chimaeras died due to cardiac failure. Their heart tubes showed abnormal looping and ventricular myocardial differentiation. Therefore, Handl is essential for differentiation of both trophoblast and cardiomyocytes, which are embryologically distinct cell lineages.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cross, J.C. et al. Hxt encodes a basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor that regulates trophoblast cell development. Development 121, 2513–2523 (1995).
Cserjesi, P., Brown, D., Lyons, G.E. & Olson, E.N. Expression of the novel basic helix-loop-helix gene eHAND in neural crest derivatives and extraembryonic membranes during mouse development. Dev. Biol. 170, 664–678 (1995).
Hollenberg, S.M., Sternglanz, R., Cheng, P.F. & Weintraub, H. Identification of a new family of tissue-specific basic helix-loop-helix proteins with a two-hybrid system. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 3813–3822 (1995).
Srivastava, D., Cserjesi, P. & Olson, E.N. A subclass of bHLH proteins required for cardiac morphogenesis. Science 270, 1995–1999 (1995).
Cross, J.C., Werb, Z. & Fisher, S.J. Implantation and the placenta: key pieces of the development puzzle. Science 266, 1508–1518 (1994).
Copp, A.J. Death before birth: clues from gene knockouts and mutations. Trends Genet. 11, 87–93 (1995).
Knudsen, T.B., Blackburn, M.R., Chinsky, J.M., Airhart, M.J. & Kellems, R.E. Ontogeny of adenosine deaminase in the mouse decidua and placenta: immunolocalization and embryo transfer studies. Biol. Reprod. 44, 171–184 (1991).
Alexander, C.M. et al. Expression and function of matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors at the maternal-embryonic boundary during mouse embryo implantation. Development 122, 1723–1736 (1996).
Nieto, M.A., Bennett, M.F., Sargent, M.G. & Wilkinson, D.G. Cloning and developmental expression of Sna, a murine homologue of the Drosophila snail gene. Development 116, 227–237 (1992).
Smith, D.E., Del Amo, F.F. & Gridley, T. Isolation of Sna, a mouse gene homologous to the Drosophila genes snail and escargot: its expression pattern suggests multiple roles during postimplantation development. Development 116, 1033–1039 (1992).
Guillemot, F., Nagy, A., Auerbach, A., Rossant, J. & Joyner, A.L. Essential role of Mash-2 in extraembryonic development. Nature 371, 333–336 (1994).
Lescisin, K., Varmuza, S. & Rossant, J. Isolation and characterization of a novel trophoblast-specif ic cDNA in the mouse. Genes Dev. 2, 1639–1646 (1988).
Jackson, L.L., Colosi, P., Talamantes, F. & Linzer, D.I. Molecular cloning of mouse placental lactogen cDNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 8496–8500 (1986).
Cheng, A.K. & Robertson, E.J. The murine LIM-kinase gene (limk) encodes a novel serine threonine kinase expressed predominantly in trophoblast giant cells and the developing nervous system. Mech. Dev. 52, 187–197 (1995).
Ilgren, E.B. Control of trophoblastic growth. Placenta 4, 307–328 (1983).
Olson, E.N. & Srivastava, D. Molecular pathways controlling heart development. Science 272, 671–676 (1996).
Nagy, A. & Rossant, J. Production of completely ES cell-derived fetuses, in Gene targeting: A practical Approach (ed. Joyner, A.) 147–179 (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1993).
Friedrich, G. & Soriano, P. Promoter traps in embryonic stem cells: a genetic screen to identify and mutate developmental genes in mice. Genes Dev. 5, 1513–1523 (1991).
Srivastava, D. et al. Regulation of cardiac mesodermal and neural crest development by the bHLH transcription factor, dHAND. Nature Genet. 16, 154–160 (1997).
Lyons, I. et al. Myogenic and morphogenic defects in the heart tubes of murine embryos lacking the homeo box gene Nkx2-5. Genes Dev. 9, 1654–1666 (1995).
Biben, C. & Harvey, R.P. Homeodomain factor Nkx2-5 controls left/right asymmetric expression of bHLH gene eHand during murine heart development. Genes Dev. 11, 1357–1369 (1997).
Shalaby, F. et a1. Failure of blood-island formation and vasculogenesis in Flk-1-deficient mice. Nature 376, 62–66 (1995).
Wurst, W. & Joyner, A. Production of targeted embryonic stem cell clones. in Gene Targeting: A Practical Approach (ed. Joyner, A.) 33–61 (Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1993).
Hogan, B., Constantini, F. & Lacy, E. Manipulating the Mouse Embryo : A Laboratory Manual, (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, 1986).
Millen, K. & Hui, C. Radioactive hybridization of tissue sections, in A Laboratory Guide to RNA: Isolation, Analysis and Synthesis (ed. Krieg, P.) 339–355 (Wiley-Liss, New York, 1996).
Lee, M.H., Reynisdottir, I. & Massague, J. Cloning of p57KIP2, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with unique domain structure and tissue distribution. Genes Dev. 9, 639–649 (1995).
Kubalak, S.W., Miller-Hance, W.C., O'Brien, T.X., Dyson, E. & Chien, K.R. Chamber specification of atrial myosin light chain-2 expression precedes septation during murine cardiogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 16961–16970 (1994).
Sassoon, D.A., Garner, I. & Buckingham, M. Transcripts of alpha-cardiac and alpha-skeletal actins are early markers for myogenesis in the mouse embryo. Development 104, 155–164 (1988).
Lints, T.J., Parsons, L.M., Hartley, L., Lyons, I. & Harvey, R.P. Nkx-2.5: a novel murine homeobox gene expressed in early heart progenitor cells and their myogenic descendants. Development 119, 419–431 (1993).
Arceci, R.J., King, A.A.J., Simon, M.C., Orkin, S.H. & Wilson, D.B. Mouse GATA-4: a retinoic acid-inducible GATA-binding transcription factor expressed in endodermally derived tissues and heart. Mol. Cell. Biol. 13, 2235–2246 (1993).
Edmondson, D.G., Lyons, G.E., Martin, J.F. & Olson, E.N. Mef2 gene expression marks the cardiac and skeletal muscle lineages during mouse embryogenesis. Development 120, 1251–1263 (1994).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riley, P., Anaon-Cartwight, L. & Cross, J. The Hand1 bHLH transcription factor is essential for placentation and cardiac morphogenesis. Nat Genet 18, 271–275 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0398-271
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0398-271
This article is cited by
-
RGS2 promotes estradiol biosynthesis by trophoblasts during human pregnancy
Experimental & Molecular Medicine (2023)
-
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell–Based Modeling of Single-Ventricle Congenital Heart Diseases
Current Cardiology Reports (2023)
-
Mapping cis-regulatory elements in the midgestation mouse placenta
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
Hyperactivated Wnt-β-catenin signaling in the absence of sFRP1 and sFRP5 disrupts trophoblast differentiation through repression of Ascl2
BMC Biology (2020)
-
Spatiotemporal coordination of trophoblast and allantoic Rbpj signaling directs normal placental morphogenesis
Cell Death & Disease (2019)