Abstract
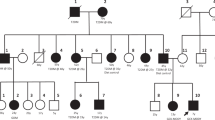
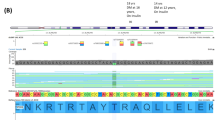
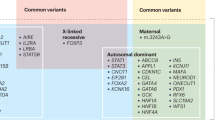
We describe a codon 299 mutation in the glucokinase gene in a British pedigree with maturity–onset diabetes of the young (MODY) resulting in a substitution of glycine to arginine. One out of fifty patients diagnosed with classical late–onset type 2 diabetes mellitus was also found to have this mutation. All nine relatives of this patient who have inherited the mutation have type 2 diabetes, although six others without the mutation are also present with diabetes. The discovery that glucokinase mutations can cause MODY and was also found in ten affected members of a pedigree with type 2 diabetes in which MODY had not previously been considered indicates that diagnosis based on molecular pathology will be helpful in understanding the aetiology of type 2 diabetes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnett, A.H., Eff, C., Leslie, R.D.G. & Pyke, D.A. Diabetes in identical twins. Diabetologia 20, 87–93 (1981).
O'Rahilly, S., Wainscoat, J.S. & Turner, R.C. Type 2 (non-insulin dependent) diabetes mellitus: new genetics for old nightmares. Diabetologia 31, 407–414 (1988).
Froguel, Ph. et al. The glucokinase locus on chromosome 7p is closely linked to early onset non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature 356, 162–164 (1992).
Hattersley, A.T. et al. Type 2 diabetes is linked to the glucokinase gene in a large pedigree. Lancet 339, 1307–1310 (1992).
Vionnet, N. et al. Nonsense mutation in the glucokinase gene causes early-onset non-insulin-dependent diabetes. Nature 356, 721–722 (1992).
Meglasson, M.D. & Matschinsky, F.M. New perspectives on pancreatic islet glucokinase. Am. J. Physiol. 246, E1–E13 (1984).
Stoffel, M. et al. Human glucokinase gene: isolation, characterization, and identification of two missense mutations linked to early-onset non-insulin-dependent (Type 2) diabetes mellitus. Proc. natn Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (in the press).
Orita, M., Suzuki, Y., Sekiya, T. & Hayashi, K. Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics 5, 874–879 (1989).
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. & Coulson, A.R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 5463–5467 (1977).
Lathrop, G.M. & Ireland, J.M. Easy calculation of LOD scores and genetic risks on small computers. Am. J. hum. Genet. 36, 460–465 (1985).
UK Prospective Diabetes Study Group. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) VIII. Study design, progress and performance. Diabetologia 34, 877–890 (1991).
O'Rahilly, S., Patel, P., Wainscoat, J.S. & Turner, R.C. Analysis of the HepG2/erythrocyte glucose transporter locus in a family with Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes and obesity. Diabetologia 32, 266–269 (1989).
Bell, G.I. et al. Gene for non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (maturity-onset diabetes of the young subtype) is linked to DNA polymorphism on human chromosome 20q. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 1484–1488 (1991).
O'Rahilly, S. et al. Linkage analysis of the human insulin receptor gene in Type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetic families and a family with maturity onset diabetes of the young. Diabetologia 31, 792–797 (1988).
Andreone, T.L., Printz, R.L., Pilkis, S.J., Magnuson, M.A. & Granner, D.K. The amino acid sequence of rat liver glucokinase deduced from cloned cDNA. J. biol. Chem. 264, 363–369 (1989).
Tanizawa, Y., Koranyi, L.I., Welling, C.M. & Permutt, M.A. Human liver glucokinase gene: cloning and sequence determination of two alternatively spliced cDNAs. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 7294–7297 (1991).
Nishi, S., Seino, S. & Bell, G.I. Human hexokinsise: sequences of amino- and carboxyl-terminal halves are homologous. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 157, 937–943 (1988).
Arora, K.K., Fanciulli, M. & Pedersen, P.L. Glucose phosphorylation in tumor cells: cloning, sequence, and overexpression in active form of a full-length cDNA encoding a mitochondrial bindable form of hexokinase. J. biol. Chem. 265, 6481–6488 (1990).
Fajans, S.S. Scope and heterogeneous nature of MODY. Diabetes Care 13, 49–64 (1990).
Lo, Y-M.D. et al. Analysis of complex genetic systems by ARMS-SSCP: application to HLA genotyping. Nucl. Acids. Res. 20, 1005–1009 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stoffel, M., Patel, P., Lo, YM. et al. Missense glucokinase mutation in maturity–onset diabetes of the young and mutation screening in late–onset diabetes. Nat Genet 2, 153–156 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1092-153
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1092-153
This article is cited by
-
Causal variants in Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY) – A systematic review
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2021)
-
Hepatic DNA methylation modifications in early development of rats resulting from perinatal BPA exposure contribute to insulin resistance in adulthood
Diabetologia (2013)
-
Serum levels of pancreatic stone protein (PSP)/reg1A as an indicator of beta-cell apoptosis suggest an increased apoptosis rate in hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha (HNF1A-MODY) carriers from the third decade of life onward
BMC Endocrine Disorders (2012)
-
Monogenic Models: What Have the Single Gene Disorders Taught Us?
Current Diabetes Reports (2012)
-
Obesity induced by a pair-fed high fat sucrose diet: methylation and expression pattern of genes related to energy homeostasis
Lipids in Health and Disease (2010)