Abstract
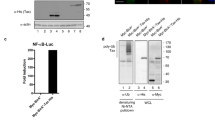
Cbl-b, a ring-type E3 ubiquitin protein ligase, is implicated in setting the threshold of T lymphocyte activation. The p85 regulatory subunit of phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase (PI3K) was identified as a substrate for Cbl-b. We have shown that Cbl-b negatively regulated p85 in a proteolysis-independent manner. Cbl-b is involved in the recruitment of p85 to CD28 and T cell antigen receptor ζ through its E3 ubiquitin ligase activity. The enhanced activation of Cbl-b−/− T cells was suppressed by the inhibition of PI3K. The results suggest a proteolysis-independent function for Cbl-b in the modification of protein recruitment.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chambers, C. A. & Allison, J. P. Costimulatory regulation of T cell function. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 11, 203–210 (1999).
Keane, M. M., Rivero-Lezcano, O. M., Mitchell, J. A., Robbins, K. C. & Lipkowitz, S. Cloning and characterization of cbl-b: a SH3 binding protein with homology to the c-cbl proto-oncogene. Oncogene 10, 2367–2377 (1995).
Thien, C. B. & Langdon, W. Y. Cbl: many adaptations to regulate protein tyrosine kinases. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2, 294–307 (2001).
Bachmaier, K. et al. Negative regulation of lymphocyte activation and autoimmunity by the molecular adaptor Cbl-b. Nature 403, 211–216 (2000).
Chiang, Y. J. et al. Cbl-b regulates the CD28 dependence of T-cell activation. Nature 403, 216–220 (2000).
Krawczyk, C. et al. Cbl-b is a negative regulator of receptor clustering and raft aggregation in T cells. Immunity 13, 463–473 (2000).
Miyake, S., Lupher, M. L. Jr, Druker, B. & Band, H. The tyrosine kinase regulator Cbl enhances the ubiquitination and degradation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor α. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 7927–7932 (1998).
Lee, P. S. et al. The Cbl protooncoprotein stimulates CSF-1 receptor multiubiquitination and endocytosis, and attenuates macrophage proliferation. EMBO J. 18, 3616–3628 (1999).
Levkowitz, G. et al. Ubiquitin ligase activity and tyrosine phosphorylation underlie suppression of growth factor signaling by c-Cbl/Sli-1. Mol. Cell 4, 1029–1040 (1999).
Joazeiro, C. A. et al. The tyrosine kinase negative regulator c-Cbl as a RING-type, E2-dependent ubiquitin-protein ligase. Science 286, 309–312 (1999).
Yokouchi, M. et al. Ligand-induced ubiquitination of the epidermal growth factor receptor involves the interaction of the c-Cbl RING finger and UbcH7. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 31707–31712 (1999).
Zheng, N., Wang, P., Jeffrey, P. D. & Pavletich, N. P. Structure of a c-Cbl-UbcH7 complex: RING domain function in ubiquitin-protein ligases. Cell 102, 533–539 (2000).
Hochstrasser, M. Ubiquitin-dependent protein degradation. Annu. Rev. Genet. 30, 405–439 (1996).
Hershko, A. & Ciechanover, A. The ubiquitin system. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 67, 425–479 (1998).
Fang, D. et al. Cbl-b, a RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase, targets phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase for ubiquitination in T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 4872–4878 (2001).
Han, J. et al. Role of substrates and products of PI 3-kinase in regulating activation of Rac-related guanosine triphosphatases by Vav. Science 279, 558–560 (1998).
Scheffner, M., Huibregtse, J. M., Vierstra, R. D. & Howley, P. M. The HPV-16 E6 and E6-AP complex functions as a ubiquitin-protein ligase in the ubiquitination of p53. Cell 75, 495–505 (1993).
Dhand, R. et al. PI 3-kinase: structural and functional analysis of intersubunit interactions. EMBO J. 13, 511–521 (1994).
Hu, P. & Schlessinger, J. Direct association of p110β phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase with p85 is mediated by an N-terminal fragment of p110β. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 2577–2583 (1994).
Rameh, L. E. & Cantley, L. C. The role of phosphoinositide 3-kinase lipid products in cell function. J. Biol. Chem. 274, 8347–8350 (1999).
Cai, Y.-C. et al. Selective CD28pYMNM mutations implicate phophatidylinositol 3-kinase in CD86-CD28-mediated costimulation. Immunity 3, 417–426 (1995).
Exley, M., Varticovski, L., Peter, M., Sancho, J. & Terhorst, C. Association of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase with a specific sequence of the T cell receptor ζ chain is dependent on T cell activation. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 15140–15146 (1994).
Shahinian, A. et al. Differential T cell costimulatory requirements in CD28-deficient mice. Science 261, 609–612 (1993).
Green, J. M. et al. Absence of B7-dependent responses in CD28-deficient mice. Immunity 1, 501–508 (1994).
Kaiser, P., Flick, K., Wittenberg, C. & Reed, S. I. Regulation of transcription by ubiquitination without proteolysis: Cdc34/SCF(Met30)-mediated inactivation of the transcription factor Met4. Cell 102, 303–314 (2000).
Hoppe, T. et al. Activation of a membrane-bound transcription factor by regulated ubiquitin/proteasome-dependent processing. Cell 102, 577–586 (2000).
de Aos, I. et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the CD3ɛ subunit of the T cell antigen receptor mediates enhanced association with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in Jurkat T cells. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 25310–25318 (1997).
Wulfing, C. & Davis, M. M. A receptor-cytoskeletal movement triggered by costimulation during T cell activation. Science 282, 2266–2269 (1998).
Viola, A., Schroeder, S., Sakakibara, Y. & Lanzavecchia, A. T lymphocyte costimulation mediated by reorganization of membrane microdomains. Science 283, 680–682 (1999).
Kane, L. P., Andres, P. G., Howland, K. C., Abbas, A. K. & Weiss, A. Akt provides the CD28 costimulatory signal for up-regulation of IL-2 and IFN-γ but not Th2 cytokines. Nature Immunol. 2, 37–44 (2001).
Zhang, W., Sloan-Lancaster, J., Kitchen, J., Trible, R. P. & Samelson, L. E. LAT: the ZAP-70 tyrosine kinase substrate that links T cell receptor to cellular activation. Cell 92, 83–92 (1998).
Okada, T., Maeda, A., Iwamatsu, A., Gotoh, K. & Kurosaki, T. BCAP: the tyrosine kinase substrate that connects B cell receptor to phosphoinositide 3-kinase activation. Immunity 13, 817–827 (2000).
Murphy, M. A. et al. Tissue hyperplasia and enhanced T-cell signalling via ZAP-70 in c-Cbl-deficient mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 18, 487–4882 (1998).
Naramura, M., Kole, H. K., Hu, R.-J. & Gu, H. Altered thymic positive selection and intracellular signals in Cbl-deficient mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 95, 15547–15552 (1998).
Wang, H. Y. et al. Cbl promotes ubiquitination of the T cell receptor ζ through an adaptor function of Zap-70. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 26004–26011 (2001).
Elly, C. et al. Tyrosine phosphorylation and complex formation of Cbl-b upon T cell receptor stimulation. Oncogene 18, 1153–1162 (1999).
Qiu, L. et al. Recognition and ubiquitination of Notch by Itch, a Hect-type E3 ubiquitin ligase. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 35734–35737 (2000).
Acknowledgements
We thank C. Elly, B. Gao and Y. Altman for technical assistance; A. Altman and members of the Division of Cell Biology for support and suggestions; M. Naramura and H. Gu for Cbl-b−/− mice; and J. Penninger for discussions. Supported by National Institutes of Health Grant RO1DK56558 and arthritis foundation (Y.-C. L.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, D., Liu, YC. Proteolysis-independent regulation of PI3K by Cbl-b–mediated ubiquitination in T cells. Nat Immunol 2, 870–875 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni0901-870
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni0901-870
This article is cited by
-
Integrative proteomics reveals an increase in non-degradative ubiquitylation in activated CD4+ T cells
Nature Immunology (2019)
-
The ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in adult and pediatric brain tumors: biological insights and therapeutic opportunities
Cancer and Metastasis Reviews (2017)
-
K48-linked KLF4 ubiquitination by E3 ligase Mule controls T-cell proliferation and cell cycle progression
Nature Communications (2017)
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF128 promotes innate antiviral immunity through K63-linked ubiquitination of TBK1
Nature Immunology (2016)
-
C-terminal domain of p42 Ebp1 is essential for down regulation of p85 subunit of PI3K, inhibiting tumor growth
Scientific Reports (2016)