Abstract
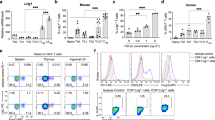
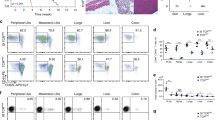
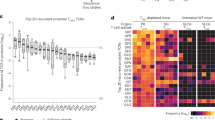
The mouse protein Qa-1 (HLA-E in humans) is essential for immunological protection and immune regulation. Although Qa-1 has been linked to CD8 T cell–dependent suppression, the physiological relevance of this observation is unclear. We generated mice deficient in Qa-1 to develop an understanding of this process. Qa-1-deficient mice develop exaggerated secondary CD4 responses to foreign and self peptides. Enhanced responses to proteolipid protein self peptide were associated with resistance of Qa-1-deficient CD4 T cells to Qa-1-restricted CD8 T suppressor activity and increased susceptibility to experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. These findings delineate a Qa-1-dependent T cell–T cell inhibitory interaction that prevents the pathogenic expansion of autoreactive CD4 T cell populations and consequent autoimmune disease.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cantor, H. T-cell receptor crossreactivity and autoimmune disease. Adv. Immunol. 75, 209–233 (2000).
Bouneaud, C., Kourilsky, P. & Bousso, P. Impact of negative selection on the T cell repertoire reactive to a self-peptide: a large fraction of T cell clones escapes clonal deletion. Immunity 13, 829–840 (2000).
Goldrath, A.W. & Bevan, M.J. Selecting and maintaining a diverse T-cell repertoire. Nature 402, 255–262 (1999).
Slifka, M.K. et al. Preferential escape of subdominant CD8+ T cells during negative selection results in an altered antiviral T cell hierarchy. J. Immunol. 170, 1231–1239 (2003).
Martin, D.A. et al. Defective CD95/APO-1/Fas signal complex formation in the human autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome, type Ia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96, 4552–4557 (1999).
Kearney, E.R., Pape, K.A., Loh, D.Y. & Jenkins, M.K. Visualization of peptide-specific T cell immunity and peripheral tolerance induction in vivo . Immunity 1, 327–339 (1994).
Anderton, S.M., Radu, C.G., Lowrey, P.A., Ward, E.S. & Wraith, D.C. Negative selection during the peripheral immune response to antigen. J. Exp. Med. 193, 1–11 (2001).
Panoutsakopoulou, V. et al. Analysis of the relationship between viral infection and autoimmune disease. Immunity 15, 137–147 (2001).
von Herrath, M.G. & Harrison, L.C. Antigen-induced regulatory T cells in autoimmunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3, 223–232 (2003).
Gavin, M. & Rudensky, A. Control of immune homeostasis by naturally arising regulatory CD4+ T cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 15, 690–696 (2003).
Wood, K.J. & Sakaguchi, S. Regulatory T cells in transplantation tolerance. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 3, 199–210 (2003).
Noble, A., Zhao, Z.-S. & Cantor, H. Suppression of immune responses by CD8 cells: II. Qa-1 on activated B-cells stimulates CD8 cell suppression of Th2-dependent antibody responses. J. Immunol. 160, 566–571 (1998).
Jiang, H. & Chess, L. The specific regulation of immune responses by CD8+ T cells restricted by the MHC class Ib molecule, Qa-1. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 18, 185–216 (2000).
Jiang, H., Zhang, S.-L. & Pernis, B. Role of CD8+ T cells in murine experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Science 256, 1213–1215 (1992).
Jiang, H. et al. T cell vaccination induces TCR Vβ specific, Qa-1 restricted regulatory CD8+ T cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 95, 4533–4537 (1998).
Aldrich, C.J. et al. T cell recognition of QA-1b antigens on cells lacking a functional Tap-2 transporter. J. Immunol. 149, 3773–3777 (1992).
Lo, W.F., Ong, H., Metcalf, E.S. & Soloski, M.J. T cell responses to gram-negative intracellular bacterial pathogens: a role for CD8+ T cells in immunity to Salmonella infection and the involvement of MHC class Ib molecules. J. Immunol. 162, 5398–5406 (1999).
Lo, W.F. et al. Molecular mimicry mediated by MHC class Ib molecules after infection with gram-negative pathogens. Nat. Med. 6, 215–218 (2000).
Sullivan, B.A., Kraj, P., Weber, D.A., Ignatowicz, L. & Jensen, P.E. Positive selection of a Qa-1-restricted T cell receptor with specificity for insulin. Immunity 17, 95–105 (2002).
Transy, C. et al. A low polymorphic mouse H-2 class I gene from the Tla complex is expressed in a broad variety of cell types. J. Exp. Med. 166, 341–361 (1987).
Soloski, M.J., DeCloux, A., Aldrich, C.J. & Forman, J. Structural and functional characteristics of the class IB molecule, Qa-1. Immunol. Rev. 147, 67–89 (1995).
Moser, J.M., Gibbs, J., Jensen, P.E. & Lukacher, A.E. CD94-NKG2A receptors regulate antiviral CD8+ T cell responses. Nat. Immunol. 3, 189–195 (2002).
Jiang, H. et al. Regulatory CD8+ T cells fine-tune the myelin basic protein-reactive T cell receptor Vβ repertoire during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 8378–8383 (2003).
Davies, A. et al. A peptide from heat shock protein 60 is the dominant peptide bound to Qa-1 in the absence of the MHC class Ia leader sequence peptide Qdm. J. Immunol. 170, 5027–5033 (2003).
Tompkins, S.M., Kraft, J.R., Dao, C.T., Soloski, M.J. & Jensen, P.E. Transporters associated with antigen processing (TAP)-independent presentation of soluble insulin to α/β T cells by the class Ib gene product, Qa-1(b). J. Exp. Med. 188, 961–971 (1998).
Seaman, M.S., Perarnau, B., Lindahl, K.F., Lemonnier, F.A. & Forman, J. Response to Listeria monocytogenes in mice lacking MHC class Ia molecules. J. Immunol. 162, 5429–5436 (1999).
Vance, R.E., Kraft, J.R., Altman, J.D., Jensen, P.E. & Raulet, D.H. Mouse CD94/NKG2A is a natural killer cell receptor for the nonclassical MHC class I molecule Qa-1b . J. Exp. Med. 188, 1841–1847 (1998).
Noble, A., Pestano, G.A. & Cantor, H. Suppression of immune responses by CD8 T cells: I. Superantigen-activated CD8 cells induce unidirectional Fas-mediated apoptosis of antigen-activated CD4 cells. J. Immunol. 160, 559–565 (1998).
Koh, D.R. et al. Less mortality but more relapses in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis in CD8−/− mice. Science 256, 1210–1213 (1992).
Jansson, M., Panoutsakopoulou, V., Baker, J., Klein, L. & Cantor, H. Attenuated experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Eta-1/osteopontin-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 168, 2096–2099 (2002).
Steinman, L. Immunotherapy of multiple sclerosis: the end of the beginning. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 13, 597–600 (2001).
Hauben, E. et al. Posttraumatic therapeutic vaccination with modified myelin self-antigen prevents complete paralysis while avoiding autoimmune disease. J. Clin. Invest. 108, 591–599 (2001).
Jahng, A.W. et al. Activation of natural killer T cells potentiates or prevents experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J. Exp. Med. 194, 1789–1799 (2001).
Schott, E., Bonasio, R. & Ploegh, H.L. Elimination in vivo of developing T cells by natural killer cells. J. Exp. Med. 198, 1213–1224 (2003).
Sakaguchi, S. et al. Immunologic tolerance maintained by CD25+ CD4+ regulatory T cells: their common role in controlling autoimmunity, tumor immunity, and transplantation tolerance. Immunol Rev. 182, 18–32 (2001).
von Herrath, M.G., Dockter, J. & Oldstone, M.B. How virus induces a rapid or slow onset insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in a transgenic model. Immunity 1, 231–242 (1994).
Kumar, V. & Sercarz, E.E. The involvement of T cell receptor peptide-specific regulatory CD4+ T cells in recovery from antigen-induced autoimmune disease. J. Exp. Med. 178, 909–916 (1993).
Valitutti, S., Muller, S., Salio, M. & Lanzavecchia, A. Degradation of T cell receptor (TCR)-CD3-ζ complexes after antigenic stimulation. J. Exp. Med. 185, 1859–1864 (1997).
Liu, H., Rhodes, M., Wiest, D.L. & Vignali, D.A. On the dynamics of TCR:CD3 complex cell surface expression and downmodulation. Immunity 13, 665–675 (2000).
Avery, A.C. et al. Resistance to herpes stromal keratitis conferred by an IgG2a-derived peptide. Nature 376, 431–434 (1995).
Zhao, Z.-S., Granucci, F., Yeh, L., Schaffer, P.A. & Cantor, H. Molecular mimicry by herpes simplex virus-1: autoimmune disease after viral infection. Science 279, 1344–1347 (1998).
Acknowledgements
We thank J. Horner and R.A. DePinho (Dana Farber Cancer Institute) and A. Sharpe (Brigham and Women's Hospital) for the expertise provided by their transgenic mouse facilities; S. Kissler for technical advice and assistance; and A. Angel for assistance with preparation of the manuscript and figures. Supported in part by National Institutes of Health (AI 13600, AI37562 and AI 48125 to H.C.; and AI 07386 to D.H.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, D., Ikizawa, K., Lu, L. et al. Analysis of regulatory CD8 T cells in Qa-1-deficient mice. Nat Immunol 5, 516–523 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1063
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1063
This article is cited by
-
An angel or a devil? Current view on the role of CD8+ T cells in the pathogenesis of myasthenia gravis
Journal of Translational Medicine (2024)
-
Dynamics of the gut microbiome, IgA response, and plasma metabolome in the development of pediatric celiac disease
Microbiome (2023)
-
CD8+ T cells in neurodegeneration: friend or foe?
Molecular Neurodegeneration (2022)
-
Characterization of gene expression profiles in the mouse brain after 35 days of spaceflight mission
npj Microgravity (2022)
-
Therapeutic effect of various ginsenosides on rheumatoid arthritis
BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies (2021)