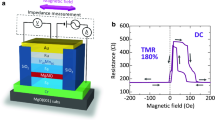
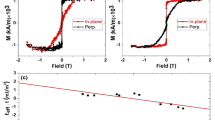
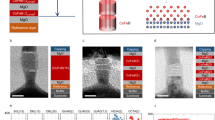
Abstract
Magnetically engineered magnetic tunnel junctions (MTJs) show promise as non-volatile storage cells in high-performance solid-state magnetic random access memories (MRAM)1. The performance of these devices is currently limited by the modest (<∼70%) room-temperature tunnelling magnetoresistance (TMR) of technologically relevant MTJs. Much higher TMR values have been theoretically predicted for perfectly ordered (100) oriented single-crystalline Fe/MgO/Fe MTJs. Here we show that sputter-deposited polycrystalline MTJs grown on an amorphous underlayer, but with highly oriented (100) MgO tunnel barriers and CoFe electrodes, exhibit TMR values of up to ∼220% at room temperature and ∼300% at low temperatures. Consistent with these high TMR values, superconducting tunnelling spectroscopy experiments indicate that the tunnelling current has a very high spin polarization of ∼85%, which rivals that previously observed only using half-metallic ferromagnets2. Such high values of spin polarization and TMR in readily manufactureable and highly thermally stable devices (up to 400 °C) will accelerate the development of new families of spintronic devices.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Parkin, S. S. P. et al. Magnetically engineered spintronic sensors and memory. Proc. IEEE 91, 661–680 (2003).
Parker, J. S., Watts, S. M., Ivanov, P. G. & Xiong, P. Spin polarization of CrO2 at and across an artificial barrier. Phys. Rev. Lett. 88, 196601 (2002).
Julliere, M. Tunneling between ferromagnetic films. Phys. Lett. A 54, 225–226 (1975).
Moodera, J. S., Kinder, L. R., Wong, T. M. & Meservey, R. Large magnetoresistance at room temperature in ferromagnetic thin film tunnel junctions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 74, 3273–3276 (1995).
Miyazaki, T. & Tezuka, N. Giant magnetic tunneling effect in Fe/Al2O3/Fe junction. J. Magn. Magn. Mat. 139, L231–L234 (1995).
Meservey, R. & Tedrow, P. M. Spin-polarized electron tunneling. Phys. Rep. 238, 173–243 (1994).
Maekawa, S. & Shinjo, T. (eds) Spin Dependent Transport in Magnetic Nanostructures (Taylor & Francis, London, 2002).
Sun, J. Z., Abraham, D. W., Roche, K. & Parkin, S. S. P. Temperature and bias dependence of magnetoresistance in doped manganite thin film trilayer junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 73, 1008–1010 (1998).
Jo, M. -H., Mathur, N. D., Todd, N. K. & Blamire, M. G. Very large magnetoresistance and coherent switching in half-metallic manganite tunnel junctions. Phys. Rev. B 61, R14905–R14908 (2000).
O'Donnell, J., Andrus, A. E., Oh, S., Colla, E. V. & Eckstein, J. N. Colossal magnetoresistance magnetic tunnel junctions grown by molecular-beam epitaxy. Appl. Phys. Lett. 76, 1914–1916 (2000).
Bowen, M. et al. Nearly total spin polarization in La2/3Sr1/3MnO3 from tunneling experiments. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 233–235 (2003).
Worledge, D. C. & Geballe, T. H. Maki analysis of spin-polarized tunneling in an oxide ferromagnet. Phys. Rev. B 62, 447–451 (2000).
Parkin, S. S. P., More, N. & Roche, K. P. Oscillations in exchange coupling and magnetoresistance in metallic superlattice structures: Co/Ru, Co/Cr and Fe/Cr. Phys. Rev. Lett. 64, 2304–2307 (1990).
Wang, D., Nordman, C., Daughton, J. M., Qian, Z. & Fink, J. 70% TMR at room temperature for SDT sandwich junctions with CoFeB as free and reference layers. IEEE Trans. Magn. 40, 2269–2271 (2004).
Mavropoulos, P., Papanikolaou, N. & Dederichs, P. H. Complex band structure and tunneling through ferromagnet/insulator/ferromagnet junctions. Phys. Rev. Lett. 85, 1088–1091 (2000).
Butler, W. H., Zhang, X. -G., Schulthess, T. C. & MacLaren, J. M. Spin-dependent tunneling conductance of Fe|verbar;MgO|Fe sandwiches. Phys. Rev. B 63, 054416 (2001).
Mathon, J. & Umerski, A. Theory of tunneling magnetoresistance of an epitaxial Fe/MgO/Fe(001) junction. Phys. Rev. B 63, 220403 (2001).
Bowen, M. et al. Large magnetoresistance in Fe/MgO/FeCo(001) epitaxial tunnel junctions on GaAs(001). Appl. Phys. Lett. 79, 1655–1657 (2001).
Faure-Vincent, J. et al. High tunnel magnetoresistance in epitaxial Fe/MgO/Fe tunnel junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 82, 4507–4509 (2003).
Yuasa, S., Fukushima, A., Nagahama, T., Ando, K. & Suzuki, Y. High tunnel magnetoresistance at room temperature in fully epitaxial Fe/MgO/Fe tunnel junctions due to coherent spin-polarized tunneling. Jpn J. Appl. Phys. 43, L588–L590 (2004).
Worledge, D. C. & Trouilloud, P. L. Magnetoresistance measurement of unpatterned magnetic tunnel junction wafers by current-in-plane tunneling. Appl. Phys. Lett. 83, 84–86 (2003).
Simmons, J. G. Generalized formula for the electric tunnel effect between similar electrodes separated by a thin insulating film. J. Appl. Phys. 34, 1793–1803 (1963).
Mitani, S., Moriyama, T. & Takanashi, K. Fe/MgO/FeCo(100) epitaxial magnetic tunnel junctions prepared by using in situ plasma oxidation. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 8041–8043 (2003).
Kiyomura, T., Maruo, Y. & Gomi, M. Electrical properties of MgO insulating layers in spin-dependent tunneling junctions using Fe3O4. J. Appl. Phys. 88, 4768–4771 (2000).
Bredow, T. & Gerson, A. R. Effect of exchange and correlation on bulk properties of MgO, NiO, and CoO. Phys. Rev. B 61, 5194–5201 (2000).
Pedersen, R. J. & Vernon, F. L. Effect of film resistance on low-impedance tunneling measurements. Appl. Phys. Lett. 10, 29–31 (1967).
Veerdonk, R. J. M. v. d., Nowak, J., Meservey, R., Moodera, J. S. & Jonge, W. J. M. d. Current distribution effects in magnetoresistive tunnel junctions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 71, 2839–2841 (1997).
De Teresa, J. M. et al. Role of metal-oxide interface in determining the spin polarization of magnetic tunnel junctions. Science 286, 507–509 (1999).
Reohr, W. et al. Memories of tomorrow. IEEE Circuits Device 18, 17–27 (2002).
Meyerheim, H. L. et al. Geometrical and compositional structure at metal-oxide interfaces: MgO on Fe(001). Phys. Rev. Lett. 87, 076102 (2001).
Acknowledgements
We thank Daniel Worledge for the CIPT measurements. Christian Kaiser is also at RWTH Aachen, Physikalisches Institut (IIA), 52056 Aachen, Germany. This work is partially supported by the DARPA spintronics and SPINS programs.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parkin, S., Kaiser, C., Panchula, A. et al. Giant tunnelling magnetoresistance at room temperature with MgO (100) tunnel barriers. Nature Mater 3, 862–867 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1256
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat1256
This article is cited by
-
Controlling the helicity of light by electrical magnetization switching
Nature (2024)
-
Observation of Josephson harmonics in tunnel junctions
Nature Physics (2024)
-
Large and tunable magnetoresistance in van der Waals ferromagnet/semiconductor junctions
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Electrical manipulation and detection of antiferromagnetism in magnetic tunnel junctions
Nature Electronics (2023)
-
Electrically tunable magnetic fluctuations in multilayered vanadium-doped tungsten diselenide
Nature Electronics (2023)