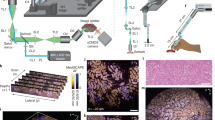
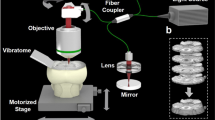
Abstract
In vivo imaging of small animals offers several possibilities for studying normal and disease biology, but visualizing organs with single-cell resolution is challenging. We describe rotational side-view confocal endomicroscopy, which enables cellular imaging of gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts in mice and may be extensible to imaging organ parenchyma such as cerebral cortex. We monitored cell infiltration, vascular changes and tumor progression during inflammation and tumorigenesis in colon over several months.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xavier, R.J. & Podolsky, D.K. Nature 448, 427–434 (2007).
Mizgerd, J.P. N. Engl. J. Med. 358, 716–727 (2008).
Miller, M.J., Wei, S.H., Parker, I. & Cahalan, M.D. Science 296, 1869–1873 (2002).
Jain, R.K., Munn, L.L. & Fukumura, D. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 266–276 (2002).
Kiesslich, R., Goetz, M., Vieth, M., Galle, P.R. & Neurath, M.F. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 4, 480–490 (2007).
Hsiung, P.L. et al. Nat. Med. 14, 454–458 (2008).
Becker, C., Fantini, M.C. & Neurath, M.F. Nat. Protoc. 1, 2900–2904 (2006).
Funovics, M.A., Alencar, H., Montet, X., Weissleder, R. & Mahmood, U. Gastrointest. Endosc. 64, 589–597 (2006).
Jung, J.C., Mehta, A.D., Aksay, E., Stepnoski, R. & Schnitzer, M.J. J. Neurophysiol. 92, 3121–3133 (2004).
Llewellyn, M.E., Barretto, R.P.J., Delp, S.L. & Schnitzer, M.J. Nature 454, 784–788 (2008).
Kim, P., Puoris'haag, M., Cote, D., Lin, C.P. & Yun, S.H. J. Biomed. Opt. 13, 010515 (2008).
Boirivant, M. et al. Gastroenterology 135, 1612–1623 (2008).
Hung, K.E. et al. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 107, 1565–1570 (2010).
Sanhai, W.R., Sakamoto, J.H., Canady, R. & Ferrari, M. Nat. Nanotechnol. 3, 242–244 (2008).
Murayama, M. et al. Nature 457, 1137–1195 (2009).
Guizar-Sicairos, M., Thurman, S.T. & Fienup, J.R. Opt. Lett. 33, 156–158 (2008).
Bettelli, E. et al. Nature 441, 235–238 (2006).
Belteki, G. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 33, 10 (2005).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Wellman Center for Photomedicine, Human Frontier Science Program (cross-disciplinary fellowship 2006), Tosteson Fellowship, National Research Foundation of Korea (R31-2008-000-10071-0) and the US National Institutes of Health (R21AI081010, RC1DK086242, RC2DK088661, U54CA143837, U01CA084301, R01CA85140, P01CA08124, R01CA96915 and R01CA126642).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
P.K. developed endomicroscopy, performed experiments and wrote the manuscript. E.C. and H.Y. performed the conditional-knockout procedure and helped with angiogenesis imaging. K.E.H. developed the conditional-knockout procedure. A.M. designed the colitis model. R.K., D.F. and R.K.J. designed the tumor model and angiogenesis study. S.H.Y. directed the overall project, developed endomicroscopy and wrote the manuscript with input from other authors.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–9 (PDF 1601 kb)
Supplementary Video 1
Virtual cellular colonoscopy visualizing the microvasculature of normal colonic mucosa. (MOV 4039 kb)
Supplementary Video 2
Real-time endoscopic view of the blood vessels in the normal colon. (MOV 2730 kb)
Supplementary Video 3
Fly-through movie showing the blood vessels of esophageal mucosa. (MOV 2246 kb)
Supplementary Video 4
Time-lapse movie showing the interaction of dendritic cells (green) and Ovalbumin (OVA) allergen (red) at 12 h after OVA challenge. (MOV 735 kb)
Supplementary Video 5
Real-time movie showing the angiogenic blood vessels near the tumor at week 16 after conditional Apc knockout. (MOV 1912 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, P., Chung, E., Yamashita, H. et al. In vivo wide-area cellular imaging by side-view endomicroscopy. Nat Methods 7, 303–305 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1440
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.1440
This article is cited by
-
Activation of mechanoluminescent nanotransducers by focused ultrasound enables light delivery to deep-seated tissue in vivo
Nature Protocols (2023)
-
Double-layer polarization-independent achromatic metasurface array for optical fiber bundle coupling in microendoscope
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Clear optically matched panoramic access channel technique (COMPACT) for large-volume deep brain imaging
Nature Methods (2021)
-
Phonon imaging in 3D with a fibre probe
Light: Science & Applications (2021)
-
Handheld endomicroscope using a fiber-optic harmonograph enables real-time and in vivo confocal imaging of living cell morphology and capillary perfusion
Microsystems & Nanoengineering (2020)