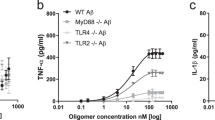
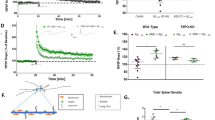
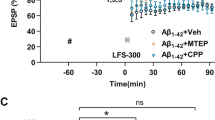
Abstract
Amyloid-β1–42 (Aβ) is thought to be a major mediator of the cognitive deficits in Alzheimer's disease. The ability of Aβ to inhibit hippocampal long-term potentiation provides a cellular correlate of this action, but the underlying molecular mechanism is only partially understood. We found that a signaling pathway involving caspase-3, Akt1 and glycogen synthase kinase-3β is an important mediator of this effect in rats and mice.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walsh, D.M. et al. Nature 416, 535–539 (2002).
Shankar, G.M. et al. Nat. Med. 14, 837–842 (2008).
Hsieh, H. et al. Neuron 52, 831–843 (2006).
Li, S. et al. Neuron 62, 788–801 (2009).
Mattson, M.P. Nature 430, 631–639 (2004).
Cho, J.H. & Johnson, G.V. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 54716–54723 (2004).
Chong, Y.H. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 20315–20325 (2006).
Allen, J.W. et al. J. Neurosci. Res. 65, 45–53 (2001).
Li, Z. et al. Cell 141, 859–871 (2010).
Phiel, C.J. et al. Nature 423, 435–439 (2003).
Peineau, S. et al. Neuron 53, 703–717 (2007).
Bain, J. et al. Biochem. J. 408, 297–315 (2007).
Wang, Q. et al. J. Neurosci. 24, 3370–3378 (2004).
Kotilinek, L.A. et al. Brain 131, 651–664 (2008).
Palop, J.J. & Mucke, L. Nat. Neurosci. 13, 812–818 (2010).
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the UK Alzheimer's Research Trust (K.C.), Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (K.C.), Medical Research Council (G.L.C.) and The Royal Society (J.J.). G.L.C. is a World Class University International Scholar and D.J.W. is an UK Alzheimer's Research Trust–funded Ph.D. student.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The study was conceived by K.C. The experiments were designed by K.C., M.S. and G.L.C. and carried out by J.J., D.J.W., K.M.O., T.L.K., J.S.L., G.B., B.D. and S.S. The manuscript was written by G.L.C., M.S. and K.C.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
K.M.O., S.-C.L. and M.S. are employees of Genentech.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1, 2 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 368 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jo, J., Whitcomb, D., Olsen, K. et al. Aβ1–42 inhibition of LTP is mediated by a signaling pathway involving caspase-3, Akt1 and GSK-3β. Nat Neurosci 14, 545–547 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2785
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2785
This article is cited by
-
Therapeutic potential of ADAM10 modulation in Alzheimer’s disease: a review of the current evidence
Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
Exendin-4 improves long-term potentiation and neuronal dendritic growth in vivo and in vitro obesity condition
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
A screened PirB antagonist peptide antagonizes Aβ42-mediated inhibition of neurite outgrowth in vitro
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2021)
-
Potentiation of amyloid beta phagocytosis and amelioration of synaptic dysfunction upon FAAH deletion in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease
Journal of Neuroinflammation (2021)
-
Physical exercise during exposure to 40-Hz light flicker improves cognitive functions in the 3xTg mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy (2020)