Abstract
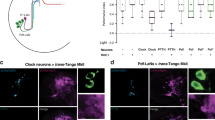
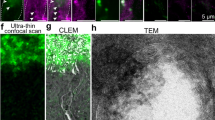
Fic domains can catalyze the addition of adenosine monophosphate to target proteins. To date, the function of Fic domain proteins in eukaryotic physiology remains unknown. We generated genetic models of the single Drosophila Fic domain–containing protein, Fic. Flies lacking Fic were viable and fertile, but blind. Photoreceptor cells depolarized normally following light stimulation, but failed to activate postsynaptic neurons, as indicated by the loss of ON transients in electroretinograms, consistent with a neurotransmission defect. Functional rescue of neurotransmission required expression of enzymatically active Fic on capitate projections of glia cells, but not neurons, supporting a role in the recycling of the visual neurotransmitter histamine. Histamine levels were reduced in the lamina of Fic null flies, and dietary histamine partially restored ON transients. These findings establish a previously unknown regulatory mechanism in visual neurotransmission and provide, to the best of our knowledge, the first evidence for a role of glial capitate projections in neurotransmitter recycling.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yarbrough, M.L. et al. AMPylation of Rho GTPases by Vibrio VopS disrupts effector binding and downstream signaling. Science 323, 269–272 (2009).
Brown, M.S., Segal, A. & Stadtman, E.R. Modulation of glutamine synthetase adenylylation and deadenylylation is mediated by metabolic transformation of the P II regulatory protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 68, 2949–2953 (1971).
Broberg, C.A. & Orth, K. Tipping the balance by manipulating post-translational modifications. Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 13, 34–40 (2010).
Müller, M.P. et al. The Legionella effector protein DrrA AMPylates the membrane traffic regulator Rab1b. Science 329, 946–949 (2010).
Worby, C.A. et al. The fic domain: regulation of cell signaling by adenylylation. Mol. Cell 34, 93–103 (2009).
Kinch, L.N., Yarbrough, M.L., Orth, K. & Grishin, N.V. Fido, a novel AMPylation domain common to fic, doc, and AvrB. PLoS ONE 4, e5818 (2009).
Benzer, S. Behavioral mutants of Drosophila isolated by countercurrent distribution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 58, 1112–1119 (1967).
Melzig, J. et al. Genetic depletion of histamine from the nervous system of Drosophila eliminates specific visual and mechanosensory behavior. J. Comp. Physiol. A 179, 763–773 (1996).
Alawi, A.A. & Pak, W.L. On-transient of insect electroretinogram: its cellular origin. Science 172, 1055–1057 (1971).
Heisenberg, M. Separation of receptor and lamina potentials in the electroretinogram of normal and mutant Drosophila. J. Exp. Biol. 55, 85–100 (1971).
Stowers, R.S. & Schwarz, T.L. A genetic method for generating Drosophila eyes composed exclusively of mitotic clones of a single genotype. Genetics 152, 1631–1639 (1999).
Pantazis, A. et al. Distinct roles for two histamine receptors (hclA and hclB) at the Drosophila photoreceptor synapse. J. Neurosci. 28, 7250–7259 (2008).
Stowers, R.S., Megeath, L.J., Gorska-Andrzejak, J., Meinertzhagen, I.A. & Schwarz, T.L. Axonal transport of mitochondria to synapses depends on milton, a novel Drosophila protein. Neuron 36, 1063–1077 (2002).
Fabian-Fine, R. et al. Endophilin promotes a late step in endocytosis at glial invaginations in Drosophila photoreceptor terminals. J. Neurosci. 23, 10732–10744 (2003).
Lin, D.M. & Goodman, C.S. Ectopic and increased expression of Fasciclin II alters motoneuron growth cone guidance. Neuron 13, 507–523 (1994).
Sepp, K.J., Schulte, J. & Auld, V.J. Peripheral glia direct axon guidance across the CNS/PNS transition zone. Dev. Biol. 238, 47–63 (2001).
Zhu, Y., Nern, A., Zipursky, S.L. & Frye, M.A. Peripheral visual circuits functionally segregate motion and phototaxis behaviors in the fly. Curr. Biol. 19, 613–619 (2009).
Gavin, B.A., Arruda, S.E. & Dolph, P.J. The role of carcinine in signaling at the Drosophila photoreceptor synapse. PLoS Genet. 3, e206 (2007).
Melzig, J., Burg, M., Gruhn, M., Pak, W.L. & Buchner, E. Selective histamine uptake rescues photo- and mechanoreceptor function of histidine decarboxylase–deficient Drosophila mutant. J. Neurosci. 18, 7160–7166 (1998).
Wagner, S. et al. Drosophila photoreceptors express cysteine peptidase tan. J. Comp. Neurol. 500, 601–611 (2007).
Burg, M.G., Sarthy, P.V., Koliantz, G. & Pak, W.L. Genetic and molecular identification of a Drosophila histidine decarboxylase gene required in photoreceptor transmitter synthesis. EMBO J. 12, 911–919 (1993).
Borycz, J.A., Borycz, J., Kubow, A., Kostyleva, R. & Meinertzhagen, I.A. Histamine compartments of the Drosophila brain with an estimate of the quantum content at the photoreceptor synapse. J. Neurophysiol. 93, 1611–1619 (2005).
Richardt, A., Rybak, J., Stortkuhl, K.F., Meinertzhagen, I.A. & Hovemann, B.T. Ebony protein in the Drosophila nervous system: optic neuropile expression in glial cells. J. Comp. Neurol. 452, 93–102 (2002).
Richardt, A. et al. Ebony, a novel nonribosomal peptide synthetase for beta-alanine conjugation with biogenic amines in Drosophila. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 41160–41166 (2003).
Romero-Calderón, R. et al. A glial variant of the vesicular monoamine transporter is required to store histamine in the Drosophila visual system. PLoS Genet. 4, e1000245 (2008).
Edwards, T.N. & Meinertzhagen, I.A. The functional organisation of glia in the adult brain of Drosophila and other insects. Prog. Neurobiol. 90, 471–497 (2010).
Borycz, J., Borycz, J.A., Loubani, M. & Meinertzhagen, I.A. tan and ebony genes regulate a novel pathway for transmitter metabolism at fly photoreceptor terminals. J. Neurosci. 22, 10549–10557 (2002).
Sunio, A., Metcalf, A.B. & Kramer, H. Genetic dissection of endocytic trafficking in Drosophila using a horseradish peroxidase–bride of sevenless chimera: hook is required for normal maturation of multivesicular endosomes. Mol. Biol. Cell 10, 847–859 (1999).
Stark, W.S. & Carlson, S.D. Ultrastructure of capitate projections in the optic neuropil of Diptera. Cell Tissue Res. 246, 481–486 (1986).
Meinertzhagen, I.A. & Wang, Y. Drosophila mutants tan and ebony have altered numbers of capitate projections, glial invaginations into photoreceptor terminals. in Neurobiology: From Membrane to Mmind, vol II (eds. N. Elsner & H. Wässle) 457 (Georg Thieme Verlag, Stutgart, 1997).
Tan, Y. & Luo, Z.Q. Legionella pneumophila SidD is a deAMPylase that modifies Rab1. Nature 475, 506–509 (2011).
Neunuebel, M.R. et al. De-AMPylation of the small GTPase Rab1 by the pathogen Legionella pneumophila. Science 333, 453–456 (2011).
Mukherjee, S. et al. Modulation of Rab GTPase function by a protein phosphocholine transferase. Nature 477, 103–106 (2011).
Engel, P. et al. Adenylylation control by intra- or intermolecular active-site obstruction in Fic proteins. Nature 482, 107–110 (2012).
Rost, B., Yachdav, G. & Liu, J. The PredictProtein server. Nucleic Acids Res. 32, W321–326 (2004).
Williamson, W.R., Wang, D., Haberman, A.S. & Hiesinger, P.R. A dual function of V0-ATPase a1 provides an endolysosomal degradation mechanism in Drosophila melanogaster photoreceptors. J. Cell Biol. 189, 885–899 (2010).
Akbar, M.A., Ray, S. & Kramer, H. The SM protein Car/Vps33A regulates SNARE-mediated trafficking to lysosomes and lysosome-related organelles. Mol. Biol. Cell 20, 1705–1714 (2009).
Sharma, A., Mariappan, M., Appathurai, S. & Hegde, R.S. In vitro dissection of protein translocation into the mammalian endoplasmic reticulum. Methods Mol. Biol. 619, 339–363 (2010).
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to R. Hiesinger for help and advice with the ERG measurements and the use of his ERG setup, W. Pak, B. Hoveman and the Bloomington Stock center for fly lines, M. Buszczak for antibodies, C. Gilpin from the Molecular and Cellular Imaging Facility at UT Southwestern, S.H. Kim and B. Tu for technical help, and to E. Kavalali and A. Haberman for helpful discussions. This work was supported by grants to H.K. from the US National Institutes of Health National Eye Institute (EY10199 and EY021922) and Visual Science Core grant EY020799. K.O. and H.H. are supported by grants from the US National Institutes of Health (Allergy and Infectious Disease, R01-AI056404 and R01-AI087808) and the Welch Foundation (I-1561). K.O. is a Burroughs Wellcome Investigator in Pathogenesis of Infectious Disease and a W.W. Caruth Jr. Biomedical Scholar.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.R. and H.K. performed the fly genetic studies. X.L. and Y.S. performed the electron microscopy studies. H.H. performed the molecular biology and biochemistry studies. H.K., M.R. and K.O. designed the study and analyzed the data. H.K. and K.O. wrote the paper. All of the authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figure 1 and Supplementary Table 1 (PDF 7650 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rahman, M., Ham, H., Liu, X. et al. Visual neurotransmission in Drosophila requires expression of Fic in glial capitate projections. Nat Neurosci 15, 871–875 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3102
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3102
This article is cited by
-
A convolutional neural network based tool for predicting protein AMPylation sites from binary profile representation
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
Specificity of AMPylation of the human chaperone BiP is mediated by TPR motifs of FICD
Nature Communications (2021)
-
FICD activity and AMPylation remodelling modulate human neurogenesis
Nature Communications (2020)
-
CRY-dependent plasticity of tetrad presynaptic sites in the visual system of Drosophila at the morning peak of activity and sleep
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
High-throughput identification of proteins with AMPylation using self-assembled human protein (NAPPA) microarrays
Nature Protocols (2015)