Abstract
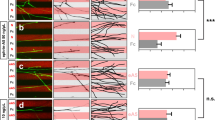
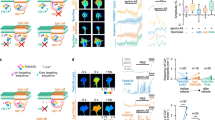
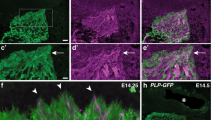
Guidance cues and signal transduction mechanisms acting at the nerve growth cone are fairly well understood, but the intracellular mechanisms operating to change the direction of axon outgrowth remain unknown. We now show that growth cones integrate myosin II–dependent contraction for rapid, coordinated turning at borders of laminin stripes in response to signals from laminin-activated integrin receptors; in the absence of myosin II activity, outgrowth continues across the borders.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hopker, V.H., Shewan, D., Tessier-Lavigne, M., Poo, M. & Holt, C. Nature 401, 69–73 (1999).
Stevens, A. & Jacobs, J.R. J. Neurosci. 22, 4448–4455 (2002).
Nakamoto, T., Kain, K.H. & Ginsberg, M.H. Curr. Biol. 14, R121–R123 (2004).
Suter, D.M. & Forscher, P. J. Neurobiol. 44, 97–113 (2000).
Mitchison, T. & Kirschner, M. Neuron 1, 761–772 (1988).
Schmucker, D. Neuron 40, 4–6 (2003).
Dent, E.W. & Gertler, F.B. Neuron 40, 209–227 (2003).
Gundersen, R.W. Dev. Biol. 121, 423–431 (1987).
Bridgman, P.C., Dave, S., Asnes, C.F., Tullio, A.N. & Adelstein, R.S. J. Neurosci. 21, 6159–6169 (2001).
Straight, A.F. et al. Science 299, 1743–1747 (2003).
Golomb, E. et al. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 2800–2808 (2004).
Limouze, J., Straight, A.F., Mitchison, T. & Sellers, J.R. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 25, 337–341 (2004).
Rochlin, M.W., Itoh, K., Adelstein, R.S. & Bridgman, P.C. J. Cell Sci. 108, 3661–3670 (1995).
Bridgman, P.C., Brown, M.E. & Balan, I. Methods Cell Biol. 71, 353–68 (2003).
Brown, M.E. & Bridgman, P.C. J. Cell Sci. 116, 1087–1094 (2003).
Acknowledgements
G. Philips and D. Morris provided technical support. We thank J. Cooper for comments on the manuscript. The US National Institutes of Health provided financial support (NS26150 to P.C.B.)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Supplementary information
Supplementary Fig. 1
Slow outgrowth on PLO is converted to faster outgrowth by blebbistatin treatment. (JPG 73 kb)
Supplementary Fig. 2
Myosin IIC is present in growth cones, and myosin IIB is asymmetrically distributed in growth cones at borders. (JPG 440 kb)
Supplementary Table 1
Relationship between outgrowth rates on different substrates and turning frequencies. (PDF 35 kb)
Supplementary Video 1
Time-lapse of control neurites at laminin-1 borders. A control culture growing on PLO+LN1 (red overlay) shows turning at the border with PLO. (MOV 2507 kb)
Supplementary Video 2
Time-lapse of blebbistatin-treated control neurites at laminin-1 borders. Turning is rare in a blebbistatin treated control culture. (MOV 2837 kb)
Supplementary Video 3
Time-lapse of myosin IIB knockout neurites at laminin-1 borders. A myosin IIB knockout culture shows intermediate behavior; only some neurites turn at the border. (MOV 2642 kb)
Supplementary Video 4
Time-lapse of a myosin IIB knockout neuron transfected with GFP–myosin IIB at a laminin-1 border. A myosin IIB knockout neuron that was transfected with GFP-myosin IIB is shown. The neurite crosses the border, turns and then grows along the border on the side with LN1. Note the periodic extensions toward the border. A small vestigial branch persists at the original border contact site. The substrate is covered with gold particles from biolistics. (MOV 2608 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Turney, S., Bridgman, P. Laminin stimulates and guides axonal outgrowth via growth cone myosin II activity. Nat Neurosci 8, 717–719 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1466
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn1466
This article is cited by
-
The Axonal Actin Filament Cytoskeleton: Structure, Function, and Relevance to Injury and Degeneration
Molecular Neurobiology (2024)
-
Carbon nanotube micropillars trigger guided growth of complex human neural stem cells networks
Nano Research (2019)
-
Strong contact coupling of neuronal growth cones with height-controlled vertical silicon nanocolumns
Nano Research (2018)
-
Integration of neurogenesis and angiogenesis models for constructing a neurovascular tissue
Scientific Reports (2017)
-
Design of Cultured Neuron Networks in vitro with Predefined Connectivity Using Asymmetric Microfluidic Channels
Scientific Reports (2017)