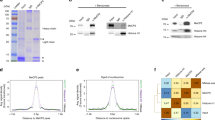
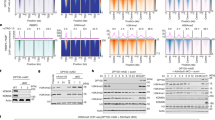
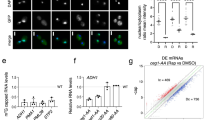
Abstract
Methylation of the mRNA 5′ guanosine cap is essential for efficient gene expression. The 5′ methyl cap binds to eIF4E, which is the first step in the recruitment of mRNA to the 40S ribosomal subunit. To investigate whether mRNA cap methylation is regulated in a gene-specific manner, we established a method to detect the relative level of cap methylation on specific mRNAs. We found that two transcription factors, c-Myc and E2F1, induce cap methylation of their transcriptional target genes, and therefore, c-Myc and E2F1 upregulate gene expression by simultaneously inducing transcription and promoting translation. c-Myc-induced cap methylation is greater than transcriptional induction for the majority of its target genes, indicating that this is a major mechanism by which Myc regulates gene expression.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bentley DL . (2005). Rules of engagement: co-transcriptional recruitment of pre-mRNA processing factors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17: 251–256.
Blais A, Dynlacht BD . (2007). E2F-associated chromatin modifiers and cell cycle control. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19: 658–662.
Boon K, Caron HN, van Asperen R, Valentijn L, Hermus MC, van Sluis P et al. (2001). N-myc enhances the expression of a large set of genes functioning in ribosome biogenesis and protein synthesis. EMBO J 20: 1383–1393.
Bush A, Mateyak M, Dugan K, Obaya A, Adachi S, Sedivy J et al. (1998). c-myc null cells misregulate cad and gadd45 but not other proposed c-Myc targets. Genes Dev 12: 3797–3802.
Cowling VH, Chandriani S, Whitfield ML, Cole MD . (2006). A conserved Myc protein domain, MBIV, regulates DNA binding, apoptosis, transformation, and G2 arrest. Mol Cell Biol 26: 4226–4239.
Cowling VH, Cole MD . (2006). Mechanism of transcriptional activation by the Myc oncoproteins. Semin Cancer Biol 16: 242–252.
Cowling VH, Cole MD . (2007). The Myc transactivation domain promotes global phosphorylation of the RNA polymerase II carboxy-terminal domain independently of direct DNA binding. Mol Cell Biol 27: 2059–2073.
Dang CV, O'Donnell KA, Zeller KI, Nguyen T, Osthus RC, Li F . (2006). The c-Myc target gene network. Semin Cancer Biol 16: 253–264.
Gingras AC, Raught B, Sonenberg N . (1999). eIF4 initiation factors: effectors of mRNA recruitment to ribosomes and regulators of translation. Annu Rev Biochem 68: 913–963.
Gomez-Roman N, Felton-Edkins ZA, Kenneth NS, Goodfellow SJ, Athineos D, Zhang J et al. (2006). Activation by c-Myc of transcription by RNA polymerases I, II and III. Biochem Soc Symp 73: 141–154.
Gu M, Lima CD . (2005). Processing the message: structural insights into capping and decapping mRNA. Curr Opin Struct Biol 15: 99–106.
Guo QM, Malek RL, Kim S, Chiao C, He M, Ruffy M et al. (2000). Identification of c-myc responsive genes using rat cDNA microarray. Cancer Res 60: 5922–5928.
Iaquinta PJ, Lees JA . (2007). Life and death decisions by the E2F transcription factors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19: 649–657.
Jacobson A, Peltz SW . (1996). Interrelationships of the pathways of mRNA decay and translation in eukaryotic cells. Annu Rev Biochem 65: 693–739.
Kim S, Li Q, Dang CV, Lee LA . (2000). Induction of ribosomal genes and hepatocyte hypertrophy by adenovirus-mediated expression of c-Myc in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97: 11198–11202.
McCracken S, Fong N, Rosonina E, Yankulov K, Brothers G, Siderovski D et al. (1997). 5′-Capping enzymes are targeted to pre-mRNA by binding to the phosphorylated carboxy-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II. Genes Dev 11: 3306–3318.
Moteki S, Price D . (2002). Functional coupling of capping and transcription of mRNA. Mol Cell 10: 599–609.
Muller H, Bracken AP, Vernell R, Moroni MC, Christians F, Grassilli E et al. (2001). E2Fs regulate the expression of genes involved in differentiation, development, proliferation, and apoptosis. Genes Dev 15: 267–285.
Nikiforov MA, Chandriani S, Park J, Kotenko I, Matheos D, Johnsson A et al. (2002). TRRAP-dependent and TRRAP-independent transcriptional activation by Myc family oncoproteins. Mol Cell Biol 22: 5054–5063.
Schmidt EV . (2004). The role of c-myc in regulation of translation initiation. Oncogene 23: 3217–3221.
Schuhmacher M, Kohlhuber F, Holzel M, Kaiser C, Burtscher H, Jarsch M et al. (2001). The transcriptional program of a human B cell line in response to Myc. Nucleic Acids Res 29: 397–406.
Schwer B, Mao X, Shuman S . (1998). Accelerated mRNA decay in conditional mutants of yeast mRNA capping enzyme. Nucleic Acids Res 26: 2050–2057.
Schwer B, Saha N, Mao X, Chen HW, Shuman S . (2000). Structure-function analysis of yeast mRNA cap methyltransferase and high-copy suppression of conditional mutants by AdoMet synthase and the ubiquitin conjugating enzyme Cdc34p. Genetics 155: 1561–1576.
Shatkin AJ . (1976). Capping of eucaryotic mRNAs. Cell 9: 645–653.
Shatkin AJ, Manley JL . (2000). The ends of the affair: capping and polyadenylation. Nat Struct Biol 7: 838–842.
Shuman S . (2002). What messenger RNA capping tells us about eukaryotic evolution. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3: 619–625.
Sims III RJ, Mandal SS, Reinberg D . (2004). Recent highlights of RNA-polymerase-II-mediated transcription. Curr Opin Cell Biol 16: 263–271.
von der Haar T, Gross JD, Wagner G, McCarthy JE . (2004). The mRNA cap-binding protein eIF4E in post-transcriptional gene expression. Nat Struct Mol Biol 11: 503–511.
Zeller KI, Jegga AG, Aronow BJ, O'Donnell KA, Dang CV . (2003). An integrated database of genes responsive to the Myc oncogenic transcription factor: identification of direct genomic targets. Genome Biol 4: R69.
Acknowledgements
We thank Klara Acs for much helpful advice. We thank Kristian Helin for the E2F1-ER construct. This study was funded by NIH grants to MDC and an MRC grant to VHC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cole, M., Cowling, V. Specific regulation of mRNA cap methylation by the c-Myc and E2F1 transcription factors. Oncogene 28, 1169–1175 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.463
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.463
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The effects of MYC on tumor immunity and immunotherapy
Cell Death Discovery (2023)
-
Arabidopsis DXO1 activates RNMT1 to methylate the mRNA guanosine cap
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Construction of N-7 methylguanine-related mRNA prognostic model in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma based on multi-omics data and immune-related analysis
Scientific Reports (2022)
-
The broken cycle: E2F dysfunction in cancer
Nature Reviews Cancer (2019)
-
MYC: connecting selective transcriptional control to global RNA production
Nature Reviews Cancer (2015)