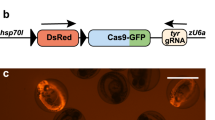
Abstract
The zebrafish has emerged as a powerful genetic model of cancer, but has been limited by the use of stable transgenic approaches to induce disease. Here, a co-injection strategy is described that capitalizes on both the numbers of embryos that can be microinjected and the ability of transgenes to segregate together and exert synergistic effects in forming tumors. Using this mosaic transgenic approach, gene pathways involved in tumor initiation and radiation sensitivity have been identified.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berghmans S, Murphey RD, Wienholds E, Neuberg D, Kutok JL, Fletcher CD et al. (2005). tp53 mutant zebrafish develop malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 407–412.
Burns CE, Traver D, Mayhall E, Shepard JL, Zon LI . (2005). Hematopoietic stem cell fate is established by the Notch–Runx pathway. Genes Dev 19: 2331–2342.
Halloran MC, Sato-Maeda M, Warren JT, Su F, Lele Z, Krone PH et al. (2000). Laser-induced gene expression in specific cells of transgenic zebrafish. Development 127: 1953–1960.
Haramis AP, Hurlstone A, van der Velden Y, Begthel H, van den Born M, Offerhaus GJ et al. (2006). Adenomatous polyposis coli-deficient zebrafish are susceptible to digestive tract neoplasia. EMBO Rep 7: 444–449.
Jessen JR, Jessen TN, Voge SS, Lin S . (2001). Concurrent expression of recombination activating genes 1 and 2 in zebrafish olfactory sensory neurons. Genesis: the Journal of Genetics and Development 29: 156–162.
Kratz E, Eimon PM, Mukhyala K, Stern H, Zha J, Strasser A et al. (2006). Functional characterization of the Bcl-2 gene family in the zebrafish. Cell Death Differ 13: 1631–1640.
Langenau DM, Feng H, Berghmans S, Kanki JP, Kutok JL, Look AT . (2005a). Cre/lox-regulated transgenic zebrafish model with conditional myc-induced T cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102: 6068–6073.
Langenau DM, Jette C, Berghmans S, Palomero T, Kanki JP, Kutok JL et al. (2005b). Suppression of apoptosis by bcl-2 overexpression in lymphoid cells of transgenic zebrafish. Blood 105: 3278–3285.
Langenau DM, Keefe MD, Storer NY, Guyon JR, Kutok JL, Le X et al. (2007). Effects of RAS on the genesis of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. Genes Dev 21: 1382–1389.
Langenau DM, Traver D, Ferrando AA, Kutok JL, Aster JC, Kanki JP et al. (2003). Myc-induced T cell leukemia in transgenic zebrafish. Science 299: 887–890.
Le X, Langenau DM, Keefe MD, Kutok JL, Neuberg DS, Zon LI . (2007). Heat shock-inducible Cre/Lox approaches to induce diverse types of tumors and hyperplasia in transgenic zebrafish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104: 9410–9415.
Oda E, Ohki R, Murasawa H, Nemoto J, Shibue T, Yamashita T et al. (2000). Noxa, a BH3-only member of the Bcl-2 family and candidate mediator of p53-induced apoptosis. Science 288: 1053–1058.
Patton EE, Widlund HR, Kutok JL, Kopani KR, Amatruda JF, Murphey RD et al. (2005). BRAF mutations are sufficient to promote nevi formation and cooperate with p53 in the genesis of melanoma. Curr Biol 15: 249–254.
Pyati UJ, Webb AE, Kimelman D . (2005). Transgenic zebrafish reveal stage-specific roles for Bmp signaling in ventral and posterior mesoderm development. Development 132: 2333–2343.
Sabaawy HE, Azuma M, Embree LJ, Tsai HJ, Starost MF, Hickstein DD . (2006). TEL-AML1 transgenic zebrafish model of precursor B cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103: 15166–15171.
Traver D, Paw BH, Poss KD, Penberthy WT, Lin S, Zon LI . (2003). Transplantation and in vivo imaging of multilineage engraftment in zebrafish bloodless mutants. Nat Immunol 4: 1238–1246.
Traver D, Winzeler A, Stern HM, Mayhall EA, Langenau DM, Kutok JL et al. (2004). Effects of lethal irradiation in zebrafish and rescue by hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood 104: 1298–1305.
Tropepe V, Coles BL, Chiasson BJ, Horsford DJ, Elia AJ, McInnes RR et al. (2000). Retinal stem cells in the adult mammalian eye. Science 287: 2032–2036.
Xiao T, Shoji W, Zhou W, Su F, Kuwada JY . (2003). Transmembrane sema4E guides branchiomotor axons to their targets in zebrafish. J Neurosci 23: 4190–4198.
Yang HW, Kutok JL, Lee NH, Piao HY, Fletcher CD, Kanki JP et al. (2004). Targeted expression of human MYCN selectively causes pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors in transgenic zebrafish. Cancer Res 64: 7256–7262.
Acknowledgements
We thank Anna Burrows for expert technical help and David Bellovin and David Adamovich for critical review of this manuscript. DM Langenau is the Edmond J Safra Foundation Fellow from the Irvington Institute and CJ Ceol is supported by a Damon Runyon Fellowship (DRG-1855-05). Funding for this work was provided by NIH Grant 5R01 CA103846-02 (LI Zon), #1RO1 CA119066-01, CA93152-05, CA104605-03, HL-088664 and CA68484-11 (AT Look), #1KO1 DK074555-01 (CA Jette).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on the Oncogene website (http://www.nature.com/onc)
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Langenau, D., Keefe, M., Storer, N. et al. Co-injection strategies to modify radiation sensitivity and tumor initiation in transgenic Zebrafish. Oncogene 27, 4242–4248 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.56
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.56
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Mutant IL7R collaborates with MYC to induce T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia
Leukemia (2022)
-
The Zebrafish model in dermatology: an update for clinicians
Discover Oncology (2022)
-
The pre-rRNA processing factor DEF is rate limiting for the pathogenesis of MYCN-driven neuroblastoma
Oncogene (2017)
-
Overexpression of PDGFRA cooperates with loss of NF1 and p53 to accelerate the molecular pathogenesis of malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors
Oncogene (2017)
-
Endothelial Cords Promote Tumor Initial Growth prior to Vascular Function through a Paracrine Mechanism
Scientific Reports (2016)